Herbalism Directory
“A person who finds a herb has found a cure”
Below is a curated directory of medicinal herbs and mushrooms that can be used in a variety of ways, from supplement pills to tea to aromatherapy. This is presented for informational purposes, please consult a health expert before use.
Categories
Tongkat Ali
Tongkat ali is a potent testosterone booster through its interactions with SHBG and aromatase. Tongkat ali is also a cognitive enhancer, has anti-cancer properties, and has shown promise as an herbal supplement for athletic enhancement. Tongkat is popular for its aphrodisiac and libido enhancing effects which can help with sexual dysfunction and infertility. Learn more about Eurycoma longifolia.
Article by Stefan Burns - Updated December 2022. Join the Wild Free Organic email newsletter!
There are a few herbs that exist which powerfully boost testosterone levels and are considered overall androgenic.
Tongkat Ali, known in the Linnaean classification as Eurycoma longifolia, is one of those special herbs.
Tongkat ali interacts with the hormone system to raise testosterone levels, unbind testosterone from sex hormone binding globulin (SHBG) which increases the circulating levels of free testosterone, and also limits the aromatization of testosterone into estrogen by the aromatase enzyme. In other words, tongkat ali exerts effects along the entire chain of testosterone release and utilization, keeping the body in an androgenic state while keeping estrogen levels in normal ranges. This makes tongkat ali beneficial for anyone in a testosterone deficit who as a result are experiencing hormonal imbalances.
Young tongkat ali (Eurycoma longifolia) plant. Photo by Mokkie - CC3.0
In this herbal encyclopedia page the following topics are covered. Click the links to quick jump to that section.
Table of Contents
*Note - If there is something you’d like covered not found here please leave a comment below or contact me with your question and I will reply back and cover it in a Stefan Says Q&A via the Wild Free Organic Email Newsletter.
Tongkat Ali and its Cultivation
The roots and bark of the Tongkat ali (Eurycoma longifolia) plant contain the highest levels of its main active compound, eurycomanone, and its typically the roots that are harvested and prepared for use. Tongkat ali is native to the tropical environments of Southeast Asia, namely Malaysia, Indonesia, and Thailand, and it is commonly found growing in the rainforest as a shrub up to a medium sized tree. Malaysian ginseng as it is also known has a long use in the traditional medicine culture of that region.
Eurocoma longifolia names: Malaysian ginseng, Tongkat ali, long jack, pasak bumi
The primary folk medicine use for long jack can be inferred from that very name, as it’s commonly used to treat sexual dysfunction, as an aphrodisiac, to improve fertility, and boost overall male sexual function. Secondary uses are to increase strength, improve recovery, boost immunity, reduce osteoporosis, for fevers and malaria, and for general aging and anti-cancer benefits. More nuanced uses of tongkat ali as it may be recommended by an experienced traditional medicine doctor would be for gut health problems, appetite stimulation, weight loss, glandular swelling, stress and anxiety, diabetes, and syphilis (1).
Some of those benefits and uses may seem contradictory, and that goes to show you the nuanced effects herbs can have on an individual depending on the person’s age, gender, and state of biology. With a better understanding of exactly how tongkat ali interacts with the body it’s possible to fully appreciate its wide range of health and wellness uses.
Tongkat ali has been increasing in popularity for its well reported testosterone boosting properties which has created global demand for the herb.
Tongkat ali is wild harvested, grown using traditional farming practices, and also cultivated with modern hydroponic techniques. Once Eurycoma longifolia plants are established they are grown for several years until they reach maturity and then harvested, with the roots and bark of the plant being of the most value. The quality and safety of tongkat ali products and supplements depends on the health of the environment in which it’s grown, climate and stressors, the cultivator, harvesting techniques, and processing.
Phytochemicals of Eurycoma longifolia
As with every herb, tongkat ali contains a rich assortment of plant phytochemicals which have various biologic effects. A special group of terpenes known as quassinoids make up the majority of the phytonutrients that make up the roots of Eurycoma longifolia. Quassinoids are quite bitter in taste and the main one found in tongkat ali is eurycomanone. Research into the pharmacological properties of eurycomanone with animals and humans indicates its the main compound responsible for the testosterone boosting effect of tongkat ali. Other eurypeptides exist with similar biologic properties.
Other bioactive compounds found in tongkat ali include alkaloids, lactones, saponins, and flavonoids. The phytochemical composition of each Eurycoma longifolia plant depends on its unique life experience, and thus variations exist between individual plants, grow operations on a whole, and geographic regions. Product processing also has an influence over the final phytochemical composition. Whatever the final status of a tongkat ali supplement, it’s phytocomposition interacts synergistically with the body in what’s known as the entourage effect.
Individual phytochemicals of tongkat ali have their measurable biologic effects, and the larger health effects like androgen modulation, anti-inflammatory and anti-cancer properties, increased insulin sensitivity, and improved mood are from all the compounds working together holistically. While a lot has been learned about how tongkat ali interacts with humans biologically from its traditional folk-use and recent scientific analysis, research is ongoing to better understand tongkat ali.
Eurycomanone (quassinoid)
Eurycomanone is found in the highest concentrations in the roots of Eurycoma longifolia. Research indicates that its primarily the activity of quassinoids, specifically eurycomanone, that are responsible for tongkat ali’s androgenic effect.
Eurycomanone boosts testosterone production, improves spermogensis, increases libido and fertility, and increases semen volume all to significant values over placebo. Eurycomanone in this way is a potent phytochemical to be utilized for remediating sexual dysfunction or to improve sexual function beyond normal in the absence of dysfunction. Eurycomanone also exhibits anti-estrogen activity.
Quassinoids in general are effective in inhibiting cell growth even at extremely low concentrations, showing strong anti-cancer activity across various tumor lines.
Flavonoids
Flavonoids are plant pigments responsible for the vivid colors of many flowers, fruits, vegetables, and herbs. Beverages made from fruits and herbs like juice, wine, and tea contain flavonoids. Tongkat ali is a rich source of flavonoids, especially if the plants harvested were grown in nutrient-rich conditions.
Flavonoids have antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and antimicrobial properties, which makes them great for improving metabolism, reducing inflammation throughout the body, improving cognition, assisting digestion, and increasing immunity, these factors being governed in large part by the beneficial microbiome interactions flavonoids have.
*Note - one of nature’s most powerful flavonoids is apigenin.
Tongkat Ali Testosterone Optimization
Testosterone optimization is usually the main reason people first hear of tongkat ali and have an interest in using the herb. What is testosterone though and how do you optimize it safely?
Testosterone is an anabolic (growth) hormone that is produced by both men and women; for men in the testes by Leydig cells and for women in the ovaries by theca cells. The adrenal glands which are well known for their cortisol (stress hormone) releasing function in the endocrine system also produce small amounts of testosterone. Testosterone is a vital hormone to have in the right amounts for overall health, wellness, and reproduction. Testosterone plays a key role in the development of male sex organs and other characteristics such as facial and pubic hair. Testosterone also triggers muscle protein synthesis and maintains bone density by regulating calcium deposition. For both men and women testosterone is important for overall sexual function, fertility, and libido.
Testosterone has a high binding affinity for a variety of receptors and is therefore not the most stable compound, and this is why oxidative stress plays a key role in male infertility (2). If the body is in an inflammatory state with abundant free-radicals, unbound free testosterone is more likely to be reacted with and altered into a derivative compound. A downward trend in testosterone, sperm count, and semen volume has been reported worldwide since the 1970’s, and while this is a multi-factorial problem, increasing amounts of stress and chronic inflammation are key culprits.
One of the most effective ways to treat male infertility, sexual dysfunction, libido problems, to build muscle and strength, and to increase athletic performance is to increase free testosterone levels in the body while keeping estrogen levels from rising too high, and this is exactly what tongkat ali appears to do.
Tongkat Ali binds to SHBG Increasing Free Testosterone
Scientific research on rats and humans suggest that tongkat ali has an effect on sex hormone-binding globulin (SHBG). SHBG is produced by the liver and binds to sex hormones like testosterone to protect them and decrease their oxidative potential. In this way SHBG regulates the availability of testosterone throughout the body. It’s possible to have high total testosterone but low free testosterone because SHBG levels are elevated.
Conditions and activities that are associated with both lower total and free testosterone are severe weight-loss dieting, chronic fatigue syndrome and depression, and athletic overtraining.
While evidence does show that tongkat ali has an ability to raise total testosterone levels for men by enhancing testosterone steroidogenesis in testicular Leydig’s cells, the greater androgenic effect from tongkat ali comes from its ability to unbind greater amounts of testosterone from SHBG. It’s free testosterone that is able to bind to androgen receptors, and by having this free testosterone stimulating effect, tongkat ali is an androgenic adaptogen particularly useful for people with below-normal testosterone levels.
One mechanism for how tongkat ali raises total testosterone levels is because eurypeptides stimulate dihydroepiandosterone (DHEA), which in turn initiates the conversion of androstenedione and androstenediol to testosterone and estrogen, respectively. These quassinoids also indirectly increase testosterone levels and insulin sensitivity by suppressing the expression of particular glycoproteins. In other words tongkat ali works in many ways at the cellular level to support optimal testosterone levels
Tongkat Ali reduces Testosterone Aromatization
The base building block of hormones is cholesterol. Cholesterol is then transformed into different hormones via a complex sequence of enzymatic reactions as shown in the simplified graphic below:
If you look closely you’ll see that estradiol, the most bioactive form of estrogen, is made from testosterone due to the actions of aromatase (an enzyme). Aromatase can be found in fat, muscle, and brain tissue. With this known you can see why higher body fat levels are associated with lower testosterone levels and greater estrogen levels; because more aromatase is present. This makes loosing excess body fat (>12%) helpful in improving testosterone levels.
Aromatization is a vitally important biological process as it plays a key role in balancing testosterone and estrogen levels in the body. Both testosterone and estrogen are important for men and women, but when the ratios between the two hormones become out of balance then health complications like heart disease and cancer can result.
Tongkat ali influences the aromatization process by limiting the actions of aromatase, thereby keeping testosterone levels elevated in the body. This effect certainly plays out for those with sub-optimal testosterone levels, and anecdotal evidence from users around the world supports the claim that tongkat ali will also limit testosterone from aromatizing even when testosterone concentrations are elevated above normal.
Tongkat Ali for Athletes
These androgenic actions make tongkat ali an herbal supplement of interest for athletes looking to improve their performance, increase in strength and power, and build more lean body mass (3). By working with the adrenal glands, tongkat ali appears to raise testosterone levels while reducing cortisol production, which aids in recovery, and then the androgenic effect is boosted even further by the interactions tongkat ali has with the testes.
Tongkat ali appears to generally favor cortisol reduction and testosterone increase amongst athletes, creating more optimal anabolic states. Tongkat ali also increases insulin sensitivity which is of benefit to athletes because it improves energy uptake and nutrient partitioning.
Tongkat Ali Supplement Recommendation
The tongkat ali supplement that I would use is sold by Nootropics Depot. I used tongkat ali in the past, and since then I have come to greatly value the quality of the herbal extracts sold by Nootropics Depot.
The Eurycoma longifolia extract sold by Nootropics Depot contains a minimum of 2% eurycomanone, the most active phytochemical found in tongkat ali. By standardizing the herbal extract to contain 2% eurycomanone, with each serving you receive a standard, and eventually understood intuitively, effect.
Switching suppliers exposes you to fake supplements or changing quality of herb, which generally reduces the felt effect, so I recommend you find one brand you trust and stick with it, and after having tried many different supplements from various companies, Nootropics Depot is my first choice.
Nootropics Depot also sells 10% Eurycomanone Tongkat Ali Capsules if you wish to experiment with more concentrated dosages. While tongkat ali is generally regarded as a very safe herb as we’ll discuss more thoroughly in the Tongkat Ali Side Effects and Safety section, perform your due diligence and be cautious in using more concentrated/higher doses of tongkat ali as it is a very stimulating herb.
Other Tongkat Ali Benefits
The health benefits of tongkat ali don’t stop with its ability to regulate the endocrine system to increase testosterone and reduce cortisol, tongkat ali also interacts with the brain, heart, and has anti-malarial and anti-cancer properties.
-
Tongkat ali interacts with the brain and nervous system in a few ways, some of which explains its aphrodisiac effects. Supplementation of tongkat ali (in rats) increased concentrations of dopamine in the cerebral cortex and hippocampal regions (4). The hippocampi are two parts of the brain, one on each side located at the temples, that are associated with memory, learning, time and spatial awareness, and neurogenesis (i.e. the growth of new brain cells). The cerebral cortex is the large part of the brain where higher cognitive processes occur, and higher dopamine concentrations in these parts of the brain ehances muscular control, motivation and reward circuits, and improve intra-cellular communication.
Like testosterone dopamine has an ability to bind to many different receptors and therefore it is a relatively unstable molecule. The lower the inflammatory state of the body, the greater dopamine concentrations can reach as they’ll be less likely to react with free radicals. Antioxidants greatly contribute to this effect, and that’s why its a common attribute of herbal aphrodisiacs to increase dopamine concentrations, because they contain phytochemicals which are able to pass through the blood-brain barrier and protect neurotransmitters and hormones from oxidative reactions. Tongkat ali contains many plant antioxidants, and in this way it has a neuroprotective effect.
-
Some studies with rodents showed that tongkat ali exerts a protective function on the heart. Tongkat ali also appears to have a cholesterol lowering effect. This may be due to the plant phenols that tongkat ali possesses, as phenolic compounds are associated reduced risk of heart and cardiovascular diseases (5). More research needs to be done to better understand the heart protective effects of tongkat ali.
-
Tongkat ali’s significant antioxidant and therefore anti-inflammatory activity makes it useful for preventing and treating inflammation-based diseases like cancer. Eurycoma longifolia has demonstrated cytotoxic and antiproliferative effects on a number of human cancer cell lines and solid tumors, including lung, breast, gastric, and cervical cancers.
One of tongkat ali’s traditional medicine uses is for the treatment of malaria, a parasite carried by mosquitos. Phytotochemicals eurycomanone and 7-methoxy-β-carboline-1- propionic acid found in tongkat ali in research settings have shown significant antimalarial activity against P. falciparum strains, and a good anti-malaria effect may exist at standard doses of 200-400 mg/day. Tongkat ali’s anti-malarial effects is a result of its ability to inhibit the growth of malaria parasites.
-
Tongkat ali is a herb of value for men who have osteoporosis as it helps to maintain bone calcium levels because of its testosterone stimulating properties.
Tongkat ali increases insulin sensitivity by enhancing glucose uptake and suppressing lipid accumulation, making it a herb of potential value for the treatment of diabetes.
Tongkat ali possess bitterants, flavonoids, and other phytochemicals which possess antimicrobial activities. Overtime, these antimicrobial effects may be of benefit in reshaping the gut microbiome away from pathogenesis to symbiosis.
Using Tongkat Ali to Increase Libido
An aphrodisiac is something which increases sexual desire and performance. Stimulating libido is a complex process in the brain and body and is governed in large part by the autonomic (unconscious) nervous system (which regulates heart rate, breathing, digestion, etc). The best aphrodisiacs are those that not only stimulate sexual desire, but also those that improve sexual performance. Tongkat ali does both of those in addition to improving parameters of male fertility.
Sexual desire starts with a stimulus, sensory or imaginative, and from there various regions of the brain work together to unleash a cascade of signals, hormones, and various chemicals to activate the sex organs. The hypothalamus in particular is relevant here because not only does it regulate base biologic functions such as appetite, body temperature, and sleep, it also has the ability to secrete testosterone. Low testosterone levels are well associated with reduced libido and sexual dysfunction.
The amygdala is also linked to libido as it is the part of the brain the processes emotions and pleasure. As discussed earlier, it’s been shown that supplementing with tongkat ali improves subjective measures of well-being, improving overall mood while reducing anxiety and depression (6).
Tongkat ali exerts a powerful influence over the endocrine system, boosting androgenic potential, and it also appears to have broad neurocognitive effects, which together make Eurycoma longifolia a potent stimulator of sexual arousal and an aphrodisiac worth trying if currently dealing with low libido.
Tongkat Ali for Erectile Dysfunction
There are many different phytochemicals in tongkat ali and it has proven difficult to identify the main compounds in tongkat ali that help treat erectile dysfunction. For this reason taking a tongkat ali supplement that isn’t fully standardized and is still mostly “raw” is useful.
Not much research has been performed on tongkat ali and erectile dysfunction, but anecdotally people report a variety of benefits such as having an easier time getting and maintaining an erection, a reduced latency period (time in-between ejaculations), and bigger and harder erections. If you encounter erectile dysfunction frequently and are looking for a natural solution to improve your erection quality and duration, then tongkat ali is a promising herb to try.
A popular aphrodisiac used in ancient Egypt was blue lotus flower (Nymphaea caerulea), a type of water lily found in Africa with blue to purple flowers. The phytochemicals found in blue lotus flower modulate dopamine and serotonin in the brain and activate certain regions in the brain, increasingly libido and promoting stronger erections. Another powerful herbal aphrodisiac and testosterone booster to turn your attention to is cistanche, a plant which grows in the harsh deserts of Asia.
I have used tongkat ali, blue lotus flower, and cistanche, and in my experience tongkat ali is the weakest aphrodisiac of the three, so if you are interested in increasing your libido I recommend you experiment with blue lotus flower and cistanche too. I haven’t tried combining tongkat ali with cistanche or blue lotus flower yet, but cistanche and blue lotus flower together have a synergy to them and the libido enhancing effect from that combo can be quite strong.
You can purchase cistanche powder from Nootropics Depot and blue lotus flower to use with a dry-vaporizer like the Fury Edge from Schmerbals Herbals.
Using Tongkat Ali to Treat Male Infertility
In addition to tongkat ali’s aphrodisiac qualities, it also is useful for treating male infertility. When tongkat ali is taken for an extended period of time (30+ days), it has been observed that semen volume, sperm concentration, sperm motility, and sperm morphology all increase/improve (7).
Fertility problems amongst couples wishing to conceive are often placed upon the woman, but in many cases it is male infertility which is a contributing or causative factor for a failure to start a pregnancy. A large number of men are infertile owing to abnormalities in sperm production, especially severe defects in sperm morphology, which render the sperm dysfunctional and thereby greatly reduce the partner’s chances of pregnancy. From one study with 75 final participants who completed 9 months of daily supplementation with 200 mg of a tongkat ali extract, 15% of the participants experienced a “spontaneous pregnancy”, a significant finding (7). This makes tongkat ali an inexpensive herbal remedy worth trying first in hopes of success before moving onto more complex and pricy fertility-enhancing techniques like intra-uterine insemination or in vitro fertilization.
Methods of Using Tongkat Ali and Dosing
The typical dosage of tongkat ali used in human studies is 50-200 mg/day. Based on its safety profile, the daily upper limit for tongkat ali supplementation can be raised considerably, but that is an individual decision to be made only if proper safety measures are put into place and after consulting with a natural medicine specialist.
The serving size for the Tongkat Ali Powder sold by Nootropics Depot is 200 mg, standardized to 2% eurycomanone but overall containing >2% eurypeptides (though what this percentage is we don’t know). If using this brand of tongkat ali I recommend starting supplementation with 100 mg for 1 week and then increasing to 200 mg. If no noticeable effects are felt at the standard serving size then the dosage can be increased to 200 mg twice daily.
Tongkat ali contains many chemicals known as bitterants and therefore it’s quite bitter. Depending on your taste buds its flavor can range from mildly unpleasant to very bitter and astringent. The way I take tongkat ali is to mix it in with a shot of water and shoot that followed by a shot of apple cider vinegar, clearing the taste buds with water afterwards. It’s also quite popular to add tongkat ali to coffee (which is something I do with the herb cistanche) so experiment with this if you drink coffee to see if that helps to mask the bitterness. It’s best to take tongkat ali on a mostly empty stomach so it is absorbed into the bloodstream effectively and without delay.
A general rule of thumb to follow when using any herb that alters the endocrine system is to cycle off the herb for as long as you used it. For example, if you use tongkat ali for 60 days, don’t use tongkat ali or any other androgenic herbs for the next 60 days. This allows the endocrine system to operate normally without the presence of a modifying herb/drug while maintaining many of the hopefully beneficial adaptations that took place, allowing for a “locking in” of any improvements made. In this way, the endocrine system over time - and from the effects of various androgenic herbs like tongkat ali and cistanche - can be optimized to more naturally keep testosterone levels high while estrogen stays in the normal range.
How long does it take Tongkat Ali to Work?
In my experience tongkat ali is noticeably felt after the first dose and also more generally after a week or two.
If you’re sensitive, in the hours immediately after the first dose of tongkat ali you may experience a boost to your overall energy, focus, and concentration. As tongkat unbinds testosterone from SHBG, you may find yourself feeling more confident, stronger during your workouts, and more willing to engage in “risky” activities. If you have a regular workout schedule I recommend you take tongkat ali 1-2 hours before exercise in order to capitalize on the energy and testosterone boosting effect.
Over the course of a couple weeks stretching into months, supplementing with tongkat ali will be observable through larger anabolic changes. You may experience increases in strength, power, and lean body mass. You may also notice overall androgenic changes like a deepening voice, more and thicker body/facial hair, and improved mood, confidence, and decisiveness.
To best track how tongkat ali is benefitting you I recommend you keep a supplement observation journal and track your observations while using the herb.
Tongkat Ali Side Effects and Safety
There are no reported adverse side effects for humans with the dosages used in research studies (~200 mg/daily). The LD50 for rodents is very high (>1500 mg/kg bodyweight) and translated to humans this equates to a lethal dose 50% of minimum 120 mg/kg. For a 75 kg individual this is 9 grams of extract powder. This may not be the real human LD50 dose.
One 2-month human supplementation trial enlisting 20 healthy males found 600 mg/day of Eurycoma longifolia extract to have no influence on blood profiles or any deleterious effects on measures of liver or renal function (8). That said, some people have reported experiencing nausea, stomach upset, and diarrhea after taking tongkat ali, likely due to its astringency and extreme bitterness. In rare cases, tongkat ali may cause allergic reactions, such as skin rash or difficulty breathing. Tongkat ali also sometimes causes joint point and can be excessively stimulatory.
Is there a Better Alternative to Tongkat Ali?
For pure testosterone optimization tongkat ali is one of the best, but given its potential side effects like joint pain better options may exist for you and what desired effect(s) you wish:
Cistanche: When your ultimate goal is to improve athletic performance through a testosterone boosting effect, then I recommend cistanche as it doesn’t cause joint pain. Take cistanche with dandelion root powder for best effect. Cistanche is also a better libido enhancer in my experience.
Ashwagandha: If your overall goal is to improve your hormonal levels and their equilibrium to each other, then ashwagandha is a better hormone modulating herb to use than tongkat ali. Ashwagandha can still raise testosterone modestly, measured in one study by an average of 15% (9) but it does this by working primarily with the adrenal system, the autonomic nervous system, and DHEA and less with Leydig testosterone synthesis and SHBG directly. Ashwagandha and tongkat ali would be a synergistic combination to consider.
Blue Lotus Flower: If you’re desiring a potent aphrodisiac effect, blue lotus flower is superior to tongkat ali. Blue lotus flower gets you in the mood easier and quicker via dry vaporization, has an overall better neurocognitive effect, and won’t dry your skin out like tongkat ali might.
Other Hormone Modulating Herbs
Medical Disclaimer: All information, content, and material of this website is for informational purposes only and is not intended to serve as a substitute for the consultation, diagnosis, and/or medical treatment of a qualified physician or healthcare provider.
Disclosure: Wild Free Organic is a member of various affiliate programs and if a purchase is made through one of our affiliate links a small commission is received. This does not affect your purchase price. Visit our disclosure page for more information.
Research:
Rehman S, Choe K, Yoo H. Review on a traditional herbal medicine, eurycoma longifolia jack (Tongkat ali): its traditional uses, chemistry, evidence-based pharmacology and toxicology. Molecules. 2016;21(3):331.
Sikka SC. Relative impact of oxidative stress on male reproductive function. Curr Med Chem. 2001;8(7):851-862.
Talbott SM. Human performance and sports applications of tongkat ali(Eurycoma longifolia). In: Nutrition and Enhanced Sports Performance. Elsevier; 2013:501-505.
Ezzat SM, Ezzat MI, Okba MM, et al. Brain cortical and hippocampal dopamine: a new mechanistic approach for eurycoma longifolia well-known aphrodisiac activity and its chemical characterization. Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine. 2019;2019:1-13.
Khanam Z, Wen CS, Bhat IUH. Phytochemical screening and antimicrobial activity of root and stem extracts of wild Eurycoma longifolia Jack (Tongkat ali). Journal of King Saud University - Science. 2015;27(1):23-30.
Talbott SM, Talbott JA, George A, Pugh M. Effect of Tongkat Ali on stress hormones and psychological mood state in moderately stressed subjects. Journal of the International Society of Sports Nutrition. 2013;10(1):28.
Bin Mohd Tambi MI, Imran MK. Eurycoma longifolia Jack in managing idiopathic male infertility. Asian J Androl. 2010;12(3):376-380.
Tambi, M. I., and A. A. Kadir. Human toxicology and clinical observations of Eurycoma longifiola on men’s health. Int J Andrology 28.Suppl 1 (2005): 37-38.
Lopresti AL, Drummond PD, Smith SJ. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, crossover study examining the hormonal and vitality effects of ashwagandha (withania somnifera) in aging, overweight males. Am J Mens Health. 2019;13(2):155798831983598.
Blue Lotus Flower
Blue lotus flower has a rich thousands of years long use as a psychic potentiator, and with the advent of worldwide supply chains, blue lotus flower can now be used by anyone, no longer just the Egyptians. Blue lotus flower has a rich phytopharmacology and combined with cannabis provides an entrance to the holy spiritual journey.. This is your complete guide.
Article by Stefan Burns - Updated October 2022. Join the Wild Free Organic email newsletter!
In the oldest Egyptian cosmogony, the world began when the Sun God Ra (Atum) emerged from a blue water lily growing in a dark pool of nothingness symbolizing chaos (Nun). This blue water lily is a plant that was sacred to Egyptian culture since the earliest dynasties thousands of years ago. Overtime the flower of the blue water lily (Nymphaea caerulea) evolved into a symbol of the cycle of life and death and was featured prominently in tomb motifs of the pharaohs and members of the highest caste, being one of the primary offerings the high ranking dead were decorated with for their journey into the afterlife. Blue lotus flower was used extensively in the religious and healing ceremonies of the high priests of Egypt, and Nymphaea caerulea was a herb revered because of its unique plant pharmacology which bestow upon it transcendental mind-altering properties.
Blue lotus flower contains an assortment of plant phytochemicals like alkaloids and flavonoids that together make it mildly psychoactive, sedative, and it’s a strong aphrodisiac. Blue lotus flower has these properties primarily because it normalizes the activity of the central nervous system by acting on dopamine and serotonin receptors in the brain. Little human-based research has been completed on blue lotus flower, but abundant research exists on its main chemical constituents apomorphine, nuciferine, and antioxidant flavonoids. In addition to this its rich history of use across many different cultures supports its use in treating mental health issues like depression, paranoia, and insomnia, as well as neurodegenerative problems like Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s disease. I have also personally experimented with the herb in a variety of ways and share my insights here.
Beyond its potential health and wellness uses, blue lotus flower is a herb that can be used to facilitate spiritual growth by tuning human consciousness to different dimensions of reality, and this shamanistic effect of blue lotus flower is especially powerful when combined with other psychedelic herbs like cannabis. Blue lotus flower can be consumed in a variety of ways for its wellness, spiritual, or recreational uses, most commonly as a tea or dry-vaporized or taken sublingually. In this article we take a deep dive into blue lotus flower and start by exploring the unique plant pharmacology which bestows upon it, as some would say, its psychic effects.
Table of Contents
Phytochemicals of Blue Lotus Flower
Blue lotus lily (Nymphea caerulea) is an African water lily, the flowers of which contain alkaloids apomorphine and nuciferine alongside many diverse flavonoids. Flavonoids are potent antioxidants with many beneficial biologic effects throughout the body, and the main flavonoids found in blue lotus flower are anthocyanins and different versions of quercetin, myricetin, and kaempferol, with “rare” versions of kaempferol and quercetin having been isolated before. All these phytochemicals all work together in an “entourage” effect giving blue lotus flower its unique physiological and psychological effects.
Before going into specifics, the basics of how blue lotus flower works is that apomorphine/apomorphine-like alkaloids non-selectively stimulate dopamine and serotonin receptors, nuciferine modulates dopamine transport and also stimulates certain dopamine and serotonin receptors, while flavonoids keep dopamine from destabilizing and oxidizing which creates cellular damage. This combination of chemicals, which all easily pass the blood-brain-barrier, is able to powerfully alter brain neurochemistry and promote neurogenesis.
Dopamine is an important hormone and neurotransmitter with many different functions throughout the brain, regulating emotions, learning, memory, and neuroplasticity, and it also helps govern motor control throughout the body. The direct precursor for dopamine is L-DOPA, which is synthesized in the brain and kidneys.
Serotonin in another important neurotransmitter that modulates mood, appetite, sleep, learning, memory, and general cognition, in addition to physiological acts like vomiting and vasoconstriction. About 90% of serotonin is produced in the intestinal tract through interactions between the digestive system and microbiome.
Apomorphine
Apomorphine has been described as a psychoactive alkaloid and is a non-selective dopamine agonist. Apomorphine is also a strong antioxidant being generally regarded as neuroprotective. Apomorphine was first synthesized by humans in 1845, though its medicinal and spiritual usage stretches back thousands of years because it is naturally found in the flowers of the African water lily Nymphaea caerulea.
Apomorphine can be produced by heating morphine in an acid solution (like hydrochloric acid), and apomorphine’s chemical formula (C17H17NO2) is similar to morphine (C17H19NO3) minus a water molecule (H2O). In spite of its name and similar chemical formula, “apomorphine has none of the habit-forming characteristics of morphine…no more like morphine than sawdust is like sugar” according to apomorphine advocate Dr. John Y Dent back in 1934.
Apomorphine is very lipophilic (likes fats) and is moderately soluble in water and normal saline solution. Apomorphine oxidizes rapidly with air and light exposure. Because of its high lipid solubility, APO equilibrates rapidly between blood and tissue compartments, and transient brain concentrations of apomorphine have been measured up to 8x greater than in plasma. The fact that apomorphine is highly soluble in lipids is relevant later in how it works nicely with cannabis (see Blue Lotus Flower and Cannabis).
Apomorphine Receptor Science
Apomorphine has a powerful action on the central nervous system and in multiple parts of the brain, but not on the vagus nerve, due to how to stimulates various neurotransmitter receptors. Specifically, apomorphine activates the cerebral cortex and attenuates inhibition of the thalamus by the internal globus pallidus. The thalamus sits deep within the brain and acts as a central hub which processes and relays sensory information (except smell) to the cerebral cortex for interpretation. Apomorphine is a non-selective dopamine receptor agonist and also activates serotonergic receptors and α-adrenergic receptors.
Blue lotus flower contains significant levels of apomorphine and apomorphine-like alkaloids, and this allows blue lotus flower to influence dopamine and serotonin pathways in addition to increasing the sensory throughput of the thalamus, aiding its mentally stimulating and mind-altering effects. In my experience, covered more in the later section Blue Lotus Flower and Cannabis, the psychedelic effects of blue lotus flower are only really noticeable when combined with another psychedelic like cannabis, or as the ancient Egyptians reportedly did with mandrake fruit and opium poppies.
Physiological Effects of Apomorphine
The main physiological effects of apomorphine are:
Lowers blood pressure
Lowers body temperature
Reduces sympathetic nervous system activity
Reduces prolactin secretion
Increases growth hormone
Promotes relaxation
Improves male sexual function
Dilates the pupils
Apomorphine is a highly potent antioxidant and free radical scavenger with a neuroprotective effect. This is quite valuable because dopamine, which apomorphine interacts with, is highly unstable and oxidizes easily which can cause cellular damage under certain conditions. Some of apomorphine’s neuroprotective effects are receptor mediated, and some are non-receptor mediated. One example of how apomorphine is neuroprotective is that activation of the D4 dopamine receptor inhibits oxidative stress-induced nerve cell death, and as a non-selective dopamine receptor agonist, apomorphine can bind to an activate the D4 receptor.
Apomorphine has a rapid onset of action and a relatively brief duration of effect of about 60-90 minutes long, though its pharmacodynamic effects last up to 30 minutes after its plasma concentrations fall below its “peak ineffective threshold”.
Apomorphine Metabolism and Bioavailability
Apomorphine is a high clearance compound that is mainly metabolized and excreted by the liver, with less than 5% of apomorphine introduced into the body being excreted unchanged in the urine.
Oral administration of apomorphine is not recommended because of its poor bioavailability and significant first-pass metabolism by the liver. In fact, very large doses of apomorphine can lead to an accumulation of a liver-produced nephrotoxic (kidney damaging) metabolite. Sublingual administration of apomorphine bypasses liver first-pass metabolism. Apomorphine does not require decarboxylation to be activated (like cannabinoids do), and it readily diffuses across the blood-brain-barrier.
There are many ways to consume blue lotus flower, and in the context of receiving the most apomorphine, then sublingual use of a 10:1 or 20:1 blue lotus flower extract will be one of the most effective methods. I have tried this before, taking a pea-sized amount of 20:1 blue lotus flower extract sublingually by itself, and didn’t notice anything other than a subtle improvement in mood and enhanced focus. For someone with Parkinson’s disease though, sublingual use of a blue lotus extract may reduce or eliminate their tremors and muscle spasms.
Conventional Medicinal Uses of Apomorphine
Since its first synthesis, in a clinical setting the main uses of apomorphine are for rapid gastric emptying, to promote sedation, and as an antiparkinsonian medicine which reduces tremors and muscle spasms.
Pure apomorphine was the drug of choice for any condition that required prompt emptying of the stomach until the 1970’s when better alternatives came along, because though the apomorphine induced vomiting*, it was usually followed by sleep which isn’t terribly helpful when diagnosing possibly toxic exposure.
*Note - In order to not scare anyone away from trying blue lotus flower because of apomorphine and its ability to trigger gastric emptying, the doses of pure apomorphine needed to trigger this are quite high and a lot of blue lotus flower would need to be consumed to reach this threshold. In addition to this blue lotus flower contains other plant phytochemicals which alters its overall physiological and psychological effects. Still, if you’re easily triggered into vomiting, then you should start very carefully with blue lotus flower or avoid it altogether.
The main medicinal use of apomorphine is in the treatment of Parkinson’s disease. Parkinson’s disease is characterized by chronically reduced levels of dopamine in parts of the brain that leads to a hypersensitivity of brain cells concerned with motor control.
By triggering the neurotransmitter pathways that it does, apomorphine reduces Parkinson’s tremors and involuntary movements. Long term continuous use of apomorphine for a Parkinson’s patient like a continuous drip can lead to tolerance of the chemical, but because it is high clearance, only a four hour interval is required to prevent tolerance from building up.
Compared to other dopamine agonist, long term use of apomorphine is less likely to induce dopamine dysregulation syndrome characterized by hypersexuality or addiction to medication or gambling.
The most often reported clinical adverse effect from apomorphine is headache and nausea. Apomorphine is an expensive drug, and a safe and effective dose for apomorphine is still to be elucidated for many different conditions like Alzheimer’s disease. The benefit of using blue lotus flower to naturally and holistically help treat neurodegenerative diseases is that as a natural herb it’s easier and safer to dose, comes with less risk of side effects, and has a natural entourage effect with its other phytochemicals that makes it helpful for a wide range of health conditions in a way that is likely significant, just not concretely confirmed yet via modern scientific research.
Nuciferine
In addition to containing apomorphine, blue lotus flower also contains nuciferine alkaloids. Nuciferine has a rich polypharmacology as it and its metabolites easily pass the blood-brain-barrier, it has a high number of molecular targets, and it has good protein binding capability. Nuciferine is similar in effect to anti-psychotic compounds, and this effect of nuciferine pairs nicely with apomorphine, the two together being a good combination for treating conditions like depression, anxiety, paranoia, insomnia, and schizophrenia.
Nuciferine is an alkaloid is a partial agonist of certain dopamine receptors (D2, D5), is an agonist of D4 (making it neuroprotective), and nuciferine also modulates the dopamine transporter. The D2 receptor is a highly desirable target for antipsychotic effects, and nuciferine and apomorphine both trigger it (another reason blue lotus flower pairs nicely with cannabis).
Nuciferine has antagonistic, inverse agonist, and agonist activity across the many different serotonin receptors, and it has the greatest affinity at the serotonin receptors as compared to the dopamine receptors. For example, nuciferine has an activity about 2/3rds as strong as dopamine at the D2 receptor.
Dopamine and Dopamine Transporter Inhibition
One of nuciferine’s cellular actions is that it inhibits the dopamine transporter. Dopamine transporter inhibitors can be addictive, such as cocaine and heroin, but inhibiting dopamine transport also has the potential of being useful in increasing brain plasticity and improving overall cognitive function, so finding non-addictive dopamine transporters is important.
One of the main clinical uses of apomorphine back in the late 1800’s and early 1900’s was for the treatment of addictions, and apomorphine is a dopamine receptor agonist with little ability to trigger dopamine dysregulation, one of the characteristics of which being addictive tendencies. The benefit of blue lotus flower is that by containing nuciferine and apomorphine together, it triggers the various dopamine pathways in a neuroprotective manner and modulates dopamine transport safely, increasing brain plasticity and improving cognition, without addictive tendencies developing. Nature is the best pharmacist, and the ancient Egyptians holistically knew this.
It’s useful to go more in-depth on dopamine and modulating dopamine transport because the dopamine system (along with serotonin) is the main neurotransmitter/hormone than blue lotus interacts with. Dopamine is involved in regulating synaptic plasticity, and is a crucial neurochemical mechanism underlying learning and memory.
Declining brain dopamine signaling during aging is associated with the onset of neurological impairments, and in the human brain dopaminergic signaling has been observed to decline 5-10% every decade. Elevated dopamine levels modulate synaptic neurotransmission, network activity, and synaptic plasticity. Increased dopamine levels can induce neuronal plasticity by increasing dendritic spine numbers and shifting their micromorphology toward more elaborate and thinner spine structures. Dendritic spine changes are thought to reinforce memory encoding by increasing synaptic neurotransmission, and dendritic spines generally decrease during aging.
Dopamine receptor subtypes differ in their downstream physiological outcomes, so modulating dopamine reuptake by modulating dopamine transport is a promising therapeutic strategy to balance dopamine levels.
One of the issues with dopamine is that it can oxidize to form reactive oxygen species or unstable electron-deficient quinones. The dopamine transporter is one of the proteins at high risk of oxidation by dopamine because it has a high affinity for dopamine. Under inflammatory conditions, some percentage of dopamine will oxidize and modify dopamine transport function, and another percentage of dopamine will oxidize and damage proteins, lipids, and DNA. Free radical damage is one of the main causes of neurodegenerative diseases. Dopamine oxidation products inhibit the uptake of dopamine into synaptosomes, both by interfering with dopamine transporter function and also by creating general oxidative damage. Dopamine toxicity can be prevented when it is released and transported in the presence of antioxidants.
Blue lotus flower is so valuable in the context of beneficially regulating the dopamine system because apomorphine itself is a potent antioxidant that helps dopamine from oxidizing, and nuciferine keeps dopamine transport smoothly functioning. The flavonoids blue lotus flower contains also easily enter into the brain and exert antioxidant and anti-inflammatory protective effects throughout the extracellular matrix.
Anthocyanin, Quercetin, Myricetin, and Kaempferol Flavonoids
Blue lotus flower contains a rich and rare assortment of antioxidant and anti-inflammatory flavonoids. Flavonoids are absorbed readily into the bloodstream, and if orally ingested, those that aren’t absorbed into the bloodstream make their way to the large intestine where the microbiome converts them into beneficial secondary metabolites the body uses. Flavonoids cross the blood-brain-barrier and exert their antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects throughout the brain, and blue lotus flower containing abundant flavonoids is the final piece of the phytochemical puzzle that helps to explain blue lotus flower’s many health effects and wellness benefits.
By stimulating the dopamine system, blue lotus flower promotes the secretion of dopamine, a relatively unstable and easily oxidized chemical. The flavonoids of blue lotus flower, in addition to apomorphine and nuciferine help to keep the cellular environment of the brain free of dopamine-induced oxidative damage, which allows dopamine to better perform its critical biologic tasks and keeps the cellular infrastructure of the brain functioning normally. Blue lotus flower can be used to help offset age-related dopamine decline.
It’s the combination of apomorphine, nuciferine, and antioxidant flavonoids that make blue lotus flower such a compelling herb to use for enhancing cognition, improving learning and memory, preventing neurodegeneration, and for normalizing the functioning of the central nervous system. Balancing the nervous system is critically important for overall wellness and lifespan because the ratio between sympathetic (stress) and parasympathetic (rest) activity governs the cellular conditions and activity that occurs throughout the body.
Blue Lotus Flower Effects
Blue lotus flower can be consumed in a variety of ways, and going beyond the trio entourage effect of apomorphine, nuciferine, and flavonoids, the ratios you get of each varies via method of consumption and what it’s consumed with.
Blue lotus flower has powerful effects on the emotional, mental, and astral (dream) planes, but it’s not easily felt on its own. In experience it acts more as a potentiator for other psychedelic transcendental herbs like cannabis, mandrake, or opium.
The ancient Egyptians combined blue lotus flower with mandrake and opium into didi, an “elixir of life”. Mandrake and opium are possibly deadly herbs yet it appears the Egyptians were able to use them fairly safely by combining them with blue lotus flower. The unique dopamine and serotonin activating combination of blue lotus flower help keeps the body relaxed and parasympathetic.
Blue Lotus Flower and Cannabis
In the modern day narcotics are popular such as cannabis and tobacco, and with these herbs blue lotus flower can be mixed with. Cannabis raises your heart rate, nicotine gets you going, both are usually smoked, and in my experience this is where I feel the effects of blue lotus flower greatest. Every time I have smoked cannabis and blue lotus flower together the high has been better than if I had smoked cannabis by itself. Adding apomorphine, nuciferine, and extra flavonoids and terpenes to cannabinoids THC and CBD makes the psychedelic experience much grander. Your senses are broader, you can access vibrational realms rarely experienced and incredibly aligning. Smoking cannabis and blue lotus flower connects you with your breath and yogic principles for spiritual growth.
Blue lotus flower creates brainwaves in the the learning and memory centers of the brain, the hippocampus, where new brain cells are created freely. A healthy hippocampus is a healthy brain, a brain that is able to connect to the Earth’s brainwaves, the Schumann resonances. By entering into electromagnetic resonance with the Schumann resonances at 8 Hz, 14 Hz, 20 Hz, 25Hz, and 33 Hz, your brain “plugs in” to the collective consciousness of all life on Earth that has ever lived. Not all the answers are there, but Earth has a pretty rich and deep database of helpful information, if you learn how to access it.
By connecting with the breath during any vibrational downloads, revelations are bestowed upon you, completely reprogramming your operating system to be more efficient. To operate more from a place of love, compassion, and empathy, free of harmful impact.
I suppose I’m writing a trip report right now, and if you decide to try it yourself after considering the safety concerns, write your trip report in the comments below for all the world to see, and see if you can imprint that feeling upon the Schumann resonances too ;)
Blue Lotus Flower Aphrodisiac Effects
Blue lotus flower is a powerful aphrodisiac for both men and women. In fact you can trace the ability of this herb to induce sexual arousal by its Linnaean name - Nymphaea caerulea.
In greek mythology a nymph is a deity that takes the form of a beautiful young maiden. A nymphomaniac is a women with excessive sexual desire. Blue lotus flower has aphrodisiac effects for men and women because it targets the dopamine and serotonin systems while also increasing parasympathetic (feed and breed) nervous system activity.
Blue Lotus Flower for Men
For men, the primary benefit of blue lotus flower is that it helps stimulate and maintain erections. As such, blue lotus flower can be an effective herbal treatment for erectile dysfunction. Blue lotus flower effectively makes it easier to go from the processing of sexual stimuli (visual, olfactory, tactile, or imaginative) to a relaxing of the smooth muscles down below that make erections possible. Apomorphine in particular reduces prolactin levels, and prolactin is well known to inhibit erections. In fact it’s prolactin that’s released after ejaculation to turn off sexual desire and stop the erection.
By working with the paraventricular nucleus (the part of the brain that initiates erection and ejaculation signals) and by opening and closing specific ion channels in smooth muscles, blue lotus flower activates the male reproductive system and is very sexual arousing, given a trigger.
Blue Lotus Flower for Women
The aphrodisiac mechanisms of blue lotus flower for women are not as well understood as they are for men, but the effect is the same. Blue lotus flower is an effective herbal treatment for female sexual dysfunction because of how it alters dopamine, serotonin, and the functioning of the paraventricular nucleus. It’s the alkaloids found in blue lotus flower like apomorphine that are chiefly responsible for its aphrodisiac effect, so using blue lotus flower in a way that delivers these alkaloids directly to the brain without first being metabolized by the liver makes the effect stronger and more noticeable.
Blue Lotus Safety Concerns
The main safety concerns for blue lotus flower revolve around apomorphine. Remember one of the old medicinal uses for apomorphine was to induce vomiting, and the first time I combined blue lotus flower with cannabis and chamomile I felt the urge but was able to surpass it. At the time I was beginning to feel sick as my mucus was very thick and I also saw something very gross by chance which triggered the reflex, so if your stomach is feeling 100% great then you should be careful with blue lotus flower. I’ve never had any gagging or vomiting issues with blue lotus flower since.
Apomorphine can also cause fatigue, weakness, frequent headaches, and nausea. There are case reports, few and far between, of exceptional cardiovascular collapse in children and adults. Make sure your cardiovascular system is healthy and you’re relatively unstressed before using blue lotus flower.
The Egyptians used blue lotus flower as part of an elixir of life, and it was consumed prodigiously by the highest caste, so if consumed properly it appears relatively safe, and I would concur based on my personal N=1 experience. Drinking blue lotus flower tea is the safest way of using it, as it extracts the least amount of alkaloids, but it still extracts some, and you can consume this tea nightly for long periods of time in order to potentiate vivid, memorable, and lucid dreams.
Blue Lotus Flower Wellness Uses
For people not interested in smoking or dry-vaporizing blue lotus flower, which allows for its active compounds to bypass liver first-pass metabolism, then drinking blue lotus flower tea is an excellent option for consumption with many beneficial health effects. Blue lotus flower wine is also an option we’ll explore.
Blue Lotus Flower Tea
Alkaloids apomorphine and nuciferine are moderately water soluble. Water temperature can be adjusted up or down to roughly determine the level of blue lotus flower phytochemical extraction. Some of the alkaloids of blue lotus flower are metabolized into metabolites toxic to the kidneys, which then require processing. The body only excretes 5% of alkaloids in original form because as antioxidants they bind or donate to free radicals easily. You have to be mindful when consuming the alkaloids found in blue lotus flower that your body can process them safely. Don’t drink any alcohol when using blue lotus flower, as alcohol damages the liver and kidneys too much.
A dream tea can be created using blue lotus flower consisting of equal parts mugwort, damiana, chamomile, and blue lotus flower. Mugwort is a dream potentiator, damiana is a gentle mood booster, chamomile promotes relaxation and brainwaves, and blue lotus flower actives the hippocampus and limbic (emotional) system. The tea has a pleasant flavor and can be sweetened with honey.
Drinking this 1:1:1:1 blue lotus flower, mugwort, damiana, and chamomile dream tea helps treat depression, anxiety, sleep problems, and nightmares. Any emotional disturbances can be balanced out with the help of blue lotus flower as it gently rewires the brain by improving neuroplasticity. With these incredible effects you may want to drink it nightly, though I feel it’s best in my experience to drink this dream tea when you feel you need it rather than consistently everyday. Trust your timing and trust any insights you receive during the brain’s mood modification upgrade.
Emotional disturbances create oxidative conditions in the brain, and by reducing emotional disturbances to a minimum, blue lotus flower helps to keep the brain in a youthful regenerative state. From this platform of clear cognition spiritual growth can be launched from.
Blue Lotus Flower Wine
The alkaloids found in blue lotus flower can also be extracted using alcohol, and one way the ancient Egyptians used blue lotus flower is they steeped the flowers for a few days in red wine and then consumed the beverage. While I typically don’t recommend drinking alcohol for wellness purposes, red wine does contain a lot of beneficial phytochemicals like resveratrol, and not much wine is needed to extract a good amount of alkaloids from blue lotus flower, only about a glasses worth (5 oz).
A glass of blue lotus flower wine can be used to help with depression and as a general mood booster, or it can be used to establish a platform for spiritual exploration depending on how much is consumed and whether other psychedelics like cannabis are used.
Blue Lotus Flower for Spiritual Growth
Nymphaea caerulea, the African blue water lily, was the plant of greatest importance to the ancient Egyptian elite. The religious class, with the pharaoh claiming himself a demi-god at the top, consumed blue lotus flower as part of trance-like healing ceremony. Under the guidance of a shaman, during this healing ceremony the spirit was believed to separate from the body and commune with entities like spirit guides, past ancestors, and gods in the astral dimensions and beyond. In these realms of higher consciousness, a metamorphosis of the spirit takes place, and upon returning to the body with a new bioelectrical code, heals the body with the “software” upgrade. Bioelectricity is what programs DNA, and if your DNA is creating stressful cellular conditions, then the body destructively ages.
Dry-Vaporizing Blue Lotus Flower
To receive the greatest benefit from blue lotus flower with the least impact on health, then it is best dry-vaporized. By heating the plant material to below combustion temperatures, alkaloids, flavonoids, terpenes, and other phytochemicals are volatized out of the herb and inhaled alongside water vapor. This herbal vapor is absorbed into the bloodstream by the lungs, allowing a majority of the active phytochemicals to cross the blood-brain-barrier unmetabolized. Dry-vaporizing blue lotus flower alongside cannabis, or smoking them for that matter, increases the overall bioavailability because Nymphaea caerulea alkaloids are highly lipid soluble and combine nicely with sticky cannabinoids.
In the modern day where mandrake and opium aren’t widely used (and for good reason) I think dry-vaporizing cannabis and blue lotus flower together is a highly compelling way to experience spiritual dimensions of reality in a way that is relatively safe and harmless to the body.
My favorite dry-vaporizers are made by Healthy Rips, I highly recommend their Fury Edge used with dosing capsules so the vaporizer stays clean. You can precisely choose the chamber temperature for precise extraction of phytochemicals like different cannabinoids, it has a long battery life, and it is very efficient, producing big clouds of vapor.
Energetic Infusion
Before you proceed with any method of consuming herbs, you can infuse them with energy of your choosing to direct your spiritual experience.
For example if you feel you need emotional stability, place any herbs you’re using, say the dream tea blend, in-between your hands and say what you want to help you achieve emotional stability. In this case you could infuse them with Earth energy, acceptance, and balance. The more psychedelic the experience, the more your affirmations at the beginning are powerfully felt and realized. Combining cannabis with blue lotus flower is a safe way to powerfully interact with the emotional, mental, and spiritual dimensions of reality. The benefit of mixing the two together is that while blue lotus flower is only subtly felt on its own, it eliminates the paranoia and anxiety that is common to cannabis. CBD also reduces paranoia and feeling of anxiety induced by THC, and adding CBD into the herbal blend improves the stability and depth of the experience even further.
Blue Lotus Hallucinations
Establishing a sacred ritual around herbal practices just as the ancient shamans used to do creates a sense of responsibility to not take the situation lightly and helps to deeply guide you in your sacred journey. Depending on to hat degree you disconnect from the material realm, your spirit body can let go of the physical body and begin to energetically travel at the speed of light, transmitting to and receiving information from different layers of consciousness around the world instantly. Use a lot of psychedelics and you begin to access the implicate order beyond space and time, and you have greater choice of whether you return to your body or not.
I’ll share a personal story. On the night before a full moon I drank blue lotus flower red wine and shared in a couple blue lotus flower and cannabis joints with friends. I was well potentiated after the wine and first joint, and shortly after the second joint, everything felt more vivid and light began to shift and sway. Looking at the full moon I saw shapes dance across its surface, enacting an endless cosmic drama to all who would simply look up. I felt connected to the wholeness of reality and felt the truth of the fact that everything happens for a reason. I felt safe and supported and in control of my destiny. This experience of higher consciousness, of not feeling like I was simply enacting out programmed behaviors beyond my control, lasted for the rest of the night and afterwards I felt I had made significant progress in tuning into and aligning with my higher spirit.
Steeped in red wine for three days, a 1/4 oz of blue lotus flower provided a broader foundation for the cannabinoids to reach upwards from. The energy of the full moon amplified everything. Your environment cannot be overlooked in its importance in determining any psychedelic or spiritual experience. If you intend to pursue the spiritual journey, then do everything you consciously can to improve your environment before embarking upon any psychedelic experience. This is the key to having good trips, and we want to avoid bad trips as they can lead to even more severe emotional and mental disturbances which require healing from on their own.
Return from the Underworld
The myth of the Egyptian god Osiris is symbolic of the life cycle of the blue water lily. For three days the flowers of the blue water lily grace the water’s surface, blooming a sweet narcotic nectar. On the third day drowsy bugs become trapped as the flower closes and the stems coils, drawing the flower back under the water’s surface, into nothingness. Similarly the Osiris myth has Osiris murdered by his brother, and for three days he explores the underworld before being resurrected. It was the life cycle of the blue lotus flower that provided the inspiration for the myth of Osiris, among many others.
Using blue lotus flower in combination with other herbs like cannabis, chamomile, mugwort, and damiana creates an environment conducive to drawing emotional and mental pains to the surface, sedating them, and then allowing them to be dragged into nothingness on the third day.
Blue lotus flower is a herb that teaches you the truth of that “to heal the body you must first cleanse the soul”.
Blue lotus flower is truly a elixir of life if used for this purpose, just be careful to not abuse this sacred plant, or you may find yourself as the drowsy bug trapped in the flower on day three.
Where to Buy Blue Lotus Flower
I have used blue lotus flower from two different vendors.
One was a local apothecary I discovered by chance while visiting Edinburgh, Scotland. The quality was quite good.
The second source, from which I’ve now purchased 5 oz from, is Schmerbals Herbals. They have a popular Etsy store, but if you go directly to their website you’ll find the prices are about 50% cheaper and you’ll get free shipping on orders over $35 using a coupon you can find in the coupon section of their website. The dried flowers I received from them (imaged at the top of the article) are of a very high quality, and are easily steeped into a tea or ground down for dry-vaporizing or smoking.
Medical Disclaimer: All information, content, and material of this website is for informational purposes only and is not intended to serve as a substitute for the consultation, diagnosis, and/or medical treatment of a qualified physician or healthcare provider.
Disclosure: Wild Free Organic is a member of various affiliate programs and if a purchase is made through one of our affiliate links a small commission is received. This does not affect your purchase price. Visit our disclosure page for more information.
Research:
Emboden W. The sacred journey in dynastic egypt: shamanistic trance in the context of the narcotic water lily and the mandrake. Journal of Psychoactive Drugs. 1989;21(1):61-75.
Auffret M, Drapier S, Vérin M. The many faces of apomorphine: lessons from the past and challenges for the future. Drugs R D. 2018;18(2):91-107.
Ribarič S. The pharmacological properties and therapeutic use of apomorphine. Molecules. 2012;17(5):5289-5309.
Farrell MS, McCorvy JD, Huang XP, et al. In vitro and in vivo characterization of the alkaloid nuciferine. Zhou H, ed. PLoS ONE. 2016;11(3):e0150602.
Berman SB, Zigmond MJ, Hastings TG. Modification of dopamine transporter function: effect of reactive oxygen species and dopamine. Journal of Neurochemistry. 2002;67(2):593-600.
Lubec J, Kalaba P, Hussein AM, et al. Reinstatement of synaptic plasticity in the aging brain through specific dopamine transporter inhibition. Mol Psychiatry. 2021;26(12):7076-7090.
Fossen T, Larsen P, Kiremire B, Andersen O. Flavonoids from blue flowers of Nymphaèa caerulea. Phytochemistry. 1999;51(8):1133-1137.
Omvik P. How smoking affects blood pressure. Blood Pressure. 1996;5(2):71-77.
Elderberry
Elderberry is a fruit well-known for its antiviral properties, helping to fight viral infections preventatively, at the early stages, and during the late cycle of infection. Elderberry has many other health benefits too thanks to its flavonoids and anthocyanins, and it's easy to prepare into a juice, syrup, extract, or tea as you'll learn with this article.
Article by Stefan Burns - Updated September 2022. Join the Wild Free Organic email newsletter!
Elderberry clusters I harvested while living in Sofia, Bulgaria
| Name: | Elderberry, Linnaean - Sambucus nigra |
| Color: | Green to purple leaves, white, yellow, and pink flowers, black berries |
| Constituents: | Glucosides (anthocyanins), terpenes, alkaloids, tannins |
| Effect: | Potent antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, anti-viral, improves digestion, improves nutrient partitioning |
| Preparation: | All parts of the elder contain poisonous cyanogenic glycosides which require heat treatment to become of use. Dried berries can be brewed into a tea, or the berries can be prepared into a syrup or jam. Can be powdered as well. |
| Dosing: | 1-5 grams brewed into a tea. 500 mg of powder for general health purposes, 1+ grams for help with an infection, and 3 grams spread out (1 gram morning, afternoon, night) for nutrient partitioning benefits. |
| General Notes: | It's the anthocyanins that are responsible for most of the health benefits from elderberry. Anthocyanins are phytopigments also found in other berries (blueberries, blackberries, strawberries) and other foods like the skin of black beans. Anthocyanins are really potent antioxidants and anti-inflammatories which elderberry an excellent digestive aid and supportive of arterial health and the circulatory system in general. Some promising evidence exists that anthocyanins help partition nutrients towards muscles instead of body fat. Elderberry is most often used to aid in the treatment of infections (cold, flu, etc). |
What is Elderberry?
Elderberry is a genus of flowering plants known as Sambucus consisting of many different species and subspecies. Elderberry plants can be found as small shrubs and bushes and if they continue to grow they can become quite large trees. Elderberry plants have a “corky” type of bark that is mottled tan to brown in color, their leaves grow in a pinnate arrangement in clusters of 5-9 leaflets, and at the end of their branches are where you’ll first observe elderflowers and then once ripened, elderberries (1). For this article, when the words “elderberry” or “elderberries” is used, I’m referring to the actual berries, and if I’m referring to the plant I’ll refer to it by it’s genus Sambucus.
Elderberries contain a wealth of unique plant phytochemicals which have various beneficial biologic interactions within the human digestive system and body (2). Elderberries contain many different polyphenols like flavonoids, as well as unique plant pigments known as anthocyanins. In particular, the predominant anthocyanin found in elderberries is cyanidin 3-glucoside, which gives elderberries their dark purple color. Anthocyanins are potent antioxidants and anti-inflammatory plant phytochemicals which are good for health and wellness because of their beneficial interactions throughout the body.
All parts of the Sambucus plant do contain cyanogenic glycosides which produce poisonous hydrogen cyanide when hydrolyzed enzymatically, but if elderberry is prepared properly then cyanide toxicity is not a concern, more on that in the Safety and Toxicity and How to Make Elderberry Juice sections below.
Types of Elderberry
There are many different species of Sambucus as the genus of plants grows worldwide, the most common are listed below:
Sambucus nigra - The most common species of elderberry found in Europe and North America. Grows mature dark purple fruits
Sambucus cerulea, a subspecies of S. nigra found in western North America
Sambucus canadensis, a subspecies of S. nigra found in eastern North America
Sambucus australis - Found in South America. Grows large dark purple fruits
Sambucus peruviana - Found in Central and South America. Grows dark purple/black fruits
Sambucus javanica - Found in subtropical and tropical Asia. Grows dark red fruits.
Sambucus sieboldiana - Found in Japan and Korea. Grows mature red fruits
Is Elderberry Antiviral?
Before going into the general health and wellness benefits of elderberry and its chemical constituents that are responsible for its beneficial effects, we’ll discuss the antiviral capabilities of elderberry because this is what most people have heard elderberry is good for and want to learn more about.
Viruses are incredibly tiny “semi-life forms” that replicate themselves (and by extension, their DNA), by infecting cells or microorganisms like bacteria. Once a virus can attach to the cell-membrane, it inserts its genetic instructions into the cell, where the cell then begins producing more copies of this code as well as the viral proteins that house it. If the virus’s plan works, then after some time the cell is chock full of new viruses and it explodes, releasing the new viruses throughout the body to repeat the replication process. Two things happen during this viral replication process.
First, infected cells use a bunch of valuable resources like amino acids to create the viruses, which eventually when the infection comes under control by the immune system (hopefully), are then processed as waste by the body. This creates a resource drain on the body commiserate to the degree of infection.
Second, infected cells eventually breakdown and trigger inflammatory pathways in the process. The release of cytokines effectively sends a signal far and wide that there is a “spill in aisle 6” that requires cleanup. The diseased or dead cell is then processed by the immune system, all of this causing a stress to the body. Now multiple this by millions and millions of cells during a viral infection and you can quickly see why viral infections have the potential of causing a huge amount of stress and fatigue to the body.
Elderberry has been shown to help with viral infections in a multitude of ways.
Anti-Influenza Activity of Elderberry
Using elderberry lessens the severity and duration of flu symptoms in several strains of influenza viruses (3). The compounds found in elderberry like anthocyanins and quercetin interfere with viral host cell receptor recognition and receptor binding, effectively suppressing viral entry and viral transmission from cell to cell. Elderberry does this by blocking the functioning of the glycoprotein spikes viruses use to connect to cells.
It’s been observed that using elderberry for its antiviral effects is effective at the onset and throughout the flu. Viral inhibition by elderberry is stronger against the late stage of the influenza cycle than it is at the early stage, so if you get the flu begin using elderberry syrup or elderberry extract as soon as possible and keep using it until the flu passes. Other elderberry products exist too that can be used, go to the end of the article to see all the natural elderberry treatment options at your disposal.
Elderberry Improves Natural Immunity
The innate immune response is the first line of defense against viruses and critically important for overcoming any type of infection. Elderberry also shows antiviral activity by activating the healthy immune system (4). The polyphenols that elderberry contains like quercetin and anthocyanins beneficially modulate the release of cytokines and their receptors. These polyphenols are also strong antioxidants, so they neutralize any inflammatory free-radicals produced during the infection, reducing the cumulative stress the body experiences during the infection. Elderberry also activates macrophages, the white blood cells that engulf and “eat” pathogens and viruses.
The anthocyanins found in high concentrations in elderberries are taken up by endothelial cells (cells that form a barrier between vessels and tissues), protecting them against oxidative stress. Many diseases are characterized by oxidative stress, and this means that in addition to the usefulness of taking elderberry for a cold or using elderberry for a flu, elderberry has the potential to help with many other health conditions like cardiovascular disease and cancer.
Elderberry and Covid
What about using elderberry for SARS-CoV-2, otherwise known as covid? Very little if any research has been done specifically examining the effect elderberry can have for a covid infection, but it’s safe to say that elderberry would be useful because of how to bolsters the natural immune system and through its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. Elderberry may have a direct neutralizing effect on covid viruses and their spike proteins, like has been demonstrated for flu viruses, but at this point the specific interactions elderberry has with SARS-CoV-2 are unknown.
Benefits of Elderberry
The health benefits any food or herb provide come down to its unique blend of constituents, these being the macronutrient ratios (fat, carb, protein), micronutrients like vitamins and minerals, and in the case of plants, the plant phytochemicals it contains like polyphenols, polysaccharides, terpenes, etc. The environment and how its grown influences the final chemical composition, and everything taken together naturally as it was grown provides the greatest holistic health effect. I mention this because it’s common to point out specific compounds, like quercetin, and attribute all the health benefits of a food to that one flavonoid, but it’s the synergy between many hundreds of chemicals together which cause the overall health effects of a food.
The many beneficial health effects of elderberry cannot be solely attributed to flavonoids or anthocyanins, but to all of its beneficial constituents working together. For this reason the less processed the elderberry product the better, and it’s why I prefer elderberry juice over extract powders or pills. The next section does go more into the specific chemicals found in elderberry, but first we’ll cover the general health and wellness benefits and other uses for elderberry beyond its antiviral uses.
Health Benefits of Elderberry
As with many different herbs, elderberry contains many different antioxidant and anti-inflammatory compounds, and with excess inflammation being a main contributing factor to the development and progression of nearly one hundred chronic diseases, elderberry can help treat those conditions (5, 6). Elderberry in particular is very effective at neutralizing reactive nitrogen species, a type of free radical. We’ll start with elderberries impact on gut health because that’s where it’ll first beneficially interact with the body.
Elderberry is good for gut health because its beneficial phytochemicals like anthocyanins are taken up by epithelial tissues protecting them from oxidative stress. The digestive system is under constant stress (unless fasting) due to the rigors of digestion, and if diet quality is poor then this stress increases further. Conditions like leaky gut are characterized by reduced intestinal mucosa and degraded epithelial cells, and elderberry is very useful for all types of gut health problems. The digestive system is also the part of the body that has the most immune system activity because its the job of the barriers of the digestive to keep pathogens from entering the body, and by improving gut health elderberry improves immunity.
If you are experiencing gut health problems, have a chronic disease, or simply want to learn more about the digestive system and microbiome, then I suggest you purchase the Holistic Gut Health Guide. In this 88 page all-in-one guide I share with you the things I personally learned that work in remedying gut health problems during my 10+ year long journey from constant IBS, leaky gut, and food intolerances to amazing gut health. Backed by the latest science on gut health and the microbiome when available, you’ll have everything you need to transform your gut health with the Holistic Gut Health Guide!
Elderberry helps the cardiovascular system in a few different ways. As touched on earlier, the anthocyanins found in elderberry are rapidly taken up by endothelial tissues of the arteries, blood vessels, and capillaries, and this helps to reduce inflammation throughout the body. Cardiovascular disease is characterized by inflammation that is no longer localized at the digestive system’s gut-blood barrier but is now more widespread throughout the body. This inflammation can be caused by a variety of factors, often many at once, such as pathogenic bacteria or too-large food particles freely circulating through in the bloodstream. The presence of these immune-stimulating factors chronically creates a stressful environment for the healthy functioning of cells, and if left unaddressed everything goes downhill.
An important component of healing from chronic inflammation, in addition to the critical component of treating the root cause of the inflammation, is to consume foods that naturally bring the bodies inflammation and autophagy systems into balance. Elderberry is one of these superfoods because it targets all three aspects that are required to really make a difference: by improving gut health, by boosting the immune system, and by making the tissues of the cardiovascular system more resilient.
Elderberry is good for treating obesity and diabetes because its anthocyanin content improves lipid metabolism, blood glucose parameters, and nutrient partitioning. These beneficial metabolic effects are also part of the reason elderberry is cardioprotective. In particular there is a lot of research that has been done using cyanidin 3-glucoside with mice and rats, showing it reduces the severity of obesity and diabetic conditions that form from eating poor quality diets when supplemented (7). The improved metabolic and nutrient partitioning properties of elderberry thanks to its anthocyanins and flavonoids are not only useful for those who are overweight, obese, pre-diabetic, and diabetic, but also for athletes and anyone who regularly exercises, as it’ll help shuttle more nutrients towards functional lean body mass and away from body fat storage.
Elderberry benefits the brain because many of its beneficial compounds are able to cross the blood-brain barrier (8). In the brain anthocyanins exert their antioxidant effects the same as they do anywhere else in the body, and unfortunately beyond that little is known of the specific ways anthocyanins interact with brain tissue. Like with any food/herbs that contain flavonoids, the flavonoids elderberry contains that make their way to the large intestine interact with the microbiome there, being synthesized by symbiotic bacteria into secondary metabolites that the body absorbs which also cross the blood-brain barrier. In this way flavonoids improve the functioning of the gut-brain axis, improving cognition and energy metabolism in the brain. The brain uses 20% of the bodies daily resting energy, and the more efficient and adaptable your metabolic systems, the more stable energy levels will be in the brain, meaning you’ll be snappier and more focused, free of brain fog.
What Can Elderberry be Used For?
These health benefits of elderberry are wonderful, but not everyone has some sort of chronic disease or health problem, some health issues are more mundane. As it translates to the day-to-day, elderberry can be used to:
Improves daily energy levels, reduces sudden sugar crashes, and lessens brain fog/fatigue
Reduce skin inflammation like rashes, autoimmune skin disorders, and clears acne
Helps ameliorate adrenal fatigue
Reduces the chance of getting sick and reduces the severity and duration of the illness
Improves meal digestion and nutrient absorption
Elderberry Micronutrients
Elderberry contains a variety of micronutrients, the most exciting from a health perspective being its flavonoids and anthocyanins. Both have been mentioned quite a bit up to this point, and now we’ll dig into the science behind these unique phytochemicals more.
Elderberry Vitamins
Vitamins present in elderberry are B vitamins, A vitamins, vitamin E (tocopherols), and vitamin C. The content of vitamin C in fresh elderberry fruits is 6–35 mg/100 g, whereas a lemon contains about 50 mg/100g of fresh juice.
Elderberry Minerals
Elderberry contains the following minerals: Potassium, calcium, iron, phosphorus, sodium, zinc, copper, manganese, selenium, chromium, nickel, and cadmium.
Elderberry Polyphenols
The most important polyphenols in elderberry fruit are generally thought to be the flavonoids and anthocyanins.
Elderberry Flavonoids
The predominant flavonoids found in elderberry are quercetin, kaempferol and isorhamnetin. Elderberry also contains flavonoids called catechins, which are most well-known for occurring in green tea such as green tea catechin EGCG.
Quercetin-type flavonoids are widely distributed in plants and are generally regarding as being some of the most biologically useful. Quercetin is a long lasting anti-inflammatory substance that effects many different cell types throughout the body. Quercetin stabilizes the functions of mast cells (immune cells that release histamine) and has gastrointestinal cytoprotective activity. Quercetin modulates inflammation and immunity, a powerful combination for many who are over-inflamed with overactive immune systems (9).
Elderberry Anthocyanins
The two main anthocyanins elderberry contains are cyanidin-3-glucoside and cyanidin-3-sambubioside. Four metabolites from these two also exist, the metabolites being peonidin-3-glucoside, peonidin-3-sambubioside, peonidin monoglucuronide, and cyanidin-3-glucoside monoglucuronide. Elderberry contains a lot of anthocyanins, reaching levels between 600-1250 mg per 100 g.
Anthocyanins have antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, immune-stimulating, antimicrobial, antiallergic, and antiviral properties. These beneficial properties make anthocyanins promising therapeutic options to help in the treatment of many different chronic degenerative diseases such as cardiovascular disease, cancer, and diabetes. Because anthocyanins are such potent antioxidants and free radical scavengers, they are also being investigated as chemoprotective agents.
The mechanisms underlying the absorption of anthocyanins is not well known, but the absorption and bioavailability of anthocyanins depends on the type and sub-form. With a large enough dose, such as 720 mg, anthocyanins levels can remain highly elevated in the blood for 4-6 hours, and levels will reach baseline by 24 hours (10).
Elderberry Safety and Toxicity
Is Elderberry Poisonous?
There are safety concerns that you should be aware of with elderberry. Elderberry is an amazing plant with many health and medicinal uses, but only if prepared properly, as elderberry contains plant molecules known as cyanogenic glycosides. When cyanogenic glycosides undergo enzymatic hydrolysis, poisonous hydrogen cyanide (HCN) is released. There are very few reported cases of elderberry consumption causing illness, though there was one incident in 1983 where a group of people at a religious center in California made a raw elderberry juice using the berries, leaves, and stems, and allowed the mixture to soak overnight before consumption. Eleven people got sick and one person who drank five cups of the mixture had to be hospitalized. No one died, and later analysis of their blood showed no elevations in serum cyanide levels (11).
CC4.0 | DOI - 10.3390/molecules26051384
Researchers who examined the American Elderberry (Sambucus canadensis) for cyanogenic potential found that stems and green berries from the plant had much more cyanogenic potential that other parts of the plant (12). Hydrogen cyanide also boils off slightly above room temperature, so any hydrogen cyanide that is present or forms during the preparation process will off gas during the boiling process, just make sure to keep your workspace well-ventilated. When preparing elderberry for use only ripe berries are to be used, never leaves or stems from the plant, and after the mashed berries are boiled for 15+ minutes, the pulp is strained and the seeds and skins are removed. More of making elderberry juice in the next section.
To answer the question of “is elderberry poisonous?”, if you prepare elderberry properly, or buy a commercial product, the total cyanogenic potential is extremely low and poses no threat to your health.
Elderberry Allergy
Avoid consuming elderberry if you have a known allergy or hypersensitivity to elder or from plants in the Caprifoliaceae (honeysuckle) family.
How to Make Elderberry Juice
There are many ways to prepare elderberry, from making elderberry juice to elderberry syrup or elderberry extract, and I encourage you to experiment with whatever different preparation methods you desire. Elderberry syrup and extract are good to make because they last for a long time, whereas elderberry juice is best consumed within 1-2 weeks of preparation.
Thus far I have made a lot of elderberry juice, as it was the easiest option available to me as I traveled around Europe for 6+ months. It’s a straightforward process as you can tell with the photo gallery below.
Elderberry Juice Recipe
Once your elderberries are plucked from the shrub/tree, destem the berries by running your fingers through the berry clusters gently. Discard the stems once completed.
With your elderberries now in the container you’ll boil them in, pluck out any stem bits that made it into the pile, as well as any bright red and green berries.
Mash and crush the elderberries into a pulp using either a masher or your good ol’ hands.. Elderberry juice rinses off easily and is only lightly staining, and using your hands makes it easy to feel the berries that are still intact and then crush them. This process will release quite a bit of juice but not enough to comfortably boil the berries.
Add water to the elderberry pulp and juice, increasing the total volume of the pots contents by 2-3x. For the volume of elderberries I processed in the images above I used 2 liters of mineral water.
Bring the elderberry mixture to a boil and then reduce heat to a low rolling boil for 15 minutes. During this time it’s good to stir the mixture occasionally, and foam from the top can be skimmed off at the beginning if desired (eventually it’ll boil off).
Once the boiling is complete separate the juice from the pump with a fine mesh strainer. Press on the pulp with a fork to release more juice, and once the berry pulp is relatively dry it can either be boiled again with the addition of more water or discarded/composed after the first use. All the seeds will be in the pulp, and you can spread the mixture around outside in the hopes of germinating a new elderberry plant (unlikely after the boiling, but hey worth a shot).
Elderberry juice has a very mild taste, it’s not sweet at all in my opinion, and you can sweeten the juice lightly with some honey, a tablespoon or two is all that’s needed. Lemon juice also makes a good addition to elderberry juice and helps it stay fresh longer due to the extra acidity and vitamin C.
Once the juice has cooled, store in an airtight container and keep in the fridge for up to 1-2 weeks, though it’ll probably be gone in just a couple days ;)
Other Elderberry Products
When fresh harvestable elderberries aren’t an option, then it’s a good idea to keep some elderberry flu medicine around the house primarily for viral prevention and treatment. Elderberry and zinc lozenges are a good combination medicine for this, as the zinc and elderberry combo coating the back of the throat helps prevent viral replication for an upper respiratory infection. Elderberry syrup is another good option for this, as is elderberry tincture, both products being sold by Mountain Rose Herbs.
Another option I like for cold prevention is elderberry tea. Elderberries can be harvested and dried oneself, or dried elderberries can be purchased from a reputable vendor like Mountain Rose Herbs. Take a spoonful of dried elderberries and steep them with boiling water for 10-15 minutes. Other herbs can be added to elderberry tea like chamomile, echinacea (another good antiviral), dandelion root, or medicinal mushrooms, play herbalist and see what you like!
Elderberry Herbalism
There are hundreds and hundreds of herbs that exist, all containing different chemical constituents and having different health effects. Some of these herbs are well studied, others less so. Elderberry is an excellent herb for a beginning herbalism to experiment with because it is easy to identify after a little study, has potent health and wellness benefits, is one of nature’s best antivirals, and is relatively common worldwide.
Please share your experiences using elderberry or ask any questions you have in the comments below!
References:
Malcom Stuart, et al. The Encyclopedia of Herbs and Herbalism. Crescent Books, New York.
Ulbricht C, Basch E, Cheung L, et al. An evidence-based systematic review of elderberry and elderflower (sambucus nigra) by the natural standard research collaboration. Journal of Dietary Supplements. 2014;11(1):80-120.
Torabian G, Valtchev P, Adil Q, Dehghani F. Anti-influenza activity of elderberry (Sambucus nigra). Journal of Functional Foods. 2019;54:353-360.
Schön C, Mödinger Y, Krüger F, Doebis C, Pischel I, Bonnländer B. A new high-quality elderberry plant extract exerts antiviral and immunomodulatory effects in vitro and ex vivo. Food and Agricultural Immunology. 2021;32(1):650-662.
Schmitzer V, Veberic R, Stampar F. European elderberry (Sambucus Nigra L.) and American Elderberry (Sambucus Canadensis L.): Botanical, chemical and health properties of flowers, berries and their products. Berries: Properties, Consumption and Nutrition. 2012:127-148.
Sidor A, Gramza-Michałowska A. Advanced research on the antioxidant and health benefit of elderberry (Sambucus nigra) in food – a review. Journal of Functional Foods. 2015;18:941-958.
Tsuda T, Horio F, Uchida K, Aoki H, Osawa T. Dietary cyanidin 3-o-β-d-glucoside-rich purple corn color prevents obesity and ameliorates hyperglycemia in mice. The Journal of Nutrition. 2003;133(7):2125-2130.
Hribar U, Ulrih NP. The metabolism of anthocyanins. Curr Drug Metab. 2014;15(1):3-13.
Li Y, Yao J, Han C, et al. Quercetin, inflammation and immunity. Nutrients. 2016;8(3):167.
Milbury PE, Cao G, Prior RL, Blumberg J. Bioavailablility of elderberry anthocyanins. Mechanisms of Ageing and Development. 2002;123(8):997-1006.
Centers for Disease Control (CDC). Poisoning from elderberry juice--California. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 1984;33(13):173-174.
Appenteng MK, Krueger R, Johnson MC, et al. Cyanogenic glycoside analysis in american elderberry. Molecules. 2021;26(5):1384.
Medical Disclaimer: All information, content, and material of this website is for informational purposes only and is not intended to serve as a substitute for the consultation, diagnosis, and/or medical treatment of a qualified physician or healthcare provider.
Disclosure: Wild Free Organic is a member of various affiliate programs and if a purchase is made through one of our affiliate links a small commission is received. This does not affect your purchase price. Visit our disclosure page for more information.
More Immune Boosting Herbs
Cannabis
Cannabis is a powerful herb which has the power to transform one's health for the better or worse, and as such great care must be taken when using cannabis in herbal practices. This cannabis herbal guide covers everything you need to know to get started and to help you determine whether cannabis may be helpful for you.
Article by Stefan Burns - Updated June 2022. Join the Wild Free Organic email newsletter!
Cannabis Quick Fact Sheet
| Name: | Cannabis, hemp, marajuana, weed, dope, grass, Linnaean - Cannabis sativa, C. indica |
| Color: | Green to purple leaves and flowers (bud) |
| Constituents: | Cannabinoids (CBD, THC, CBC, CBG, CBN, THC-V), terepenes, resins, saccharides (mono, di, poly), alkaloids, phenols |
| Effect: | Psychedelic, narcotic, anti-inflammatory, reduces blood pressure & raises heart rate, increase appetite (the cannabinoid THC-V does the opposite), nervous system adaptogen (stimulant or relaxant) |
| Preparation: | Female cannabis flowers produce sticky cannabinoids (CBD, THC, etc) and the dried & cured bud can be smoked or dry-vaporized. Cannabinoids can also be extracted via cooking in oil or by modern chemical extraction methods. |
| Dosing: | Smoking: 0.2 - 1+ grams ground bud. Vaporization: 0.05 to 0.5 grams ground bud. Edibles: 0.5-20+ mg CBD/THC. Used at a 1:1 ratio of CBD to THC is best. |
| General Notes: | As a mild psychadelic cannabis can alter the sense of time and reality, which can make it useful as a creativity enhancer. Smoking cannabis is best avoided due to the creation of carcinogens, instead being dry-vaporized or consumed via an edible. Great care should be taken with dosing edibles as the cannabinoids take a long time to enter into the bloodstream, so only small doses should be consumed, and with at least an hour in-between dosings. It's blood pressure reducing effect can be useful if BP is high but it can raise heart rate quite signifigantly (+10-20 bpm) which can cause cardiac strain. Can be useful for headaches, migraines, general pain, and as a digestive aid because of it's anti-inflammatory effects. Should not be abused in use or consumed by anyone under the age of 25 years. Can be psychologically addictive. |
What is Cannabis?
Cannabis is a genus of flowering plants that contains three species, Cannabis sativa, Cannabis indica, and Cannabis ruderalis. Cannabis is a nutritionally rich plant, and is known to contain more than 500 compounds, among them at least 113 cannabinoids, though most of the cannabinoids are minor and only produced in trace amounts.
There is a lot of information regarding cannabis, and this article will cover the characteristics of the plant as well as the most important uses it has in herbal practices. There are 3 different species of cannabis each with their own shape, size, cannabinoid ratios, and growing characteristics. Cannabis has many health benefits, especially bioelectrical and cognitive health benefits, but there are a few safety cautions regarding cannabis that are good to know before use. The reason cannabis can simultaneously have health benefits and also known adverse effects is because cannabis has a narrow therapeutic range. Too low a dose and nothing significant will occur, whereas if too much cannabis is used them bodily systems can be tipped out of balance and cause undesirable health effects. Cannabis is a very complex herb that much is still not known about and cannabis should only be used with great care and respect in an herbal practice.
Different Names for Cannabis
Cannabis is the Linnaean genus name for the plant, but cannabis is also known as weed, marijuana, ganja, grass, pot, bud, herb, Mary Jane, dope, green, and many more.
Cannabis in Herbalism
Cannabis has been a prized herb in herbal practices around the world for many thousands of years. In ancient China cannabis was mixed with wine to create a pre-surgery anesthetic, while Neolithic Europeans and the Celts made a pain-killing hashish with cannabis. Arab physicians from the 8 to 18th centuries used cannabis to treat fevers, digestive issues, pain and inflammation, and for seizures, while ancient Egyptians used hemp-based supositories as a way to treat pain from hemorrhoids. Ancient African’s also used cannabis to treat hemorrhoids, as well as a way to increase appetite, and around the world cannabis seeds were eaten raw to dispel parasites and worms from the digestive track.
Scythians of the Middle East were known to burn cannabis incense in their steam baths in order to enter into otherworldly states of mind, and other cultures the world over have incorporated cannabis into their religious and spiritual ceremonies and practices. It is said that long term cannabis use weakens the separation between the material and spiritual realms, and shamans, magicians, and mystics used cannabis as a way to access unseen dimensions and commune with spirits. Cannabis was used as an aphrodisiac to aid in pleasure rituals and orgies, and cannabis has had its historical narcotic uses throughout the centuries.
Historical Uses of Hemp
Hemp are specific subtypes of Cannabis sativa that have been cultivated to be low in cannabinoids but high in fiber, making it good for textiles. Hemp cultivation can be traced as far back as 8000 BC, and evidence of hemp being used to make rope goes back 25,000+ years. Hemp has a long history of being used in a multitude of ways, from a food source to the creation of strong textiles.
Hemp seeds are nutritionally dense and were eaten around the world. Hemp seed oil has various applications and was used to create ceramics, for lighting, and for religious purposes. Mountain Rose Herbs sells organic hulled hemp seeds which are a wonderful addition to any diet. Hemp pulp was used to make paper, and it was also used to create clothes and strong cordage. The natural sticky oils of help combined with its natural fibers make it a superior material for textiles.
All of the historical applications for hemp still exist today and are increasingly being pursued again as governments around the world loosen the restrictions on the cultivation and manufacturing of hemp products.
Types of Cannabis
There are three different weed strains that exist, C. sativa, C. indica, and C. ruderalis, though some botanists think the differences between them aren’t significant enough for them to be considered separate species. These three types of cannabis are quite different in their shape, size, growing, reproduction, and cannabinoid profiles though, and most agree with the classification of three distinct species within the Cannabis genus.
Cannabis sativa
Cannabis sativa is native to eastern Asia but is now found nearly worldwide due to its long history of cultivation. Cannabis sativa can grow to 3-6 meters in height depending on the strain and if grown in ideal warm outdoor conditions. Cannabis sativa grows tall with narrow leaflets and is loosely branched, with male plants typically taller than female plants but less full. It’s color is typically a lighter shade of green and its buds are long and thin. Has a grassy citrusy scent.
The psychoactive effect from Cannabis sativa cultivars tends to be cognitive and cerebral in nature. Cannabis sativa produces an energizing high and the presence of abundant citrus terpenes like limonene add to that effect.
Cannabis indica
Cannabis indica is native to India, and it is a short, conical, and dense plant, growing to heights of about 2 meters under ideal conditions. Grows well in cooler climates. Cannabis indica has broad leaflets and its color is typically a dark shade of green, with its buds being very dense. Has an earthy skunky scent.
Cannabis indica produces more of a relaxed and sedative body high. Cannabis indica possesses terpenes like myrcene and caryophyllene.
Cannabis ruderalis
Cannabis ruderalis is native to central Europe, eastern Europe, and Russia. It is characterized by a more sparse weedy growth and has survivalist traits such as disease and pest resistance, the ability to grow in disturbed soil conditions, and can survive on little water. Cannabis ruderalis grows to a height of up to 1 meter and grows well in any climate. It has smaller leaves and buds than sativa or indica varietals and typically has a light green color. Has a sweet earthy smell.
Cannabis ruderalis is more of a wild or feral cannabis than sativa or indica and typically has lower concentrations of cannabinoids than cultivated varietals. It produces more CBD than THC and is often bred with cannabis sativa to create high CBD hybrids.
Cannabis Growing Conditions and Characteristics
Each species of cannabis has different growing characteristics, and by breeding different strains of cannabis together it’s possible to create hybrids that combine the qualities of some or all of the three cannabis species.
Cannabis sativa has a 6-8 month grow time and will stay in a vegetative growth state indefinitely as long as it receives 16-18 hours of light a day. If grown outdoors under the natural influence of the sun, once light begins decreasing after the summer solstice Cannabis sativa will begin to switch from a vegetative growth state to a flowering growth state afterwhich the sex of the plant can then be determined. This switch from vegetative to flowering can also be triggered if growing under artificial conditions by switching the light schedule from 16/8 to 12/12 (on/off). Flowering time for sativa varietals is 10-12 weeks.
Cannabis indica has a 6-8 month grow time and like Cannabis sativa will stay in a vegetative growth state as long as it receives 16-18 hours of light every day. Being a smaller plant than sativa, indica typically has a slightly shorter flowering time, with its range being 6-12 weeks.
Cannabis ruderalis has a 3-4 month grow time and unlike sativa or indica it has an auto-flowering characteristic, meaning it will begin to flower after it reaches a certain level of maturity irrespective of its light conditions. Cannabis ruderalis autoflowering typically occurs after 10 weeks. Flowering time for ruderalis is 3-6 weeks.
Different Types of Cannabinoids
Cannabinoids like any other chemical bind to cellular receptors which give them different effects throughout the body. In order to understand the differences between the main cannabinoids listed below a quick primer on receptor science is needed.
Receptor: A protein within or on the surface of a cell that can take on an inactive an active shape. An agonist binding to a receptor causes it to shift from an inactive to active shape, functioning as an “on-switch” that begins a specific event or series of events within the cell, changing its biology.
Receptor Agonist: Binds to a receptor and activates it. A agonist can bind to and activate a receptor to its full extent, whereas a partial agonist can only partially active a receptor.
Receptor Antagonist: Binds to a receptor but does not activate it. Often receptor antagonists have greater binding efficiencies than receptor agonists, so if a receptor agonist and antagonist are both present the antagonist will displace the agonist or prevent it from binding to the receptor in the first place, terminating or preventing any agonist-induced biologic effect.
Most cannabinoids exist in cannabis plant matter as an acid precursor, for example cannabidiol (CBD) exists in a plant as cannabidiolic acid (CBDa). The acidic forms of cannabinoids are much less biologically active than their decarboxylated brethren. If cannabinoid acids are heated to a specific temperature (250-285 F, 120-140 C) they lose their carboxylic acid, a process known as decarboxylation.
Most if not all cannabinoids possess antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and antimicrobial properties, so keep that in mind for the cannabinoid highlights below.
-
Name: Cannabigerol
Vaporization Temperature: 126 F, 52 C
Receptor Binding: CBG has binding affinity for CB1 and CB2 receptors. CBG antagonizes CB1 receptors.
General: Cannabigerolic acid (CBGa) is the parent molecule from which other cannabinoids are synthesized. During plant growth most CBGa is converted to other cannabinoids, and CBG is made more elusive still by its incredibly low vaporization temperature. CBG is non-psychoactive.
-
Name: Cannabidiol
Vaporization Temperature: 329 F, 165 C
Receptor Binding: CBD has low binding affinity for CB1 and CB2 receptors but it can still act as an antagonist for these receptors. Indirectly antagonizes the actions of other cannabinoids like THC through mechanisms not yet fully understood.
General: CBD is best known for its anti-inflammatory and neurologic effects. Has anti-anxiety, anti-psychotic, and anti-spasmodic properties. CBD is non-psychoactive.
-
Name: Tetrahydrocannabinol
Vaporization Temperature: 347 F, 175 C
Receptor Binding: THC is a partial agonist of CB1 receptors and overall has a relatively low cannabinoid receptor affinity.
General: THC has three main forms, delta-8-THC, delta-9-THC, and delta-10-THC. All three are psychoactive, with Delta-9-THC having the strongest psychoactive and hallucinogenic properties. THC is known for its pain relieving, neurocognitive enhancing, and appetite stimulant properties.
-
Name: Tetrahydrocannabivarin
Vaporization Temperature: 428 F, 220 C
Receptor Binding: THC-V binds to CB1 as an antagonistic blocker, and THC-V also binds and activates CB2 as a partial agonist. Lessens the psychoactive effects of THC as a result of its CB1 antagonism.
General: THC-V is only slightly different chemically than THC, but has different biologic effects. THC-V is a high energy cannabinoid that is a powerful focus stimulant. THC-V is an appetite suppressant unlike THC, and THC-V can be found naturally in higher concentrations in certain cannabis strains like Durban Poison. THC-V is psychoactive.
-
Name: Cannabichromene
Vaporization Temperature: 428 F, 220 C
Receptor Binding: Binds poorly to CB1 receptors, but it does bind to TRPV1 and TRPA1 receptors which causes an increased release in the bodies natural endocannabinoids like anandamide.
General: CBC is the third most common cannabinoid after THC and CBD. CBC is non-psychoactive and does not affect the activity of THC. TRPV1 and TRPA1 receptors are linked to the perception of pain, and CBC’s activity on these receptors reduces feelings of pain throughout the body.
-
Name: Cannabinol
Vaporization Temperature: 365 F, 185 C
Receptor Binding: Binds to both CB1 and CB2 receptors agonistically. Compared to THC CBN has a 2x lower affinity for CB1 receptors and a 3x greater affinity for CB2 receptors. Only a partial agonist of CB1.
General: As cannabis dries and ages THC is slowly converted into CBN via oxidative processes. CBN is non-psychoactive, but when paired with THC can increase its euphoric effects.
Cannabis Health Benefits
The many health benefits of cannabis can be traced back to the individual biologic properties of the various phytochemicals that exist in cannabis, from cannabinoids to terpenes to phenols. Individually these phytochemicals have health benefits, and they also work together synergistically to provide greater health benefits throughout the human body. There is likely more we don’t about cannabis than we do at this point as it is such a chemically-rich plant. We’ll examine the specific health benefits of cannabinoids, terpenes, and phenols and then summarize the total benefits cannabis can have on human health.
Cannabinoid Health Benefits
Cannabinoids exert most of their biologic effects through their interactions with the endocannabinoid system, which consists primarily of CB1 and CB2 receptors as well as endogenous cannabinoid ligands anandamide and 2-arachidonylglycerol. CB1 receptors are present throughout the central nervous system and are densely packed in the brain. CB1 receptors are also observed in immune cells and in the tissues of the gut, reproductive organs, adrenal glands, heart, lungs, and bladder. Whereas it is notable how densely concentrated CB1 receptors are in the brain, CB2 receptors are more evenly distributed throughout the body. Produced naturally by the body, the endocannabinoids of anandamide and 2-arachidonylglycerol play a regulatory role in appetite, pain-sensation, inflammation, memory, mood, insulin sensitivity, and energy metabolism.
Each cannabinoid seems to have slightly different health effects based on their varying chemical structure and differing interactions with the endocannabinoid system, but there is also a very large overlap in their health effects. All of the cannabinoids appear to be strong antioxidants, anti-inflammatories, and antimicrobials.
THC has anti-cancer, muscle-relaxing, pain relieving, antispasmodic, and neuroprotective effects. CBD has anti-anxiety, anti-nausea, anti-arthritic, and immunomodulatory properties. CBD also has anti-psychotic effects and reduces the negative side effects of THC. When used together THC and CBD have a strong therapeutic effects on diseases of the central nervous system such as epilepsy, neurodegenerative diseases like Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s, multiple sclerosis, and schizophrenia. The combined health benefits of THC and CBD also make it useful in the treatment of cancer, stimulating appetite while also assisting the bodies natural cancer-fighting process of autophagy.
CBN is interesting because of its high affinity for CB2 receptors, and CBN therefore exerts its health benefits more broadly throughout the body and on the cells of the immune system. Beta-carophyllene is another compound found in cannabis, specifically it makes up 12-35% of cannabis essential oil, and it has a binding affinity to CB2 receptors, making it non-psychoactive but able to still exert anti-inflammatory effects throughout the body.
Terpene Health Benefits
Terpenes are key pharmacological agents of many medicinal herbs, and cannabis is no exception. Terpenes are fat-soluble compounds that easily cross cellular membranes, in particular the blood-brain barrier. Cannabis depending on the strain contains many different terpenes in various ratios, and below are the health effects of the most common terpenes found in cannabis.
The terpene β-myrcene is a potent anti-inflammatory with pain-reliving and anti-anxiety properties.
D-limonene exhibits potent anti-cancer properties and stimulates the immune system.
Linalool has anticonvulsant, pain-relieving, anti-inflammatory, and anti-anxiety properties.
The terpene α-Pinene may improve memory as an acetylcholinesteral inhibitor.
The terpene β-caryophyllene (also notably found in black pepper) possesses anti-inflammatory and gastric cytoprotector activities. Has the ability to bind to CB2 receptors.
Pentacyclic triterpenes such as β-amyrin and cycloartenol have anti-inflammatory, anti-bacterial, antifungal, and cancer fighting properties
Phenols Health Benefits
Phenolic compounds are a large class of secondary metabolites like apigenin that plants produce for various biologic functions. It has been shown with humans that a correlation exists between dietary phenolic intake and a reduced rate of chronic diseases such as cancer, cardiovascular disease, and neurodegenerative diseases.
The phenols found in cannabis overlap with terpenes and cannabinoids in their biological effects, also being anti-inflammatory, anticancer and neuroprotective.
General Cannabis Health Benefits
With the individual health benefits of cannabinoids, terpenes, and phenols illuminated its easy to see why cannabis is such a powerful healing herb. Cannabis can be used to reduce pain and inflammation in the body, calm and stabilize an overactive nervous system, reduce blood pressure, and improve digestion. Cannabis use has been linked to improvements in glaucoma (high interocular pressure which causes optic nerve damage), and in men may find the reduction in prolactin levels from cannabis use helpful for the treatment of reproductive issues like erectile dysfunction.
Because all the health benefits of cannabis are derived from the combination and synergism of its hundreds of different phytochemicals, the best way to use cannabis medicinally is to use the whole plant and alter it as little as possible before use. Cannabis bud can be dry vaporized which very efficiently extracts cannabinoids, terpenes, and some phenolics without combusting the plant material which creates 100+ carcinogenic compounds. Cannabis can also be cooked with oils like butter or coconut oil, which efficiently extracts cannabinoids and terpenes. More on how to use cannabis below, but first specific benefits cannabis has on the brain.
Cannabis Brain Benefits
Cannabis is a powerful nootropic and cognitive aid if used at the right doses. It’s a fine balance when it comes to cannabis usage, if cannabinoid concentrations are too low little effect should be expected, whereas if cannabis strains containing abundant THC are used in excess it causes neurocognitive problems. For example if cannabis is used early in life when the brain is still developing (<25 years old) cognitive developmental issues can result. Cannabis used too frequently causes memory issues and shrinks gray matter in the brain. Using cannabis with imbalanced cannabinoid ratios, such as too much THC and little to no CBD, can cause issues like anxiety and paranoia to occur. There is a more comprehensive section on the health and safety concerns of cannabis below, but I wanted to mention briefly this potential of cannabis to not be good for the brain in order to make it very clear that care and proper dosing must be taken in order to enjoy the beneficial effects of cannabis and mitigate the chance of any negative effects from occurring.
When using cannabis, especially high-THC cannabis, the general rule of thumb is to dose just a little until a beneficial effect is felt, and then the dose can be increased from there responsibly depending on the level of medication desired. So with that laid out let’s jump into the brain benefits of cannabis!
Cannabis is an anti-inflammatory and possess mild antioxidant activity which has been found to be able to protect neurons against oxidative stress. In areas that experience damage after an injury cannabis activates autophagy (cellular cleanup) and improves the mitochondrial efficiency of brain cells in general. Cannabis increases connectivity within the brain, specifically between the left and right hemispheres, which increases creativity and can help with ADHD.
Cannabis Brain Cell Regeneration
When present in the body before a traumatic brain injury, THC has a neuroprotective effect, providing impairment protection to the brain. Regular cannabis users show decreased cell mortality in the brain. Cannabinoid receptors when stimulated cause neuron progenitor cells to grow and divide, after which they migrate to different parts of the brain in a process called differentiation, changing into the type of brain cell needed at that time and location.
Cannabis and BDNF
Cannabis has the potential to prevent the negative health response from a stressful event. Stress-induced alterations that cannabis can prevent are anxiety, fear retrieval, alterations to locomotion, changes to social recognition memory, and decreases in BDNF levels in the hippocampus and prefrontal cortex.
Brain-derived neurotropic factor (BDNF) is a protein that helps maintain the process of neurogenesis, and it is necessary for normal neural development. Cannabis prevents the depressive and PTSD-like symptoms that follow the alterations in BDNF levels in the brain after a severe stressor occurs.
Cannabis Health and Safety Concerns
When cannabis is used too early in life and/or in chronic excess use it can cause health problems that are entirely avoidable. Cannabis has strong interactions with the nervous system, hormone system, brain, and heart, so care must be taken in using cannabis.
Too much high-THC cannabis used in a single setting can cause hallucinations, paranoia, anxiety, disorientation, and an increase in pain sensitivity. Impaired motor coordination, memory issues, and psychosis are also possible.
Chronic overuse of cannabis can be immunosuppressive, cause cholinergic defects, alters the hormone system causing dopamine deregulation, increases brain inflammation, and causes cognitive impairments in short and long term memory in addition to decreases in motivation and impairing decision making.
Cannabis used early in adolescence alters brain development and increases the risk of chronic psychosis disorders like schizophrenia.
Cannabis lowers blood pressure and increases heart rate, so cannabis should not be used if blood pressure levels are already low and if it will be too stressful on the heart to be elevated in heart rate for extended periods of time. Cannabis can increase heart rate by 5-20 beats per minute.
Cannabis Addiction
Cannabis isn’t addictive in the same way a chemical like nicotine is, but as a mild narcotic cannabis addiction can occur depending on an individual’s environment, lifestyle, personality traits, and brain development. With cannabinoids acting on so many different systems of the body, downregulation of various receptors, hormones, and neurotransmitters can occur which can be difficult to overcome, causing withdrawal symptoms that will need to be overcome if cannabis use is stopped cold turkey.
Cannabis Induced Psychosis
High doses of cannabis, specifically high doses of cannabis used across a long term, can induce psychosis, which is typically defined as some loss of contact with reality. People with psychosis have trouble determining what is real and what isn’t, and often hallucinate and/or are privy to strange delusions.
If you’re experiencing any of these effects from cannabis you should stop use immediately and seek the help of a medical professional.
How to Use Cannabis
There are so many ways cannabis can be used, and each method has its own particular strengths and weaknesses. Combining multiple methods together, say vaporizing cannabis while also taking a cannabis edible and applying a cannabis cream to parts of the body, is a powerful way to experience the full-body systemic effects of cannabis.
Cannabis Vaporization
Cannabinoids and terpenes reach their boiling point and vaporize into gases below the temperature of combustion of plant matter which is about 455 F (235 C). With a device that can very accurately heat up to specific sub-combustion temperatures, cannabinoids and terpenes can be efficiently vaporized out of dried cannabis flower along with some water vapor and absorbed quickly by the body upon inhalation.
By avoiding combustion and the 100+ carcinogens produced during combustion, dry vaporization of cannabis flower is a much healthier way to use cannabis and also more efficient, as the high temperatures of combustion destroy a high percentage of cannabinoids that are vaporized by the high temperatures. Dry vaporization of cannabis is my preferred way to use cannabis as it can be dosed very precisely, it’s easy on the lungs, and the effects are felt rapidly.
Healthy Rips sells a few different high-quality electronic vaporizer models that utilize heat convection and conduction to thoroughly extract all the cannabinoids and terpenes from cannabis flower, I recommend their Fury Edge vaporizer to anyone interested in incorperating cannabis into their herbal practice, or simply for those who wish to have a better high, save money, and avoid the health complications from the inhalation of smoke.
Cannabis Tea
Brewing a cannabis tea simply involves taking dried cannabis flower and steeping it in boiling water for 5-15 minutes. Since the water temperature won’t be hot enough to extract THC and other cannabinoids efficiently, cannabis tea is most often brewed with cheaper CBD-dominant hemp flower.
Cannabis tea has a sweet earthy and grassy taste, it’s a pleasant drink especially when mixed with a sweetener like honey and drinking cannabis tea promotes a general sense of ease and calm. Combine with other herbs as desired!
Cannabis Oil
Being fat-soluble lipids, cannabinoids and terpenes can be extracted quite easily from cannabis and turned into a condensed oil. Depending on the level of extraction, this can be a full-spectrum cannabis oil extract, or certain cannabinoids can be selected for, creating a CBD oil or a THC oil for example.
It is possible to extract cannabis oils oneself, but typically this is done in a laboratory setting and the cannabis oils are sold commercially. High-quality cannabis oils are CO2 extracted and are very highly concentrated, whereas low-quality cannabis oils use additives like propylene glycol and/or vitamin E acetate. If using cannabis oil for vaporization, only the highest quality extracts should be used in order to best avoid lung health problems, though I believe dry vaporization of cannabis flower is best and superior in effect due to the entourage effect.
Mountain Rose Herbs sells an organic hemp seed oil as well as an organic hemp essential oil, neither of which contain traceable quantities of THC or CBD but contain all the other health-promoting phytochemicals cannabis has to offer.
Cannabis Edibles
Homemade weed edibles are infamous for their varying strength and for their ability to blast an unsuspecting consumer off into another dimension. Following a strict scientific protocol when making a cannabis edible is the best way to ensure accurate milligram dosing of cannabinoids per serving and to avoid regrettable situations from happening in the first place.
Commercially available cannabis edibles often take the form of little cookies, brownies, or fruit gummies, with each unit clearly listing the amount of cannabinoids per serving. These edibles are made with extract cannabis oil, whereas a homemade cannabis edibles can be made using the whole bud, cannabis butter, or cannabis coconut oil.
Absorption of cannabinoids by the digestive track stands at about 6% and takes a much greater duration of time than if cannabis is smoked or vaporized. Great care should always be taken with cannabis edibles because it can take at least an hour before any effect is felt, and typically the full effect is felt by the two hour mark. Start with a low dose and only after 60-90 minutes should the dose be increased again slightly if desired.
Cannabis Combustion
The smoking of cannabis herb is the age old method of consuming the plant recreationally, medicinally, and spiritually.
One thing that a lot of people don’t realize when smoking cannabis rolled up into a joint or blunt is that the high-temperature smoke that is being generated from the end of the roll when drawn on passes through all the as-of-yet unburnt herb, vaporizing the cannabinoids and terpenes present there before final inhalation into the lungs. So even those who are combusting are actually vaporizing too, and it’s the vaporized cannabinoids that provide the greatest effect because they remain undamaged from the heat of combustion unlike the unfortunate cannabinoids present where the burning is occurring. This process also explains why the final few puffs of a joint is always so harsh, because most of the cannabinoids from the remaining herb have already been extracted and what’s left is mostly singed plant matter that easily burns but doesn’t have much more in the way of terpenes or cannabinoids to give.
If consuming cannabis via combustion it’s best to always use a filter and I also recommend having a throat soothing beverage handy like a herbal tea.
Cannabis Creams and Lotions
Cannabinoids are efficiently absorbed through the skin, and this makes cannabis-containing creams and lotions an excellent way to use cannabis for localized inflammation and pain-relief, for a generalized relaxing effect, for headaches, to sooth the gut, muscle aches and generalized fatigue, and so much more.
Cannabis creams and lotions are typically made with cannabis oil extracts and like edibles it takes longer to feel the effects of a cannabis lotion than it does when cannabis is smoked or vaporized, so when using apply a small responsible amount and wait 20-30 minutes before applying more for a stronger effect if desired.
Cannabinoid receptors are located in the sex organs, and high-THC cannabis creams applied to those areas are one way to stimulate arousal and increase pleasure during sexual activities.
References:
Malcom Stuart, et al. The Encyclopedia of Herbs and Herbalism. Crescent Books, New York.
Andre CM, Hausman JF, Guerriero G. Cannabis sativa: the plant of the thousand and one molecules. Front Plant Sci. 2016;7.
Medical Disclaimer: All information, content, and material of this website is for informational purposes only and is not intended to serve as a substitute for the consultation, diagnosis, and/or medical treatment of a qualified physician or healthcare provider.
Disclosure: Wild Free Organic is a member of various affiliate programs and if a purchase is made through one of our affiliate links a small commission is received. This does not affect your purchase price. Visit our disclosure page for more information.
More Information on Cannabis
Other Cognitive Enhancing Herbs
Chamomile
Chamomile essential oil and tea should be in everyone's medicine cabinet because of chamomile's many health benefits. Chamomile tea is a great herbal medicine for soothing digestive upset, pain and inflammation in the body, and also for quelling nervous system disorders like anxiety. Likewise chamomile essential oil when used aroma-therapeutically is very calming and helps achieve deep sleep.
Article by Stefan Burns - Updated April 2022. Join the Wild Free Organic email newsletter!
Chamomile Quick Fact Sheet
| Name: | Chamomile, Roman Chamomile, Linnaean - Chamaemelum nobile |
| Color: | Yellow-white flowers |
| Constituents: | Sesquiterpenes, flavonoids, coumarins, and polyacetylenes |
| Effect: | Relaxant, anti-inflammatory, anti-microbial, improves digestion, stimulates appetite, promotes 8-12 Hz alpha brainwaves, relieves painful menstration |
| Preparation: | Dried flower heads can be brewed as a tea, essential oil can be used for aromatherapy, can be crushed into a poultice |
| Dosing: | 0-5 grams for tea, 0-10 drops for aromatherapy |
| General Notes: | Chamomile influences the autonomic nervous system to promote parasympathetic (rest and digest) activity. Used in aromatherapy or ingested chamomile promotes endogenous 8-12 Hz brainwaves, which can be mildly stimulating or calming depending on current state of physiological arousal. Alpha brainwaves are calming in general. Overall a mild sedative with anti-inflammatory and pain-reducing effects. |
What is Chamomile Flower?
Chamomile is one of the most ancient and well-known medicinal herbs known to mankind. The two most common varieties of chamomile are Chamomilla recutita (German Camomile, Hungarian Chamomile) and Chamaemelum nobile (Roman Chamomile), with a third lesser-used variety of chamomile being Cladanthus mixtus (Moroccan Chamomile). Chamomile is identified by its small white flower petals that surround its yellow center, and it’s the chamomile flower that’s used in herbal practices. Chamomile flowers contain a wide range of biologically active chemicals such as terpenes and flavonoids that have been shown to be health promotive.
Chamomile has many health uses, and the three main ways chamomile is prepared for medicinal use is it is steeped into a tea, its essential oils are extracted, or it is powdered and mixed into a poultice. Infusions and essential oils from fresh or dried flower heads have aromatic, flavoring, and coloring properties, and not all uses of chamomile are purely health-based. Chamomile tea is a natural hair lightening agent that also has the added benefit of moisturizing the scalp.
Chamomile Flower Benefits
While some herbs contain specific compounds that have very precise health effects, other herbs like chamomile, green tea, and dandelion have strong health benefits because they are packed with a variety of health-promoting phytochemicals like terpenes and flavonoids. As such chamomile has been shown to have a wide-range of health benefits which overlap, for example healing digestive issues may resolve ongoing skin inflammation. The following is a short list of chamomile’s many benefits which will then be elaborated on in greater detail in the Chamomile Health Benefits section of this article:
Chamomile is a herb with strong antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and antimicrobial properties. These qualities are partly responsible for chamomile’s anti-cancer effects and its ability to induce apoptosis (cell death) in tumor cells while not affecting healthy cells. These antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and antimicrobial effects of chamomile also act beneficially on the blood by normalizing platelet clumping, lowering cholesterol (a consequence of lower circulatory system inflammation), promoting the growth of new blood vessels, and normalizing blood sugar levels. These effects make chamomile a very useful herb for people who have cancer, cardiovascular disease, and diabetes which are leading causes of death worldwide.
Chamomile is also effective at reducing muscle spasms, calming anxieties, and reducing depression. Chamomile is a wonderful digestive aid, possessing antidiarrheal abilities by helping to normalize digestive motility while also helping regenerate gastrointestinal mucous linings which aids in nutrient absorption and reduces the ability for pathogenic organisms to enter into the bloodstream. Chamomile has also been shown to be liver protective and reduce the inflammation caused from alcohol consumption.
Chemical Constituents of Chamomile
Like most herbs, the deeper scientist’s delve into the chemistry of a common plant like chamomile the more unique compounds they find. In addition to the normal fatty acids, proteins, amino acids, vitamins, and minerals that chamomile contains, approximately 120 secondary metabolites have been identified which include about 30 different terpenes and 35+ flavonoids. Among the flavonoids, apigenin and quercetin come in the greatest concentrations, and apigenin and quercetin are also the compounds with the most promising heath benefits. Flavonoids and phenolics are soluble in hot water and frequent consumption of chamomile tea effectively results in biologically relevant supplementation of these compounds.
In addition to its flavonoids chamomile is well known for its volatile oils, with steam distillation of chamomile flowers resulting in a 0.5-2% essential oil yield which is a combination of a variety of separate oils. The main constituents of chamomile essential oil include the terpenoids α-bisabolol and its oxides (≤78%), and the dark blue azulenes like chamazulene (1–15%). Chamomile oils range in color from a deep vibrant blue to dark green which after some time can turn into a dark yellow. It’s really quite spectacular seeing the blue color of chamomile essential oil.
Teas brewed from chamomile will extract about 10–15% of the essential oil available in the flower. Oil content of chamomile hasn’t been shown to differ greatly depending on how it’s grown (cultivated or wild), but wild growing chamomile has a wider variety of mineral elements while cultivated types have higher ratios of K/Na and Ca/Mg. Brewing chamomile tea will extract about 10-30% of the minerals present, with potassium, calcium, and magnesium being extracted the most.
Types of Chamomile Flower
Chamomile is not a single species of herb but instead the term given to a collection of very similar herbs that most notably include Roman Chamomile, German Chamomile, and Moroccan Chamomile. The applications of these different types of chamomile doesn’t differ much, but their historical uses differ because of how the different cultures that harvested them used them.
Chamaemelum nobile Uses (Roman Chamomile)
Roman chamomile is found widely throughout Europe as well as in North and South America. Some herbalist consider Roman chamomile to be the most effective type of chamomile, hence sometimes its higher price markup, but since the chemical constituents of the many chamomiles are different, it’s more likely that Roman chamomile isn’t necessarily better just more well known in how it can be used in herbal practices.
Roman chamomile has been used for thousands of years as a digestive aid, painkiller, and as a light sedative. Now Roman chamomile is a popular ingredient in skin and cosmetics products alongside its traditional herbal uses.
Matricaria recutita Benefits (German Chamomile)
German chamomile is as its name suggest found in throughout Germany as well as most of Europe. German chamomile contains more of the azulenes than Roman chamomile, and that’s why Matricaria recutita essential oil has a deep shade of blue. German chamomile is the most used type of chamomile now due to its widespread cultivation and lower cost.
German chamomile when used medicinally is most often brewed into a tea which can be used to treat gastrointestinal problems, reduce cramps from the menstrual cycle, reduce pain and inflammation, and in general calm down the nervous system.
Cladanthus mixtus Benefits (Moroccan Chamomile)
Moroccan chamomile is mostly found in the North African counties of Morocco, Algeria, Libya and Tunisia, growing only sparingly in parts of the Mediterranean. Moroccan chamomile is a distinctly different type of chamomile, some herbalists consider it to be a false chamomile (though its flowers are remarkably the same as the other chamomiles), and state that it should not be used as a substitute for Roman or German chamomile because its chemical composition is different.
That said like the other chamomiles Moroccan chamomile is used for its antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and antimicrobial effects, as a digestive aid, for its ability to calm and soothe the central nervous system, and to help with skin issues.
Chamomile Health Benefits
Chamomile has a wide variety of health benefits, a common attribute of herbs that have been used extensively & safely for thousands of years. Through it’s calming effects, chamomile increases parasympathetic (rest and digest) nervous system activity, which helps with nervous system issues such as anxiety and insomnia while also helping soothe digestive processes. The natural anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial powers of chamomile further help to ensure good digestion, and with good digestion comes a lessening of systemic inflammation of the body, thereby reducing skin issues as well as cardiovascular and cancer health concerns. The actions of chamomile in one way highlight the interconnectedness of the body and how one system out-of-balance like the nervous system places stress on other bodily systems (digestion, circulatory, etc). Below are the specific health benefits of chamomile:
Chamomile Improves Digestion
Chamomile increases parasympathetic activity which normalizes the flow of digestion (motility)
Chamomile increases gastrointestinal mucous production which improves the digestion of food while also reducing pathogenic attack vectors
Chamomile reduces gas, bloating, flatulence, diarrhea, and constipation through its improvements to gut motility
Chamomile can be used to treat motion sickness, nausea, and vomiting
As an anti-inflammatory chamomile can be used to help heal the epithelial tight junctions of the gut (increased mucous production helps with this too)
Chamomile for Treatment of Skin Conditions
As an strong anti-inflammatory chamomile can be applied directly as a poultice to inflammation-based skin issues such as rashes, acne, chicken pox, psoriasis, and eczema
Chamomile tea can be used to sooth and moisturize dried skin anywhere on the body as well as a flakey scalp
Chamomile essential oil is a useful spot treatment for conditions such as acne because of its anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial properties.
Chamomile Calms the Nervous System
Chamomile tea is calming and helps shift the autonomic nervous system from sympathetic (fight or flight) to parasympathetic nervous system activity (rest and digest)
Chamomile reduces depression, anxiety, hysteria, and insomnia
Chamomile tea improves sleep quality and can reduce instances of nightmares
Chamomile reduces muscles spasms
Chamomile Fights Cancer
Chamomile inhibits the growth of many different cancer tumors while not affecting the growth of healthy cells
Similarly chamomile increases apoptosis (programmed cell death) for cancer cells while not affecting healthy cells
As a general anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and antimicrobial chamomile can help restore to balance the normal functions of the body, which makes cancer less likely to occur in the first place.
Chamomile for Cardiovascular Health
Chamomile reduces undesirable platelet clumping in a manner similar to grounding, which improves blood flow and oxygen transport.
Chamomile lowers LDL cholesterol because it reduces overall inflammation throughout the body
Chamomile improves blood glucose levels, especially for diabetics
Chamomile can spur the creation of new blood vessels
Chamomile Healing Properties
For an acute digestive or skin flare-up chamomile can be used right away to help with the problem. For chronic digestive and/or skin issues chamomile should be used consistently for best effect. Chamomile is a general health booster and good to use/have every now and then for preventative health reasons. For sleep, depression, and anxiety issues chamomile should be used daily, as it should also be used if part of a cancer-fighting effort.
Chamomile Homeopathy
Homeopathy is an alternative medical practice that operates off two main principles: that health problems are best treated with herbs/drugs that also trigger the same dysfunctional pathways highlighted by the problem (like cures like), and that medicines are most effective when used at a “minimum effective dose”
Herbs are a popular component of homeopathic care because they tend to work slowly and with minimal side effects. For homeopathy chamomile is extracted and then diluted to a very low concentration. The enduring popularity of homeopathy for hundreds of years gives us a clue that something about it works, but the exact reasons why haven’t been conclusively identified.
One theory is that herbs which undergo extraction produce nanometer structures which remain intake even after high dilution, and these nanostructures interact with electromagnetic fields like the Schumann resonances to influence beneficial changes at the DNA and cellular level, causing positive health effects. This is by no means conclusively proven but I mention it here as a launching point for further research for the curious (see reference 5).
Chamomile Extract
This extract is made in small batches from fresh organic German chamomile flowers. The extract has a mild flavor and a floral, fruity taste. It can be taken directly or added to any drink.
Having a chamomile extract is an easy way to enjoy the full-body benefits of chamomile while on the go without the added steps required of brewing tea.
Chamomile Essential Oil
Chamomile essential oil is a very useful way to keep chamomile on hand and ready at a moments notice. Chamomile essential oil is wonderful when used for aromatherapy, either to help calm down and relax, or with a diffuser just because it smells nice. Chamomile essential oil can also be applied directly to parts of the body to lessen inflammation, as an antimicrobial, or for localized calming and pain reducing effects.
My personal favorite way of using chamomile essential oil is to apply it to my forehead, temples, and to the back of my neck before I go to sleep. By doing this I get the aroma-therapeutic effect of chamomile but also it directly targets parts of the brain (frontal lobe, hippocampus, cerebellum) that are partly responsible for thinking and autonomic nervous system activity, helping me to calm down and fall asleep nearly instantly.
I also use chamomile essential oil to moisture the ends of my hair when things get a bit dried out. Unlike other essential oils which I feel are too greasy, chamomile essential oil is quite “soft” and absorbs nicely into the hair. More on how chamomile can used for hair later.
Chamomile Lotion
Many commercial lotions now contain a small amount of chamomile, but some with many undesirable compounds. For best effect chamomile lotion can be made at home by mixing chamomile essential oil with a carrier oil, butter, or lotion. As part of a lotion, chamomile will amplify the moisturizing properties by reducing any inflammation that may be present, soothing the skin in the process.
The chamomile lotion I’ve made is very simple, I mix a few drops of chamomile essential oil with a tsp of chia seed oil and apply where needed. Chia seed oil is highly nourishing and has a lot of omega-3 fatty acids which are useful for the skin. You can also add other essential oils such as lavender to a carrier oil alongside chamomile essential oil to create a moisturizing, relaxing, pain-soothing blend.
Mountain Rose Herbs Chamomile Essential Oils
Mountain Rose Herbs is my go-to supplier of essential oils, and they carry all three types of chamomile essential oil (Roman, German, Moroccan). Try all three to discover their subtle differences, or choose which one resonates with you the most.
Blue Chamomile Essential Oil
This organic blue chamomile essential oil is steam distilled from Matricaria recutita flowers. It has a deep blue hue from the high concentrations of azulene released during distillation.
This is my personal go-to chamomile essential oil because of it’s high quality, fair price point, and high concentrations of azulene.
Roman Chamomile Essential Oil
This organic Roman chamomile essential oil is steam distilled from the flowers of Anthemis nobilis. It has a light, bright scent with notes of honey and apple.
With less color it is better used in perfumes than the blue chamomile essential oil.
Moroccan Chamomile Essential Oil
This organic Moroccan chamomile essential oil is steam distilled from the flowers of Omenis mixta.
Moroccan chamomile is considered by some not to be a “true” chamomile, but it hails from the same family and even though its chemical composition is notably different it has very similar health effects as both Roman and German chamomile.
What is Chamomile Tea Good For?
The most popular way to use chamomile is to brew it into a tea, and chamomile tea has a wide variety of uses. Chamomile tea is the best way to utilize chamomile for improving digestion, and chamomile tea has a more full-body effect in calming the nervous system down than chamomile essential oil does (unless applied very liberally).
I drink chamomile tea often as an all-in-one health solution, and often as part of a tea blend. A cup or two of chamomile tea after dinner will improve the digestion of the meal, get the body and mind into a more relaxed state, and with regular consumption will help with any ongoing skin issues like acne that may be present. Chamomile tea is also nice in the morning, though I prefer green tea then, and mixing green tea and chamomile is interesting because it really puts you into a flow state because the combination will strongly activate 8-12 Hz alpha brainwaves.
Brewing chamomile tea is easy, simply steep chamomile flowers with 70-100 C water for 5-15 minutes. Chamomile is a very sweet herb and doesn’t easily steep bitter, so I recommend steeping it for longer and with a higher temperature water in order to extract more of the beneficial active constituents present. If it does taste slightly bitter afterwards simply add some honey. If you want to stop some of the extracted essential oils from vaporizing away during the steeping process then cover the container with a lid.
Chamomile Hair Lightening
Chamomile tea also makes for a nice natural hair lightener. Bring a large container of water to a boil and add a lot of chamomile flowers or chamomile tea bags and let steep for 30-60 minutes. Remove the flowers or tea bags and once the water is cool either rinse your hair with the strong chamomile tea or better yet let your hair soak in the container for 30-60 minutes. Adding some honey to the tea enhances the lightening and moisturizing process.
You can rinse your hair afterwards with water or simply let your hair air dry which allows the active constituents of the chamomile to further nourish your hair and scalp.
Mountain Rose Herbs Chamomile Flowers
Grown in Croatia these organic Matricaria recutita flowers are harvested at the peak of freshness. Steeping chamomile flowers into tea is very simple, it just requires a tea infuser or a tea spoon.
Brewing whole organic chamomile flowers like these is much more cost-effective than buying chamomile tea-bags at the store, the flowers will be much less oxidized because they won’t have been chopped up, and therefore more of the beneficial active ingredients will be extracted out.
Chamomile Tea Side Effects
Chamomile tea has a long history of safe usage and is extremely safe. One thing to be aware of with chamomile is that it may trigger an allergic reaction for an existing ragweed allergy
Additionally since chamomile does reduce platelet clumping, care should be taken with chamomile if already using a blood thinner.
References:
Malcom Stuart, et al. The Encyclopedia of Herbs and Herbalism. Crescent Books, New York.
McKay DL, Blumberg JB. A Review of the bioactivity and potential health benefits of chamomile tea (Matricaria recutita L.). Phytother Res. 2006;20(7):519-530.
Miraj S, Alesaeidi S. A systematic review study of therapeutic effects of Matricaria recuitta chamomile (Chamomile). Electron physician. 2016;8(9):3024-3031.
Gupta. Chamomile: A herbal medicine of the past with a bright future (Review). Mol Med Rep. 2010;3(6).
Montagnier L, Aissa J, Giudice ED, Lavallee C, Tedeschi A, Vitiello G. DNA waves and water. J Phys: Conf Ser. 2011;306:012007.
Disclosure: Wild Free Organic is a member of various affiliate programs and if a purchase is made through one of our affiliate links a small commission is received. This does not affect your purchase price. Visit our disclosure page for more information.
Other Anti-Inflammatory Herbs
Dandelion
Dandelion (Taraxacum officinale) is a widely distributed wildflower that is entirely edible and has many powerful health benefits. Dandelion is a strong anti-inflammatory, improves digestion, boosts immunity, cardiovascular and metabolic aid, and also helps with liver and kidney issues. Most notably dandelion is known as a blood purifier and in this way dandelion is useful for many health issues.
Article by Stefan Burns - Updated April 2022. Join the Wild Free Organic email newsletter!
| Name: | Dandelion, Linnaean - Taraxacum officinale |
| Color: | Yellow flowers, green leaves, whiteish-tan to brown roots |
| Constituents: | Taraxacin, taraxerin, taraxerol, taraxasterol, polyphenols, carotenoids, xanthophylls, flavoxanthin, inulin, sterols, terpenes |
| Effect: | Blood purifier, improves digestion (diuretic in high doses), anti-inflammatory, |
| Preparation: | Flowers and leaves can be eaten raw or cooked. The roots can be shredded or powdered for use in tea or for supplementation. |
| Dosing: | 1-3 grams of root for tea, 1-10 grams of root powder for supplementation purposes |
| General Notes: | Dandelion flowers and leaves contain abundant levels of calcium. Dandelion root can be used as a coffee substitute. All parts of the plant are safe to use in large amounts. |
What is Dandelion?
With flowers like honey, leaves like lettuce, and roots like coffee it’s no wonder that dandelions (Taraxacum officinale) are immensely popular despite being considered only as a weed by many uneducated. Dandelion is an entirely edible wildflower whose roots, leaves, and flowers have been used as different food and herbal products, and medicinally in herbalism practices for thousands of years. Its long history as a folk remedy is now supported by modern scientific research that has taken place looking into the unique phytochemistry and health benefits of dandelion.
Dandelion in Ayurveda
In Ayurveda it is said that food is medicine, and the humble dandelion is an excellent example of this truth, being both a common food around the world while also being a premiere detoxifing herbal medicine.
In Ayurveda dandelions are recommended for reducing kapha in the body when transitioning from the winter to spring season, and the appearance of blooming dandelions during that early spring period aligns with this advice. In Ayurveda kapha is one of the three functional energies of nature, made of primarily earth and water elements. The nature of kapha energy is slow, heavy, smooth, oily, and stable. Kapha-rich foods provide warmth, stability, and comfort during cold winter months but kapha brings with it a certain dullness. Dandelion is used in Ayurveda at the beginning of spring to reduce excess kapha energy accumulated during the winter months and to promote the higher frequency vitality that is of benefit during winter and spring.
Dandelion Identification
Dandelion is widely distributed in the warmer temperate zones of the Northern Hemisphere and are found on all the continents except Antarctica. Dandelions were first brought to North America on the 1620 Mayflower voyage from Britain to Massachusetts.
The oblong 3-10” (7.5-25 cm) long leaves of a mature dandelion plant grow in a basal rosette. The leaves have a few hairs and have widely-spaced teeth that point towards the base of the plant. Dandelions have a thick fleshy taproot that is easily broken. All parts of the plant exude a milky sap when cut. A yellow dandelion flower is not a single flower but instead a composite flower head composed of many very small florets.
Dandelion Cultivation
Dandelions are easily cultivated and require very little attention once established. To grow dandelions grow in your area then harvest some dandelion seedheads and blow the seeds (and make a wish!) out over where you want the dandelions to start growing. Alternatively instead of finding dandelion seedheads to harvest you can purchase dandelion seeds from Mountain Rose Herbs.
Taraxacum officinale in the garden is highly beneficial because their deep tap roots draw water and nutrients up from soil layers inaccessible to many other plants. If harvesting from a plant pull no more than half of its leaves and/or flowers, or if digging dandelions up by the root then harvest no more than 50% of all the dandelions in an area in order to maintain a healthy stable population. If the taproot is broken during harvesting and a segment remains stuck in the ground leave it and consider it a good thing because a dandelion can regrow easily from its broken roots.
The longer a dandelion is left to grow without harvesting the bigger and more dominant it’ll become. In my garden I have a few especially large dandelions that I never harvest from so they may always function for the benefit of the garden, soil microbiome, and for continuously dandelion seeding. Dandelions are a vital source of nectar for pollinators throughout the year but especially during early spring time.
Harvesting Dandelion
Dandelion is a hardy and very adaptable wildflower than can grow in a wide variety of environments, and for this reason it’s important to be careful in sourcing dandelion from reputable sources. Dandelions can grow, even thrive, in areas contaminated with waste, and their efficient and deep taproots can draw toxins out of the soil and into their roots. Care should be taken to only wild harvest dandelions from uncontaminated areas. For example, dandelions growing along the side of a road where pollution levels are higher, or dandelions growing in a field sprayed with pesticides, should not be consumed.
The phytochemical composition of dandelion depends on the season in which it is gathered and the time of day it is harvested. Inulin content in dandelion roots is determined by the degree of conversion of inulin to laevulose and other sugars, which is ~2% during spring to ~40% in fall. Sesquiterpene is one compound that imparts a bitter taste to dandelion leaves and roots, and it’s present at greater concentrations when dandelion is harvested in the spring. Concentrations of methyl sterols are highest during the winter months, whereas sitosterol and cycloartenol esters levels are greatest during periods of sunshine of which there is more of during the summer months. The science of when to harvest dandelion to boost what health effect is still being discovered, so if using dandelion yourself as part of an herbal practice I recommend harvesting dandelions at different parts of the year, labeling the conditions under which they were harvested, and making your own observations as to the differences.
Dandelion Health Benefits
Raw dandelion greens contain high amounts of vitamins A, C, and K, contain abundant potassium, and are moderate sources of calcium, iron, and manganese. Dandelion is also one of the richest green-vegetable sources of beta-carotene (which is converted to vitamin A by the body). Dandelions also contain a variety of phytochemicals such as lactones, terpenoids, polysaccharides, phenylpropanoids, phenolic compounds, and inulin.
Modern scientific research as it is known to do is splitting apart and examining the biochemical effects of the many phytochemicals that dandelion has, which is useful to understand very precisely what phytochemical has what effect. This approach has its limits though, and with new compounds being discovered continuously it is more practical to understand the health benefits of dandelion from a holistic “whole-herb” viewpoint.
Taraxacum officinale benefits
Of all of dandelions many health effects what’s best established is that consuming dandelion has potent antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects throughout the body. It’s dandelion’s anti-inflammatory properties that are chiefly responsible for its many cardiovascular, metabolic, immunity, digestive, anti-cancer, and liver protective health benefits.
Dandelion Health Uses
Dandelion’s health benefits provide it many health uses, and the way some of it’s health benefits overlap in effects allow dandelion to be useful for common health conditions which exist downstream of the beneficial changes dandelion causes in the body, for example with skin issues. When discussing the health uses of dandelion, in general it is dandelion root that is most commonly given herbally.
Dandelion for Pain
Possessing many strong antioxidant compounds and overall being a strong anti-inflammatory, the entire dandelion plant is useful for reducing pain throughout the body, and may even work to heal the root issues causing the pain. Acute pain may require a large dosage whereas chronic pain might be eased with a lower daily dose of dandelion in the form of tea or root powder.
Dandelion is a Cardiovascular and Metabolism Aid
Dandelion improves blood cholesterol values, adapts fat metabolism towards optimal, improves blood glucose parameters, inhibits excessive platelet aggregation and reduces risk from thrombosis and other blood coagulation disorders. In general dandelion is considered a blood purifier, and by detoxifying and improving blood parameters it improves the efficiency of the heart which reduces risk from cardiovascular disease.
Dandelion has Anti-Cancer Properties
Dandelion inhibits the growth of cancer cells through anti-tumor actions, is cytotoxic to mature cancer cells and induces them to undergo apoptosis (cellular death), is immunostimulatory, and does all this while displaying no toxicity to healthy cells. Dandelion might not cure cancer on its own, but taken alongside traditional cancer treatment will improves chances of successful elimination of cancer without causing any new side effects (and more likely ameliorating to a degree the side effects of common cancer drugs and therapies).
Dandelion is a Digestive Aid and Diuretic
Dandelion reduces constipation, diarrhea, and intestinal cramping, increases thickness of the mucosal lining of the digestion system, heals gastric ulcers, increases bile production (an aid to fat utilization), stimulates healthy appetite, and possesses antimicrobial properties.
One of the root causes of many digestive ailments is the lack of mucous production sufficient to coat and protect the epithelial linings of the gastrointestinal system. Mucous is the first line of defense against the trillions and trillions of microorganisms that live in the gut, and if mucosal linings are thin then microorganisms can colonize directly on the outer digestive cellular surface, creating an inflammatory burden and stressing the capabilities of the immune system. These biofilms as they are known are difficult to dissolve/dislodge, and biofilms are one reason why many digestive issues flair back up after seeming to go away after a gut healing protocol like a 48 hour fast. By stimulating mucous production while also possessing antibacterial and immune-boosting properties, dandelion packs a one two three punch against biofilms which are a main contributor to many digestive issues. Dandelion tea taken 1-2x time a day is best for healing the digestive system.
Dandelion for Kidney Issues
Dandelion may prevent and help with the treatment of kidney stones at moderate to high dosages. Kidney stones are typically made of a mineral known as calcium oxalate. Direct supplementation of calcium can cause an slight increased chance of kidney stones, but a much bigger risk factor in developing kidney stones is a diet low in calcium. When calcium levels are low, oxalate circulates in the bloodstream at greater concentrations, and much of this oxalate eventually will wind up in urine where it is 15x more likely to precipitate calcium oxalate crystals as compared to calcium concentrations in urine.
Dandelions reduce the risk of kidney stones not only because of the effect some of its phytochemicals have on the renal system, but also because dandelion is a rich source of calcium which if consumed regularly will reduce the chance of experiencing low calcium levels.
Dandelion for Liver Issues
Dandelion modulates liver enzymes, protects against alcoholic liver damage, and is an anti-fibrotic agent for hepatic disorders like liver fibrosis. When dandelion is a regular part of the diet, supplemented directly with, or consumed often as a tea, it has a general protective effect on the liver.
The liver is the bodies master detoxifier next to the kidneys, and supporting the liver in these efforts can prevent to buildup of cellular stress and waste products which can lead to health problems from minor to serious. Being mindful of liver health is a necessary requirement for good health and longevity.
Dandelion Uses for Skin
Dandelion’s antimicrobial, cholesterol improving, blood glucose optimizing, coagulation reducing, immune boosting, and general anti-inflammatory effects demonstrate that dandelion is a first class “blood purifier”. The skin is the largest organ and since it covers so much surface area and is exposed to the outside environment, the skin is a tidy detoxification pathway. Skin inflammatory conditions such as psoriasis and eczema, or more common skin issues like acne are caused by autoimmune and immune reactions to microorganisms respectively.
As a blood purifier dandelion will reduce the use of the skin detoxification pathway because the issue (autoimmunity, excess bacteria) will be reduced in the body and better controlled, thereby not requiring skin detoxification to occur in the first place. For dandelion to work best for skin conditions, it should be eaten or supplemented with daily, and for serious skin issues a dandelion poultice from any part of the plant can be made and applied directly to the area of concern.
Other Dandelion Root Benefits
Some other benefits of dandelion root is that it is an adaptogen for the endocrine system, especially for female hormone disorders as it increases estrogen receptor expression, progesterone receptor expression, and follicle stimulating hormone receptor expression in adipose tissue and reproductive organs.
Through its blood purifying actions and the large surface area of blood vessels in the lungs, dandelion has proven useful in treating inflammatory lung conditions.
Note: Much of the research into dandelion showing these benefits has been done using animal models and therefore hasn’t been directly confirmed for humans.
Dandelion Food Products
Being a ubiquitous and plentiful herb in parts of the world (especially Europe where few dangerous pesticides are used to eliminate them), and being completely edible has led to the creation of many different dandelion foods, some being just raw parts of the plant while others are derivatives.
*Dandelion root and leaf products for purchase are listed at the end of this article.
Dandelion Flowers
Dandelion flowers can be eaten raw and are quite nice enjoyed this way. They have quite a sweet flavor but if left in the palate that sweetness will eventually turn bitter. Eat dandelion flowers by themselves as an occasional treat or add them as a salad topper for flavor and color.
I like eating dandelion flowers raw because they are high in calcium and therefore are good for the teeth. Since dandelions grow fairly ubiquitously, if a patch of happy dandelions is found growing in a good spot, picking a few and leaving a majority makes for a healthy enamel-building snack while out and about.
Dandelion Leaves
Like the flowers dandelion leaves can be eaten raw, though it’s also common to eat them steamed or sautéed. Dandelion greens are nutty and earthy in flavor but can be quite bitter. Dandelion leaves can be made less bitter through blanching, first boiling them in salty water for 1-2 minutes and then immersing them in ice water for 30 seconds.
Dandelion leaves make a great addition to a leafy green salad when added in a minimal amount so their bitterness isn’t overwhelming and the natural earthiness instead comes out. Smaller younger dandelion leaves are less bitter than larger more mature leaves.
Dandelion Tea
Dandelion tea is one of the primary ways to enjoy the heath and herbal benefits of dandelion. Dandelion tea can be made from all three parts of the plant, though it’s typically the root that is steeped. For a full extract dandelion tea steep dried dandelion root, dried dandelion leaves, and fresh dandelion blossoms all together.
The strength of a dandelion tea is determined by the water temperature used and the length of time it is steeped for. A light dandelion tea can be made by steeping dandelion root for 5-8 minutes with 170 F (75 C) water. A more potent dandelion tea more specifically used for health and herbal reasons can be made by steeping dandelion flowers, dried leaves, and dried root for 15 minutes using boiling water.
A water-based dandelion extract can be made by simmering dried dandelion root for 30-90 minutes. Though dandelion is non-toxic, this extract will be quite bitter and is best used for specific health and wellness endeavors (for example as a strong blood purifying agent)
Dandelion Jelly
One unique way to enjoy dandelions is to make a jelly from dandelion flower blossoms. Pick a 4 cups worth of dandelion flowers and remove all stems and green parts from the flower heads. Bring 4 cups of spring water to a boil and pour over the flowers, steeping them until the water is room temperature.
Once cool strain and press the mixture to extract as much rich dandelion tea as possible. In a pot bring the dandelion tea, 2 tbsp of lemon juice, and half a packet of pectin (1/4 cup & 1.5 tsp) to a boil. Stir in 4 cups of sugar and boil for 1-2 minutes. Remove from heat and let cool slightly before pouring the jelly mixture into airtight canning jars. Let the jelly rest in the refrigerator until set, about 4 hours.
Dandelion Coffee
Roasted and ground dandelion root can be used as a caffeine-free coffee alternative because it has a similar appearance and taste to coffee. For those looking to perform a caffeine tolerance reset, or for those traveling through the bush like hunters who want an easy to identify and produce early morning drink, dandelion coffee is a good alternative to coffee to enjoy. Dandelion coffee has the benefit of being high in many vitamins, minerals, and phytochemicals and is a detoxifier as well as a diuretic.
Dandelion Wine
Dandelion wine is made dandelion flower blossoms like dandelion jelly except the strong dandelion tea that is made is fermented instead of jellied. Dandelion wine has a moderate alcohol content and has been produced mostly non-commercially as a “cheap man’s wine” in Europe and North America. The general rule of thumb is one gallon of dandelion flowers will produce one gallon of dandelion wine.
Dandelion wine has many of the health benefits that other dandelion preparations have, specifically it’s a useful digestive aid that can be used to restore normal digestive function which also cleanses the microbiome (due to the alcohol content) of pathogenic microorganisms.
Is Dandelion Safe?
Dandelion is one of the safest herbs known to man. The entire plant is non-toxic and it has a long history of use in large doses.
The biggest concern with the safety of dandelion is not the plant itself but whether the plant has absorbed contamination like heavy metals from waste areas. Since dandelions can grow in conditions many other plants can’t tolerate, they can be growing in environments where they’re best left undisturbed and unharvested. Dandelions growing in waste areas detoxify and remediate the soil and are best left to that noble task.
Dandelion Dosing
Dandelion is entirely non-toxic and is useful and well-tolerated in large doses. Dandelion flowers and leaves can be consumed in large amounts similar to typical servings for leafy greens like spinach and kale, whereas dandelion root powder is often supplemented with in the 1-10 gram range.
To brew a typical cup of dandelion tea steep 1-3 grams of dandelion root in boiling water for 5-8 minutes. Serve with honey to cut the bitterness.
Brew dandelion coffee the same as you would with regular coffee. Roasted dandelion root can be combined with chaga mushroom (another coffee substitute) to create a dandelion chaga coffee substitute, which has even more beneficial health effects. Or combine coffee, roasted dandelion root, and chaga together!
Where to Buy Dandelion?
Dandelion products are available from many different suppliers, and the supplier I trust and keep returning too is Mountain Rose Herbs. Mountain Rose Herbs offers a wide range of organic herbs, spices, essential oils, and so much more. All of their dandelion products are USDA organic certified.
Dandelion Root
This dandelion root is harvested in autumn when its inulin content is highest. Dandelion root finely chopped in this way is great for steeping into a tea, I recommend buying double what you think you need because in my experience I end up using dandelion root much faster than expected.
Roasted Dandelion Root is a good caffeine-free coffee alternative.
Dandelion Root Extract absorbs quickly and powerfully into the bloodstream when taken sublingually.
Dandelion Root Powder
Powdered dandelion root is useful for taking as a raw full-spectrum supplement.
Roasted Dandelion Root Powder has a stronger earthy flavor than the unroasted powder, try both to see which you prefer!
Dandelion Root Capsules make supplementing with dandelion root easy and convenient, either at home or on the go.
Dandelion Leaf
These dandelion leaves are collected before flowering occurs. Dandelion leaves have different phytochemical ratios than dandelion root. Steep dandelion leaf and root together for a tea which holistically contains the benefits of the full plant.
References:
Malcom Stuart, et al. The Encyclopedia of Herbs and Herbalism. Crescent Books, New York.
González-Castejón M, Visioli F, Rodriguez-Casado A. Diverse biological activities of dandelion. Nutrition Reviews. 2012;70(9):534-547.
Disclosure: Wild Free Organic is a member of various affiliate programs and if a purchase is made through one of our affiliate links a small commission is received. This does not affect your purchase price. Visit our disclosure page for more information.
Other Herbs for Digestion
Ashwagandha
Ashwagandha is an adaptogenic herb which has been used in ancient medicine systems like Ayurveda for thousands of years. Ashwagandha increases general health and vitality through it's balancing actions on the metabolic, digestive, cognitive, immune, and hormonal systems. Ashwagandha is a tonic quite effective at reducing stress, reducing inflammation, and increasing stamina, and it's quite safe.
Article by Stefan Burns - Updated April 2022. Join the Wild Free Organic email newsletter!
Ashwagandha roots - CC4.0 Piyush Kothari
| Name: | Ashwagandha, Indian Ginseng, Linnaean - Withania somnifera |
| Color: | Green leaves, red berries, tan rhizomes and roots |
| Constituents: | steroidal lactones (withanolides, withaferins), saponins, alkaloids |
| Effect: | Endocrine adaptogen, stress adaptogen, reduces anxiety, anti-inflammatory, performance booster, aphrodisiac, anti-parasitic, enhances vitality, neuroprotective |
| Preparation: | The root is the part most commonly used, followed by the leaves. Both can be ground into a powder for use or extracted into a tincture |
| Dosing: | 300–600 mg of a root extract taken with meals. Doses in the 2-5 gram range of raw root powder daily may raise testosterone levels and increase male fertility. |
| General Notes: | Ashwagandha is one of the best known herbal adaptogens because it works on so many different levels, from reducing stress and anxiety to balancing hormone levels to optimal function. Has anti-inflammatory effects which make it useful for digestive, immune, and cognitive optimization. Ashwagandha is a very revered herb in the Indian Ayurvedic system of medicine |
What is Ashwagandha?
Ashwagandha (Withania somnifera) is a small evergreen shrub that produces berries and is therefore sometimes known as “Indian Winter Berry”. The roots, leaves, flowers, and seeds all have medicinal uses, though it’s the roots that are most commonly used in herbal medicine practices. The word ashwagandha means “odor of a horse” and this name was given to Withania Somnifera because the roots have a smell similar to that of a sweaty horse, and it’s also believed that consuming ashwagandha gives one the power of a horse. The name is well deserved because Ashwagandha is a powerful tonic, aphrodisiac, thermogenic, and stimulant in addition to having pain-relieving, digestive healing, and anti-parasitic properties. Ashwagandha also has powerful neurologic benefits and is increasingly being used in the treatment of various brain disorders like Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease or lesser ailments like depression and anxiety. Because of its wide range of uses, ashwagandha is well known as an adaptogen which can be used medicinally to treat acute or chronic health problems, and it can also be used preventatively or simply to boost health and function beyond normal.
Cultivation of Ashwagandha
Ashwagandha is cultivated in north-western and central parts of India and it is also found in Nepal, China, and Yemen. Ashwagandha is most commonly found growing in semi-tropical regions 1500 meters above sea level which receive 50-80 cm of annual rainfall. It grows best in sandy loam or light red soil, in partial shade, and in a 20 to 38 C temperature range.
Ashwagandha in Ayurveda
In the ancient Ayurvedic system of medicine, ashwagandha is classified first as a “rasayana” which means tonic, and is further classified as a medhyarasayana, medhya referring to the mind and intellect. Ashwagandha has the most prestige among the different rasayanas in Ayurveda because of its many effective medicinal uses. As a tonic ashwagandha is given to guard and defend against disease, to slow the aging process and rejuvenate the body, and to improve intellect and memory capabilities. Ashwagandha is most effective as a medhyarasayana following head injuries, in old age, or for children with cognitive disorders.
Ashwagandha is most commonly available as a finely milled and sieved “churna” powder produced from the roots which can be mixed with water, ghee, or honey. Often prescribed for Vata imbalances. Ashwagandha is one of the most important herbs in Ayurveda, broadly known to promote a youthful state of physical and mental health expanding overall happiness.
Ashwagandha in Other Herbal Medicinal Systems
Ashwagandha also holds a place of importance in other ancient systems of medicine in the Asian and African regions. In Traditional Chinese Medicine ashwagandha is used to balance “Qi” life force energy and is categorized as a Qi tonic. In the Tibetan System of Medicine ashwagandha is used in the treatment of respiratory disorders, to aid the functions of the liver, to strengthen the body, and to maintain heboglobin levels. In parts of Africa the leaves of Withania somnifera are used as a dressing for infections and inflammations. Finely powdered ashwagandha root is mixed with animal fat and applied as an ointment for sores and abscesses. In the Zulu culture ashwagandha is used to protect people from sorcery.
Ashwagandha Health Benefits
Ashwagandha is a powerful adaptogen that has many beneficial health effects thanks to its many (35+) unique chemical constituents. The most active of these components are:
Alkaloids | Functions: Improves energy metabolism and cell to cell signaling, neuroprotective, boosts immunity
Lactones (withanolides, withaferins) | Functions: Suppresses oxidative stress, anti-inflammatory, inhibits lipid peroxidation, neuroregenerative. Steroidal lactones are an important component of cell membranes and of steroid signaling molecules
Saponins | Functions: Anti-tumor & anti-cancer, radiation protection, boosts immunity
Together these phytonutrients broadly influence the function of the cognitive, immune, metabolic, digestive, and reproductive systems providing the following benefits:
Cognitive Benefits of Ashwagandha
Ashwagandha leaf and root extracts reduce symptoms of anxiety, comparable to pharmaceutical drugs
Ashwagandha inhibits nerve cells from over firing
Slows, stops, and even reverses neural decay by promoting the growth of new neurons and by creating new synaptic connections
Comparable to pharmaceutical drugs in reducing symptoms of depression, stabilizes mood
Normalizes dopamine levels to normal, increasing dopamine levels in those suffering from Parkinson’s disease
Intensifies acetylcholine, glutathione, and secretase enzyme activity
Inhibits the production of amyloid beta plaques in those suffering from Alzheimer’s disease
Helps to reverse addiction through its balancing actions on neurotransmitters GABA and serotonin
Digestive Benefits of Ashwagandha
Has a strong effect in preventing and healing stress-induced gastric ulcers
Helps reduce flatulence and stimulates digestive action
Has anti-parasitic properties and can clear worms from the digestive system, especially true for ashwagandha seeds
Immune System Benefits of Ashwagandha
Modulates white blood cell counts back to normal ranges if overly elevated or suppressed
Has a powerful anti-cancer effect, synergizing well with chemotherapy and radiation therapies while also reducing their side effects.
Inhibits and reduces the growth of tumors
Possesses antibacterial properties
Metabolic and Endurance Benefits of Ashwagandha
Improves stamina quite notably and reduces the stress experienced from endurance events when taken beforehand
Improves mitochondrial function through modulation of various cellular pathways
Improves metabolism and is mildly anabolic, increasing body weight (likely by increasing lean body mass)
Hormonal Benefits of Ashwagandha
Has evidence of boosting male testosterone levels by around 15% if levels are suboptimal
Has an aphrodisiac effect for some men and women
Reduces cortisol and Vitamin C depletion in the adrenal glands after endurance events, preventing adrenal fatigue
Many of the cognitive benefits of ashwagandha come from its stabilizing effects on the brain’s endocrine glands
Anti-Inflammatory Benefits of Ashwagandha
Helpful for fever and painful swellings
Applied topically ashwagandha is useful for skin inflammatory conditions such as pimples, boils, sores, etc
Has anti-arthritic effects and reduces joint pain
Ashwagandha contains many powerful antioxidants which neutralize destructive free radicals
Note: Much of the research into ashwagandha showing these benefits has been done using animal models and therefore hasn’t been directly confirmed for humans.
What is Ashwagandha Good For?
As an adaptogen ashwagandha has many uses, and in the different ancient systems of medicine such as Ayurveda and Traditional Chinese Medicine the list of its uses is nearly endless. Classifying ashwagandha as a tonic is probably the best summarization of its many health benefits as a result. In general ashwagandha is good for increasing vitality and energy while promoting balance to many of the bodies different systems (immune, digestive, metabolic, neurologic, etc).
While not new to other cultures outside India and China, ashwagandha is increasingly being discovered by people around the world who are seeking natural treatment options for mental health conditions, by men who want to boost their testosterone levels, or by women who want a natural and safe aphrodisiac. Ashwagandha is a good “introduction” to the practice of herbalism because as an adaptogen the positive health changes it brings about are likely to be felt in some way.
Ashwagandha for Anxiety and Depression
Supplementing with ashwagandha is a good treatment option for anxiety and depression because its effects are noticeably felt while being gentle on the body. Ashwagandha can reduce hyperactivity, circular overthinking, and emotional instability through its modulation of various neurologic pathways. Ashwagandha also reduces stress accumulation which is a large causal factor in mental health concerns like anxiety and depression. If experiencing anxiety, depression, or an overload of stress then supplementing with ashwagandha daily may prove highly beneficial.
Ashwagandha for Testosterone
Male hormonal health has been on a decades long downward trend, with testosterone levels and sperm count declining precipitously since the creation of plastics and pesticides. Ashwagandha is a safe an effective adaptogen for men and it has been observed to raise testosterone levels in men by ~15%. Ashwagandha also increases sperm count and in general promotes youth and vitality. If experiencing symptoms of low testosterone like fatigue, a lack of confidence, depression, low levels of lean body mass, and emotional instability then ashwagandha is a good herbal supplement to take for its endocrine balancing effects. If after supplementing with ashwagandha for some time a stronger testosterone booster is desired then the herb cistanche is a good candidate.
Ashwagandha Benefits for Women
The female menstrual cycle causes key hormones estrogen, progesterone, luteinizing hormone, and follicle stimulating hormone to rise and fall in various ways across a 28 day cycle. Sex drive is linked to the rise and fall of these hormones, specifically estrogen and progesterone, and for women who experience low sex drive either from their ups and downs of their natural menstrual cycle or because they are using birth control hormone replacement therapies which lower hormone levels, ashwagandha can serve as a useful aphrodisiac which stimulates sex drive.
The more pronounced variations in female hormone systems also influences immunity, causing it to rise and lower with the changes in secretion of various hormones like progesterone. Ashwagandha can act as an immunity buffer for women that fills in the natural dips of immune system function that may occur for pre and post-menopausal women. Through its effects on the endocrine system and adrenal glands ashwagandha has been shown to be useful in reducing symptoms of menopause like hot flashes, excessive sweating, sleep problems, and more.
How Long does it take for Ashwagandha to Work?
The benefits received from Ashwagandha depend on the length of time supplemented for. A single dose of ashwagandha before an endurance event is sufficient to greatly improve stamina and correspondingly reduce the following stress response. With sufficient dosages stimulant and aphrodisiac effects can be felt quite quickly though these benefits may take a week or more of daily supplementation to materialize. The neurological effects of Ashwagandha build over time, with the growth of new neurons and synaptic connections starting to be observed after one week of daily supplementation. Ashwagandha for parasite removal will take 2-3 weeks of daily supplementation to be effective. It takes 2-3 months of ashwagandha supplementation to observe favorable increases in body-weight and testosterone levels.
Is Ashwagandha Safe?
Ashwagandha has a strong safety profile backed by scientific research and thousands of years of usage medicinally in Ayurveda. There is no known toxicity concerns with ashwagandha if taken within recommended dosage ranges. That said, ashwagandha is a hardy plant able to grow wild in areas contaminated with waste, so care must be taken in purchasing ashwagandha either from a cultivated reputable source, or if purchasing wild-harvested ashwagandha ask the supplier where harvesting occurs.
There is some scientific contradiction to the acute toxicity of ashwagandha extract for rats. One study observed acute toxicity at 1260 mg/kg of ashwagandha extract and set the 50% death rate (LD50) at 1260 mg/kg for rats. Another study did a single acute dosing of ashwagandha extract at 500, 1000, and 2000 mg/kg which showed no toxicity, and then followed that with daily supplementation of the same extract amounts for 28 days and still observed no toxicity.
Considering the variability, it’s safer to go with the 1260 mg/kg LD50 rate for rats, and when converted to a human equivalent dose, the calculated ashwagandha extract human LD50 is 200 mg/kg of body-weight. For a 50, 75, and 100 kg individual the ashwagandha extract LD50 dosages are 10, 15, and 20 grams (a ridiculous amount). Ashwagandha is most commonly supplemented in the 250 to 600 mg range, so there is little to worry of when supplementing ashwagandha responsibly.
Ashwagandha Side Effects
The side effects that may occur when supplementing with ashwagandha are rare and more a result of other physiological changes that ashwagandha triggers. For example an increase in circulating testosterone for men may cause an increase in acne if other factors are out of balance. The minor diuretic effect of ashwagandha will be amplified when dosing beyond recommended ranges. If taking ashwagandha for or as part of a parasite cleanse then it behooves one to be aware of the side effects that may be experienced during that type of health protocol. Ashwagandha can be sedative for some individuals, and though very rare, because it affects the functions of various neurotransmitters in the brain it may cause irritability or an unstable mood depending on the unique physiological state of an individual.
Ashwagandha Dosing
The amount of ashwagandha to supplement with is dependent upon the level of extraction and the part of the plant used. Ashwagandha roots are the most common way to supplement with ashwagandha, so the dosages here are for the roots, though dosing with the leaves is of a similar amount. As a topically applied poultice ashwagandha is mixed with a carrier (water, fat, or honey) and applied at an amount sufficient to cover the desired area.
Raw ashwagandha root is most commonly dosed at 300 to 600 mg daily. To keep blood concentrations of ashwagandha’s active constituents high, split the daily dosage in two and take half in the morning and half at night. When first supplementing with ashwagandha use the lower end of the dosing range for a few days to screen for undesirable effects and then increase the dosage from there if desired.
5 grams of raw ashwagandha root powder taking daily was found effective at boosting testosterone levels for men at varying degrees of infertility, and while the results of that study show that taking 5 grams of raw ashwagandha powder daily for a few months presented no health complications, a lower dose is likely suitable for men looking to boost their testosterone levels and/or semen counts who aren’t infertile. For testosterone boosting and for athletes looking to boost their energy output and endurance, 1 gram of ashwagandha root powder taken daily split into 500 mg morning and night doses is suitable to start with.
Ashwagandha Tea
A common way of using ashwagandha is by brewing it into a tea. Premade ashwagandha tea bags typically contain 1-2 grams of the powdered root. Steep with 170 F (75 C) water for 5-8 minutes, or if desiring a more potent tea (and you don’t mind possible bitterness) steep with boiling water for 5-15 minutes.
On its own Ashwagandha tea is a great choice to keep in the tea cabinet for the many uses and health benefits discussed throughout this article. Ashwagandha can also be added to other herbs to create a synergistic tea blend for specific purposes. For example a cognitive-enhancing herbal tea could consist of equal parts ashwagandha, chaga mushroom, and gingko leaf, 1-2 cups enjoyed daily.
Where to Buy Ashwagandha Supplements?
My favorites suppliers of ashwagandha are Mountain Rose Herbs and Nootropics Depot. There are many other high-quality suppliers of ashwagandha out there, but for the level of quality and price Mountain Rose herbs and Nootropics Depot are the best, and the differences between their ashwagandha products provides different usage options.
Mountain Rose Herbs Organic Ashwagandha
Mountain Rose Herbs sells ashwagandha as chopped root, root powder, root powder capsules, root extract, and even ashwagandha seeds. They also have ashwagandha as an ingredient in different herbal extracts like their immune herbal extract and adapt care herbal extract.
Ashwagandha Root
Raw chopped ashwagandha root is ideal for steeping into a tea or for creating your own herbal extracts. Besides planting ashwagandha seeds and harvesting the roots yourself, purchasing the raw chopped root is the lowest cost option available, though the finely milled ashwagandha root powder is only slightly more expensive. Dried ashwagandha root like this oxidizes very slowly and will keep for a long time.
Ashwagandha Root Powder
If desiring to supplement with a raw ashwagandha root powder then the offering from Mountain Rose Herbs is of great quality, organic, and very economical. Great for putting into capsules or for mixing with other herbal powders for custom herbal supplement powders or capsules.
Ashwagandha Root Powder Capsules
If convenience is the ultimate goal then capsules are the best way to supplement with ashwagandha. Pills are dosed accurately and can be taken anywhere easily without need for scooping or steeping. Ashwagandha supplement pills are ideal for those who travel often, and ashwagandha is a useful travel/stress supplement to begin with.
Ashwagandha Root Extract
Taken sublingually (under the tongue) herbal extracts are absorbed quickly into the bloodstream and bypass some of the digestive processes. For those seeking the fastest effect from ashwagandha (athletes, lovers), an extract is the way to go. The extraction process condenses the active constituents and therefore taking an extract is one way of more powerfully supplementing with an herb.
Ashwagandha Seeds
Plant and cultivate ashwagandha from seed if your climatic conditions are appropriate (see Cultivation of Ashwagandha above). Alternatively, ashwagandha seeds are potent at killing parasites, simply mix some seeds with honey, chew them, and then swallow the resultant mixture (it may be quite bitter). This is also commonly done with papaya seeds for parasite removal.
Nootropics Depot Ashwagandha Supplements
Nootropics Depot carries a few different ashwagandha supplements which suit nearly every preference one may have. I encourage you to browse their full catalogue of ashwagandha products, I’m more of a traditionalist so the two variations I present here are the well-known to be effective basics.
Ashwagandha Powder (standardized 12% withanolides)
Nootropics Depot sources their ashwagandha directly from India in order to ensure a more consistent product. They also do a complete chemical analysis of every batch they receive to ensure their ashwagandha powder is balanced between the different withanolide compounds, each of which has slightly varying effects. By ensuring the withanolide ratios are close to even and then ensuring the powder contains a minimum of 12% withanolides, the ashwagandha powder sold by nootropics depot is more potent in effect than most other raw ashwagandha root powders.
Also available as capsules.
Shoden Ashwagandha Powder (standardized 35% withanolides)
The Shoden Ashwagandha powder sold by Nootropics Depot is a full spectrum extract created from the leaves and roots of the plant. The powder is tested to ensure it’s a minimum of 35% withanolides, making it even more potent that the 12% or greater withanolide standardized offering above.
For those looking for the strongest withanolides-based ashwagandha supplement look no further.
Also available as capsules.
References:
Singh N, Bhalla M, De Jager P, Gilca M. An overview on ashwagandha: a rasayana (Rejuvenator) of ayurveda. Afr J Trad Compl Alt Med. 2011;8(5S).
Zahiruddin S, Basist P, Parveen A, et al. Ashwagandha in brain disorders: A review of recent developments. Journal of Ethnopharmacology. 2020;257:112876.
Modi M, Donga S, Dei L. Clinical evaluation of ashokarishta, ashwagandha churna and praval pishti in the management of menopausal syndrome. Ayu. 2012;33(4):511.
Nair A, Jacob S. A simple practice guide for dose conversion between animals and human. J Basic Clin Pharma. 2016;7(2):27.
Ahmad MK, Mahdi AA, Shukla KK, et al. Withania somnifera improves semen quality by regulating reproductive hormone levels and oxidative stress in seminal plasma of infertile males. Fertility and Sterility. 2010;94(3):989-996.
Disclosure: Wild Free Organic is a member of various affiliate programs and if a purchase is made through one of our affiliate links a small commission is received. This does not affect your purchase price. Visit our disclosure page for more information.
Other Herbs for Hormonal Health
Chaga Mushroom
Chaga is a medicinal mushroom that has a strong safety profile which has been used for thousands of years as a health preventative and to treat a variety of health problems that affect the digestive, immune, and cardiac systems. Chaga mushroom is unique among polypore mushrooms since 40% of its dry-weight are water soluble compounds, making it ideal for easily brewing as a tea or into coffee.
Article by Stefan Burns - Updated April 2022. Join the Wild Free Organic email newsletter!
Piece of chaga mushroom. CC4.0 Christine Young
| Name: | Chaga Mushroom, Linnaean - Inonotus obliquus |
| Color: | The mycellium mass which is harvested is black on the outside, yellowish orange to brown on the inside |
| Constituents: | Polysaccharides, glycoproteins, ergosterols, triterpenoids, mycoflavonoids, melanin, oxalate, other myconutrients |
| Effect: | Antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, anti-cancer, improves autonomic nervous system function, improves digestion, endocrine adaptogen, exhibits DNA protection properties |
| Preparation: | The chaga mass is ground into a powder. Often extracted and standardized to increase beta-glucan content by weight |
| Dosing: | 250-1000mg extracted powder, 1-3g raw powder |
| General Notes: | Chaga is harvested off birth and some other trees. What is harvested is not the fruiting body but instead a mass of sterile mycelium. Can be used as a coffee substitute, thicker cut whole powder works well mixed into coffee grounds before coffee extraction. Often used daily as a general longevity and immune booster with beneficial effects on the cardiovascular system. Its high concentration of melanin make it a potent antioxidant. Has a special place of honor in traditional Chinese medicine. |
What is Chaga Mushroom?
Chaga is a type of mushroom which grows mainly on birch and much less frequently alder, witchen, and bird cherry. In the process of colonizing a tree, it forms a sterile mostly black mass made of mycelium on the outside of the tree which resembles charcoal because it contains a large amount of melanin. This mass is known as a sclerotium. The harvested sclerotium is the chaga mushroom that is used medicinally and supplemented with. Chaga mushroom contains high levels of beta-glucans and triterpenoids which have powerful health effects. In Eastern Europe medicinal preparations have been made using chaga mushroom for thousands of years. Hunters in those regions would often brew a strong tea from ground chaga which helped them sustain high energy output while traversing the wilderness. The chemical composition of chaga differs significantly from other polypore mushrooms such as reishi mushroom which makes it unique. Chaga is nontoxic, well tolerated, and has virtually no counterindications for medicinal usage.
Chaga Mushroom Identification
Chaga mushroom identification is not always easy, there are various tree rots, growths, and diseases that can look like chaga mushroom. Identification for chaga starts by positively identifying the tree species a potential conk is growing on, and then by examining the conk for chaga-specific identifying characteristics. Some tree burls can look like a chaga conk in shape and size, but aren’t blacked like chaga is, or if they aren’t they don’t possess the rich interior amber, orange, and brown colors. Chaga that is harvestable doesn’t provide a spore print because it is mycelium and not the fruiting body of chaga fungus. Chaga mushroom has no gills and is best harvested in the late summer, fall, and early winter.
Chaga from dead or fallen trees is known as “dead chaga” and will appear black inside and outside and should never be harvested as will likely contain mycotoxins. Chaga collected in ecologically unsafe areas polluted from human activity are unsafe for consumption and can contain significant levels of heavy metals such as lead, arsenic, and strontium.
Chaga Mushroom Benefits
Chaga mushroom has a wide range of positive health effects because of its unique combination of micronutrients, minerals, and myconutrients. Chaga mushroom contains high concentrations of potassium (9-10%), magnesium (0.65%), calcium (0.4%), and phosphorus (0.25%), with more minor minerals being iron, copper, zinc, and chromium. Fifteen amino acids have been identified in chaga mushroom, with glycine, aspartic acid, and glutamic acids making up about 40% of total amino acids. Chaga contains flavonoids (notably anthocyanins and quercetin), triterpenes, beta-glucans, and a high amount of antioxidant melanin pigments which protect against carcinogenic and mutagenic factors as they are involved in DNA repair and cell metabolism.
Together these chemical constituents and many others broadly influence the function of digestive, immune, cardiovascular, metabolic, and regenerative systems providing the following benefits:
Chaga Mushroom Improves Digestion
Chaga is helpful in treating gastric disorders such as stomach ulcers and intestinal pain
Chaga possesses strong antimicrobial activity and is useful in improving the microbiome
Chaga Mushroom Improves the Immune System
Increases T-Helper lymphocyte concentrations
Normalizes cytotoxic activity of natural killer cells
Blocks the receptors of tumor cells suppressing their migration
Chaga Mushroom Optimizes the Cardiac, Nervous, and Metabolic Systems
Chaga calms erratic heart rhythm variability while increasing contractile power of the heart
Modulates cell metabolism at the central and peripheral nervous system level
Increases the excitable properties of cell membranes
Chaga Mushroom helps with Healing and Repair
Many chaga constituents especially melanin are powerful antioxidants which possess anti-inflammatory and radioprotective effects.
Chaga is helpful for skin conditions such as periodontitis, eczema, dermatitis, and psoriasis
Chaga lowers risk of cancer
Chaga has a pain-relieving action
Improves wound healing and DNA repair
Note: Much of the research into chaga showing these benefits has been done using animal models and therefore hasn’t been confirmed for humans.
Chaga Mushroom Side Effects
As stated earlier, chaga is nontoxic, well tolerated, and has virtually no counterindications for medicinal usage. With that said it has been shown that the effects of chaga are dose-dependent, with small doses often being most effective while larger doses may lead to an opposite action. This U-shape relationship for chaga is most commonly observed for the functions of the cardiac and nervous systems.
Though chaga has been shown to be helpful in improving the function of the heart, sympathetic, and parasympathetic nervous systems, if these systems are dysfunctional then chaga supplementation should be done carefully with only very small dosages to start off in order to determine medicinal usage is positive or negative or negative in effect. It is highly unlikely for the usage of chaga to be deleterious but it is best to proceed with the supplementation of any new herbal with an abundance of caution and start on the low end of the recommended dosing range.
Chaga Mushroom Dosing
Chaga mushroom is dosed differently based on the intended purpose and the degree or refinement. A preventative health dosing regime of chaga mushroom will be less than the recommended dosage for someone fighting cancer who wants to improve their chances of entering into remission.
Raw chaga that hasn’t been made more potent through extraction processes can be dosed in the 0.5-3 gram range. The higher end of that range is best served when extracting chaga myconutrients using water such as when brewing chaga into a tea or with coffee.
Chaga that has been extracted and standardized is more potent and therefore is dosed lower accordingly. It is not possible for provide a dosing range for extracted chaga supplements because it depends on the level of extraction, but for example if it’s a 4:1 extraction (4x more potent), then dose the 4:1 extract at 1/4th the recommended raw dosage.
Making Chaga Tea or Chaga Coffee
Up to 40% of chaga mushroom by dry-weight are water-extractable substances which makes it a good medicinal mushroom for brewing into tea or into coffee.
To brew a chaga tea steep 2-3 grams of ground chaga mushroom in 170 F (75 C) hot water for 8-15 minutes. Best down with a removable tea ball or some other steeping implement.
To brew a chaga infused coffee, mix 2-3 grams of chaga powder into the coffee grounds and brew as normal, whether this is done via drip, French press, or other.
Where to Buy Chaga Mushroom Supplements?
My favorites suppliers of chaga medicinal mushroom are Mountain Rose Herbs and Nootropics Depot. There are many other high-quality suppliers of chaga mushroom out there, but for the level of quality and price Mountain Rose herbs and Nootropics Depot are the best, and the differences between their chaga products provides different options for use.
Mountain Rose Herbs Organic Chaga
Mountain Rose Herbs is a supplier of organic herbs, spices, oils, and other health care products. Mountain Rose Herbs is organic and sourced from hardwood forest in the northern hemisphere. They sell chaga mushroom in course and fine powders as well as in an extract.
Chaga Mushroom Powder
The Mountain Rose Herbs chaga powder is milled from the entire sclerotia. As a whole milled powder it contains the full spectrum of beneficial health compounds found in chaga such as beta-glucans and triterpenes.
Compared to the Nootropics Depot chaga it’s quite a bit more coarse and it floats, so adding it directly to a drink makes for a chunky experience which may or may not bother you. It’s coarse nature makes it great for directly brewing into a drink akin to coffee, or for mixing into coffee grounds to make a chaga coffee. Chaga is an ingredient in my “best nootropic coffee”.
Standard dose is 0.5 - 3 grams once daily.
Chaga Mushroom Extract
Mountain Rose Herb’s chaga mushroom extract is dual water and alcohol extracted and the final product has an alcohol percentage of 20-30%. It comes in 1, 2, 4, 8, 16, and 32 oz sizes.
Chaga tincture is great for direct supplementation under the tongue or with a dropper full into a favorite drink like juice, coffee, smoothie, or something stiffer.
Nootropics Depot Chaga Supplements
Nootropics Depot is a supplier of common and uncommon herbal supplements and other compounds like nootropics. They have a high standard of quality that they adhere to and maintain very transparent business practices which many supplement companies fail to do (or choose not to).
Chaga 1:1 Mushroom Extract Powder
The chaga mushroom powder sold by Nootropics Depot is very finely milled which makes it excellent for stirring directly into a drink like coffee without creating any unpleasant clumps or graininess.
Standard dose is 500 mg once daily.
Beta-Glugan (β-Glucan) minimum content: 8%
Contains Triterpenoids
References:
Shashkina MYa, Shashkin PN, Sergeev AV. Chemical and medicobiological properties of chaga (Review). Pharm Chem J. 2006;40(10):560-568.
Disclosure: Wild Free Organic is a member of various affiliate programs and if a purchase is made through one of our affiliate links a small commission is received. This does not affect your purchase price. Visit our disclosure page for more information.
More Medicinal Mushrooms
Reishi Mushroom
Reishi is a well known medicinal mushroom because of its wide-ranging heath benefits. Reishi improves the functioning of the immune system, fights cancer, improves metabolism, and is a potent antioxidant and anti-inflammatory. Reishi has many medicinal uses and is a great medicinal mushroom for beginners to supplement with.
Article by Stefan Burns - Updated April 2022. Join the Wild Free Organic email newsletter!
| Name: | Reishi, Lingzhi, Linnaean - Ganoderma lucidum, G. tsugae, G. sessile, G. lingzhi |
| Color: | White to dark reddish brown |
| Constituents: | Triterpenes, glycoproteins, germanium, myconutrients, polysaccharides, superoxide dismutase |
| Effect: | Improves metabolic health, immune system adaptogen, increases natural killer cell activity, promotes parasympathetic (rest and digest) activity |
| Preparation: | The mushroom cap is dried and either taken supplementally as a powder or sliced/shredded and brewed into a tea. For a powerful extraction simmer large amounts of reishi mushroom in water for 2-3 hours. |
| Dosing: | As a supplement take 0-5 grams daily. For brewing into tea 3-10 grams per cup/pot. |
| General Notes: | There are different species of Ganoderma that all look very similar and are used interchangably medicinally. Reishi is an adaptogen that is best known for boosting the immune system. Often used in mushroom or supplement blends for rest and sleep. |
What is Reishi Mushroom?
Reishi or Lingzhi is the common name for a subgroup of polypore mushrooms that belong to the Ganoderma genus, the main members of this group being Ganoderma lucidum, Ganoderma lingzhi, Ganoderma sessile, and Ganoderma tsugae.
The Ganoderma species that are classified as Reishi are medicinal mushrooms considered by many as a panacea for all types of diseases and have been used in herbal medicine practices for thousands of years.
Reishi Mushroom Identification
The different reishi species are found growing in deciduous forests worldwide. Reishi in the wild is quite rare but it’s hard to misidentify because of it’s unique appearance and key identification features. Reishi has a cork-like texture and its underside is covered with small pores instead of gills, from which it releases its spores. The underside is white if unbruised and will turn yellow to brown if bruised. Reishi typically has a banded appearance which goes from white on the edge to orange and then reddish-brown traveling towards the stem. Older reishi caps will turn a dark mahogany color but still have some striping preserved. For a complete guide on identification, health benefits, and how to brew reishi into a tea watch the video I made below:
Reishi Mushroom Benefits
In Traditional Chinese Medicine reishi (also known as Ling Zhi) is known as the Mushroom of Immortality, and for good reason. Reishi is a powerful adaptogenic mushroom that has many beneficial health effects on the body due to its unique chemical constituents. The most active of these components are:
Polysaccharides (includes beta-glucans) | Functions: Improves energy metabolism and cell to cell signaling, neuroprotective, boosts immunity
Triterpenes | Functions: Anti-tumor & anti-cancer, radiation protection, anti-viral, important components of cell membranes and of steroid signaling molecules
Germanium | Functions: Anti-tumor & anti-cancer, radiation protection, boosts immunity, improves oxygen transport
Together these chemical constituents and others like superoxide dismutase plus an abundant assortment of micronutrients broadly influence the function of the immune, cardiovascular, metabolic, digestive, and cognitive systems providing the following benefits:
Reishi Microbiome Improvements
Inhibits the growth of gram positive and gram negative bacteria
Increases the effectiveness of antibiotics
Demonstrates anti-microbial activity even against multidrug resistant bacteria
Inhibits the growth of fungal infections
Reishi Metabolic Improvements
Lowers blood glucose levels and increases insulin levels for diabetics
Normalizes bodyweight and appetite
Lowers blood cholesterol levels and triglycerides while simultaneously boosting HDL cholesterol
Increases oxygen uptake and transport
Reishi Fights Cancer and Boosts the Immune System
Polysaccharides potentiate immune function increasing anti-tumor activity
Triterpenes are potent anti-viral agents and cytotoxic to cancer cells
Decreases the growth of new blood vessels to cancer cells
Useful in the treatment of androgen-induced diseases such as benign prostatic hyperplasia and prostate cancer
Increases the proliferation and functional activity of macrophages, T lymphocytes, B lymphocytes, and natural killer cells
Strongly inhibits the multiplication of HIV-1
Demonstrates antiherpetic activity
Reishi Anti-inflammatory and Antioxidant Effect
Has superoxide radical and hydroxyl radical scavenging abilities
Decreases the oxidation of LDL cholesterol and other lipids
Increases glutathione peroxidase levels
Exhibits both systemic and topical anti-inflammatory effects
Ganoderic acid C was found to be responsible for most of the anti-inflammatory activity
Reishi Protects the Liver
Provides protection against liver injury
Reverses the symptoms of liver injury
Potentially able to reverse liver fibrosis
Reishi Improves Cognition
Promotes neurogenesis
Has anti-depressive effects
Protect neurons from hypoxia/reoxygenation injury
Protects dopaminergic neurons and ameliorates behavioral deficits in Parkinson’s disease
Note: Much of the research into reishi showing these benefits has been done using animal models and therefore hasn’t been directly confirmed for humans.
How Long does it take for Reishi to Work?
The effectiveness of supplementing with reishi will depend on the quality of the supplement/extract, the amount taken, and the length of time for which it is taken consistently. Using reishi, either as a supplement or extracted into a tea will be useful immediately in the context of a viral infection or inflammatory condition, but for best effect reishi should be taken daily so the benefits may accrue with time. It may take a few weeks of using reishi for the more serious anti-cancer, neuroprotective, and anti-diabetic effects to become noticeable, and even then the effect may be subtle.
A single influx of myconutrients is useful in the context of improving health but it’s really the consistent loading of the many heath-promoting compounds found in reishi and other herbals that culminates in therapeutically relevant health improvements.
For best effect and observation of health improvements I recommend using reishi for at least 30-60+ days. If used at high dosages it should be cycled off occasionally for the length of time it was used for.
Reishi Mushroom Side Effects
Medicinal mushrooms like reishi have a record of safe usage proven over thousands of years, and side effects are rare from short-term or long-term usage. Reishi is an immune-potentiator so those with autoimmune issues should exercise caution in using reishi though it should improve symptoms of autoimmunity by normalizing the functioning of the immune system.
One potential issue to be aware of when supplementing with reishi or really any herbal supplement for the matter of contamination, especially from heavy metals. Reishi is widely cultivated on a variety of growing mediums like logs, woodchips, and sawdust, and while some growers follow strict sourcing protocols and test for pesticides, heavy metals, and molds, other growers may be less discriminate and follow zero quality control protocols. Make sure to source reishi from a reputable producer who follows the required health guidelines, or if foraging only pick reishi from lands that haven’t been exposed to chemical waste in the past or present.
One side effect anecdote of mine I can provide is that when I drank 3 cups of a potent reishi tea all in one sitting on an empty stomach while fasting I experienced some slight visual distortions. These visuals were characterized by fractal patterns of light on the periphery of my vision. Though slightly alarming at first it went away within 15 minutes and didn’t appear to cause any problems. I have read a couple other anecdotal reports of the same phenomenon from people who consumed a very high dose of reishi. I do not recommend trying this or consuming reishi at such high dosages.
Reishi Mushroom Tea
There are a few ways to make a reishi mushroom tea. The traditional method is to cut the reishi fruiting body into strips or pieces which are then boiled for 2-3 hours which produces a very potent reishi tea. Once prepared the tea can be stored in a fridge and used over the course of a couple weeks.
A simpler method is to take some whole reishi and shred it using a blade grinder and add some of the shredded reishi “fluff” to a tea ball/strainer. Steep for 5-15 minutes with hot water along with any other herbal ingredients desired. This will extract a lot of the beneficial compounds from the reishi but overall produce a milder reishi tea than the traditional method. Some of the beneficial compounds like triterpenes won’t be extracted in great quantities if reishi is brewed into a tea because they are not water soluble, instead being alcohol soluble.
One more option for creating a reishi tea is to mix reishi powder with a liquid. This method might produce a slightly grainy liquid but will ensure all the beneficial compounds found in reishi are consumed. Reishi coffee or hot chocolate can be prepared using a reishi supplement powder.
The simple reishi tea is best for supplementing with reishi daily as a preventative health measure. The traditional method of preparation is preferable when dealing with serious health concerns that require a more powerful effect.
Reishi Dosing
Reishi can be used in many ways, from powders to teas to tinctures, and each method of supplementation has its own dosing recommendation.
For a raw reishi powder the recommended dosing range is 0.5 - 2 grams. More can be taken than that but it should be done carefully and only after using a lower dosage for an extended period of time confirms no side effects are being experienced. An extracted reishi powder should be supplemented at a lower amount than a raw powder, a recommended range being 250 - 1000 mg.
To brew a simple reishi tea, 2-3 grams of shredded reishi is sufficient, and if a powerful reishi tea is prepared in the traditional method of boiling reishi strips for many hours, then the recommended dosing range would be 4-8 oz of tea.
Where to Buy Reishi Supplements?
Reishi supplements are sold by many companies and I have used many different reishi products sold by a variety of sellers. The reishi blends sold by Four Sigmatic are good, are dosed appropriately, and come in interesting variations like mushroom coffee, mushroom hot chocolate, or in medicinal mushroom blends. They’re definitely worth checking out for use on the go.
Overall I prefer reishi products and supplements that I can more easily dose myself and are more economical, such as those sold by Mountain Rose Herbs and Nootropics Depot.
Mountain Rose Herbs Organic Reishi
Mountain Rose Herbs sells organic reishi mushroom as a whole cap, slices, powder, or extract.
Reishi Whole Cap
I bought a pound of whole reishi caps from Mountain Rose Herbs before and was surprised when I received four huge caps. They’re quite lightweight and though tough can be cut apart with scissors. The reishi sold from Mountain Rose Herbs is USDA organic certified and is the best band for your buck in how much you get. Brewing reishi tea 3-4x a week 1 lb of caps will last many months, possibly even up to a year.
Finely Milled Reishi Powder
The reishi powder is more expensive than the whole caps or slices on a per pound basis but very economical compared to the reishi supplement powders sold by Nootropics Depot (more information below). The grind of the powder is medium fine and if mixed into a liquid will settle to the bottom with some chunks being larger. The larger grain size of the powder is not an issue if brewed like a coffee might, or even in conjunction with coffee. For an ultra-fine reishi supplement powder that mixes effortlessly into a drink I recommend the reishi powders from Nootropics Depot.
Reishi Tincture
The reishi tincture sold by Mountain Rose Herbs is double extracted to bring forth both the water and alcohol soluble constituents into the extract. Using a tincture is an excellent way to supplement with reishi directly, either under the tongue or into a drink without having to worry about the mixing and settling of powders.
Nootropics Depot Reishi Supplements
Nootropics Depot sells two reishi supplement powders. One is a raw powder and the other is a 8:1 extract powder.
Reishi 1:1 Hot Water Extracted Powder
The Nootropics Depot 1:1 reishi mushroom powder is the whole mushroom turned into a powder where during the process the chitin (protective outer layer of the cell) is broken down using hot water to make the beneficial components of the mushrooms more bioavailable. None of the initial mushroom material is lost so the beta-glucan content is very high. The 1:1 reishi extract powder is full spectrum and contains every beneficial compound within the Ganoderma lucidum mushroom.
Beta-Glugan (β-Glucan) minimum content: 35%
Reishi 8:1 Water and Alcohol Extracted Powder
The Nootropics Depot 8:1 reishi mushroom powder is a combination of the 1:1 hot water extracted reishi powder and a 16:1 alcohol extracted reishi powder. Mixed in equal quantities they combine into a 8:1 dual water and alcohol extracted reishi mushroom powder.
Beta-glucans are not ethanol soluble but triterpenes are. Combining the 1:1 powder which is high in beta-glucans with the 16:1 powder which is high in triterpenes creates a “best of both worlds” extracted reishi supplement powder more likely to have more potent immune system and cognitive boosting effects than the 1:1 whole powder.
Beta-Glucan (β-Glucan) minimum content: 20%
Note: Laboratory methods for testing beta-glucan can be inaccurate and unreliable, and the numbers provided by any supplier of medicinal mushrooms should be taken with a grain of salt.
If purchasing reishi from a Chinese pharmacy you may have to ask for Ling Zhi which is often how they refer to reishi.
Medical Disclaimer: All information, content, and material of this website is for informational purposes only and is not intended to serve as a substitute for the consultation, diagnosis, and/or medical treatment of a qualified physician or healthcare provider.
References:
Batra P, Sharma AK, Khajuria R. Probing lingzhi or reishi medicinal mushroom ganoderma lucidum (Higher basidiomycetes): a bitter mushroom with amazing health benefits. Int J Med Mushr. 2013;15(2):127-143.
Huang S, Mao J, Ding K, et al. Polysaccharides from ganoderma lucidum promote cognitive function and neural progenitor proliferation in mouse model of alzheimer’s disease. Stem Cell Reports. 2017;8(1):84-94.
Disclosure: Wild Free Organic is a member of various affiliate programs and if a purchase is made through one of our affiliate links a small commission is received. This does not affect your purchase price. Visit our disclosure page for more information.
More Medicinal Mushrooms
Cordyceps Mushroom
Cordyceps is a parasitic fungi of which there are 500+ species. Cordyceps has been shown to have strong anti-cancer effects, enhances immune function, and improves metabolism and exercise performance. In Traditional Chinese Medicine cordyceps was used as a tonic given to the weak to help them recover. Learn more!
Article by Stefan Burns - Updated April 2022. Join the Wild Free Organic email newsletter!
Cordyceps militaris. CC3.0 Andreas Kunze
| Name: | Cordyceps, Dong Chong Xia Cao, Linnaean - Cordyceps militaris, C. sinensis, 500+ other species |
| Color: | Yellow-orange stalk or powder |
| Constituents: | Cordycepin, polysaccharides (beta glucans, arabinoxylane, glucose, xylose, galactose and mannose), glycoproteins, ergosterols, triterpenoids, other myconutrients |
| Effect: | Anti-cancer, enhances ATP production, improves oxygen uptake, enhances immune function |
| Preparation: | The mushroom is ground into a powder and taken directly. |
| Dosing: | 0-3 grams daily |
| General Notes: | Cordyceps is used primarily to improve athletic performance as it boosts metabolism and augents natural energetic pathways. Cordyceps also supports the immune system and cognitive function. |
What is Cordyceps Mushroom?
Cordyceps is a parasitic fungus that grows on insects (famously caterpillars and ants), insect larvae, and even other fungi. There are 500+ species that have been identified in the Cordyceps genus. When a cordyceps fungus attacks a host, the mycelium invades its tissues and alters the behaviors of the host. Eventually the cordyceps mycelium replaces the tissue of its host and then produces an elongated fruiting body which then sporulates in order to reproduce and infect new hosts. Luckily for humans Cordyceps is unable to infect humans in this way so you can rest easy knowing that using cordyceps won’t turn you into a zombie like depicted in the video game “The Last of Us”.
Cordyceps species are found throughout Asia, being particularly abundant in humid temperate and tropical forests. Cordyceps has been used in Traditional Chinese Medicine (known as Dong Chong Xia Cao) for thousands of years and is considered one of the best tonics for returning strength and vitality to weak individuals.
Types of Cordyceps
The two main species of cordyceps that are cultured for herbal use are Cordyceps militaris and Cordyceps sinensis. The mycelium of both C. militaris and C. sinensis are able to be grown on a plant-based medium such as oats or rice. There are some differences in the chemical constituents between the many different cordyceps species, but overall these differences are minor and doesn’t affect the use of cordyceps as a herbal supplement.
Benefits of Cordyceps
Cordyceps has many effects throughout the body because of its unique combination of chemical constituents. The most active of these components are:
Cordycepin | Functions: Anti-cancer, anti-microbial, insecticidal, cognitive enhancer, metabolism booster
Polysaccharides | Functions: Neuroprotective, antioxidant, reduces fatigue, increases energy metabolism
Other Myconutrients | Functions: Anti-malarial, anti-fungal, immunomodulatory, anti-cancer, anti-oxidant, anti-inflammatory
Together these chemical constituents and many others broadly influence the function of immune, cardiovascular, renal, metabolic, and cognitive systems providing the following benefits:
Cordyceps Metabolic Improvements
Alleviates fatigue and improves physical endurance
Stimulates mitochondrial electron transport and ATP production
Lowers fasting blood glucose and insulin levels
Lowers blood urea levels
Improves oral glucose tolerance
Increases whole-body insulin sensitivity
Enhances skeletal muscle glucose utilization
Increase DNA synthesis
Lowers total cholesterol, especially LDL and VLDL cholesterol while raising HDL.
Cordyceps Immune-Boosting Effect
Suppresses the growth of tumors
Inhibits metastasis (spread) of cancer
Enhances antibody response
Increases the number of T helped cells
Enhances natural killer cell activity
Potent intestinal immune-system-modulating activity
Balances Th1/Th2 cytokines
Promotes apoptosis
Cordyceps Antioxidant Protection
Down-regulates inflammation related genes in the kidneys
Improves lung function by reducing airway inflammation
Possibly useful treatment for endotoxin shock or sepsis
Inhibits lipid peroxidation and increases the activity of antioxidant enzymes
Enhances repair of damaged DNA
Free radical scavenging capability
Suppresses the oxidation of low-density lipoprotein (LDL cholesterol)
Note: Much of the research into cordyceps showing these benefits has been done using mice and rats and therefore hasn’t been confirmed for humans.
I share my personal experience in supplementing with Cordyceps militaris in this conversation on cordyceps with my friend Rob Nelson. A lot of good information in this podcast, I suggest tuning in and listening to the full conversation when possible. You can find more useful information regarding cordyceps on Untamed Science.
How Long does it take for Cordyceps to Work?
Cordyceps is a herbal supplement that works best when taken daily and for a consistent length of time, typically 2 weeks or greater. It is possible to feel an immediate boost in endurance and exercise performance from a large acute dose of cordyceps, but typically the beneficial effects of cordyceps on exercise performance are felt after a few weeks.
The immunopotentiating effects of Cordyceps are useful over short and long time durations. If dealing with a viral or bacterial infection, supplementing with cordyceps should begin helping immediately to some degree and increase in efficacy the longer its used.
Supplementing with cordyceps for 30+ days ensures that its beneficial effects culminate to a point of being relevant and noticeable. Cordyceps has a long history of being used in Traditional Chinese Medicine for extended periods of time as a tonic, but as with all herbals I recommend cycling off of cordyceps at a 1:1 ratio. For example if cordyceps is supplemented for 3 months, it shouldn’t be used for 3 months afterwards in order to allow the natural systems of the body to return to balance.
Cordyceps Side Effects
The most likely side effects to be encountered when using cordyceps is digestive discomfort, which can possibly happen if too large a dose is taken. Cordyceps is generally considered safe with a very good long term safety profile thanks to its use for thousands of years in Traditional Chinese Medicine.
Cordyceps is very effective at stimulating the immune system, increasing the production of many different types of immune cells and boosting their activity. It’s for this reason that cordyceps has such strong anti-cancer activity, and it also increases apoptosis (preprogrammed cell death). If the systems of the body are healthy, then further stimulating the immune system beyond normal may not be helpful unless done carefully for prophylactic reasons.
Cordyceps Dosing
Whole cordyceps powder that hasn’t been further extracted or standardized is typically dosed at 500 mg - 3 grams daily.
Extracted cordyceps powder is more potent and is dosed at smaller amounts of 100 - 500 mg.
When first using cordyceps, start with the lowest dose and only after some time has passed should the dose be increased if desired.
Where to Buy Cordyceps Supplements?
Because cordyceps mycelium is able to be cultivated on a variety of plant mediums like oats or rice, there are many different providers of cordyceps powders and supplements.
I have used cordyceps from Four Sigmatic in the past and now use cordyceps from either Mountain Rose Herbs or Nootropics Depot.
Mountain Rose Herbs Cordyceps Supplement
The cordyceps from Mountain Rose Herbs is milled from Cordyceps militaris mycelial biomass grown on organic oats. The cordyceps from Mountain Rose Herbs is very competitively priced and is 100% organic.
Nootropics Depot Cordyceps Supplements
Nootropics Depot offers whole 1:1 cordyceps powder or a dual water/alcohol 10:1 cordyceps extract. The cordyceps sold by Nootropics Depot is reasonably priced and tested often to confirm purity and potency.
1:1 Cordyceps Mushroom Powder
The Nootropics Depot 1:1 Cordyceps Mushroom powder is similar to the cordyceps powder offered by Mountain Rose Herbs, and which one to choose is really up to personal preference. If planning on taking cordyceps 4-7 times a week I recommend using a whole powder versus a more concentrated extract like Nootropics Depot 10:1 cordyceps supplement. There is a lot of value in consuming an herbal supplement in its raw form without having undergone any extraction, as nothing is left out and removed from the product, and because the amount of active ingredients is lower side effects are less likely to be encountered.
10:1 Cordyceps Mushroom Extract Powder
The 10:1 extract means that 10 units of Cordyceps militaris was used to create 1 unit of 10:1 Cordyceps militaris extract. The Nootropics Depot 10:1 Cordyceps Beta-Glucan (β-Glucan) minimum content is 20% while the Cordycepin content is 0.3% as measured by high-performance liquid chromatography. The 10:1 cordyceps extract can be used as the same frequency as the 1:1 powder if desired, and it’s more effective when used for one offs or shorter frequency dosing protocols because it’s more highly concentrated. If really experimenting with cordyceps then I recommend purchasing both the 1:1 and 10:1 products in order to feel the differences between them yourself.
If purchasing cordyceps from a Chinese pharmacy ask for Dong Chong Xia Cao, which is how they refer to cordyceps.
Medical Disclaimer: All information, content, and material of this website is for informational purposes only and is not intended to serve as a substitute for the consultation, diagnosis, and/or medical treatment of a qualified physician or healthcare provider.
References:
Ng TB, Wang HX. Pharmacological actions of Cordyceps , a prized folk medicine. Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmacology. 2010;57(12):1509-1519.
Das SK, Masuda M, Sakurai A, Sakakibara M. Medicinal uses of the mushroom Cordyceps militaris: Current state and prospects. Fitoterapia. 2010;81(8):961-968.
Hirsch KR, Smith-Ryan AE, Roelofs EJ, Trexler ET, Mock MG. cordyceps militaris improves tolerance to high-intensity exercise after acute and chronic supplementation. Journal of Dietary Supplements. 2017;14(1):42-53.
Disclosure: Wild Free Organic is a member of various affiliate programs and if a purchase is made through one of our affiliate links a small commission is received. This does not affect your purchase price. Visit our disclosure page for more information.
More Metabolism Boosting Herbs
Cistanche
Cistanche is a perennial parasitic herb that grows in the arid deserts of Eurasia. Cistanche has been used for 2000 years in Traditional Chinese Medicine and is considered a superior tonic, being called the "Ginseng of the Desert". Cistanche has been shown to enhance cognition, act as an aphrodisiac and boost testosterone, improve immunity, and have anti-cancer effects. Learn more!
Article by Stefan Burns - Updated April 2022. Join the Wild Free Organic email newsletter!
| Name: | Cistanche, Rou Cong-Rong, Linnaean - C. tubulsa, C. deserticola, C. phelypaea |
| Color: | Stem: yellow, brown, tan, purple. Flowers: yellow, purple, pink |
| Constituents: | Volatile oils, non-volatile phenylethanoid glycosides (most notably echinacoside and acteoside), iridoids, lignans, alditols, oligosaccharides, polysaccharides. |
| Effect: | Anti-fatigue, endocrine adaptogen, boosts testosterone, aphrodisiac, neuroprotective, improves circulatory system, reduces cholesterol, anti-microbial, anti-inflammatory, improves immunity, anti-cancer |
| Preparation: | The stem is ground into a powder. Often extracted and standardized to increase echinacoside and acetoside content by weight |
| Dosing: | 100-400mg extracted powder, 3-5g raw powder. For boosting testosterone use daily and then cycle off after 1-3 months. |
| General Notes: | Cistanche is an excellent herbal for men looking to optimize their hormones and boost their testosterone levels. Cistanche improves cholesterol metabolism and transport, lowering blood cholesterol to increase hormone production. Still being researched for it's effects on neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer's and parkinson's disease. Has a good safety profile but since it has a potent effect on the endocrine system care should taken with supplementing cistanche. Improves exercise endurance. Strong morning wood is a common side-effect for men. Sometimes called the "ginseng of the desert". |
What is Cistanche?
Cistanche is a genus of perennial herbs consisting of 22 known species that grow in warm arid deserts throughout northwest China, Mongolia, Iran, and India. Cistanche is a parasitic herb that lacks chlorophyll, instead attaching to the roots of sand-fixing plants to draw water and nutrients from them. Cistanche only grows well under extreme environmental conditions characterized by an extremely arid climate, depauperate soils, intensive sunshine, large temperature differences, and annual precipitation <250mm. These rare growing conditions and it’s popularity of use in Traditional Chinese Medicine (known as Rou Cong-Rong) has led to Cistanche being an endangered wild species.
Cistanche is one of the most popular tonics in Traditional Chinese Medicine, being known as the “Ginseng of the Deserts” because of its wide-ranging beneficial health effects, and it’s increasingly becoming a popular herbal worldwide, especially in the treatment of renal problems, to boost testosterone levels, and to help treat neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s disease.
Types of Cistanche
Cistanche deserticola and Cistanche tubulosa are the two main species of cistanche that are harvested and prepared into herbal supplements and extracts. They differ slightly in the composition of their chemical constituents but overall are similar enough to be used interchangeably. Cistanche tubulosa is more commonly found as a supplement than Cistanche deserticola.
Benefits of Cistanche
Herba cistanche has many effects throughout the body because of its unique combination of chemical constituents. The most active of these components are:
Phenylethanoid Glycosides | Functions: Antioxidant, neuroprotective, enhances sexual function, enhances immunity, hepatoprotection (prevents liver damage)
Echinacoside | Functions: Neuroprotective, antioxidant
Acteoside | Functions: Endothelium-dependent relaxation, neuroprotective, anti-allergy
Tubuloside B | Functions: Neuroprotective
Together these chemical constituents and many others broadly influence the function of immune, cardiovascular, renal, endocrine, and digestive systems providing the following benefits:
Cistanche Improves Brain Function
Prevents brain neuron apoptosis (programmed cell death)
Blocks amyloid plaque deposition
Promotes the production of neurons by accelerating growth of neurites
Increases dopamine, noadrenaline, and serotonin neurotransmitter concentrations in the brain
Cistanche Metabolism Improvements
Enhances mitochondrial respiration
Enhances glutathione antioxidant status
Remedies Hypothalamic-Pituitary-Adrenal (HPA) axis dysfunction and chronic fatigue syndrome
Increases autonomic activity
Improves exercise endurance
Decreases post-exercise blood lactic acid and blood urea nitrogen levels
Increases longevity
Prevents bone loss by regulating bone metabolism genes
Cistanche’s Aphrodisiac Effect
Increases sex hormone concentrations by inducing testicular steroidogenic enzymes
Changes gene expression of genes responsible for testosterone synthesis
Increases number of germ cells
Reduces latency period in-between erections
Improves testes function
Vaso-relaxing properties
Cistanche’s Immune-boosting effect
Increases lymphoid cells
Increases the kill rate of cancer cells
Activates phagocytic function of macrophages
High levels of polysaccharides enhance immunity
Stimulates the proliferation of antibody-producing cells
Decreases level of peripheral memory T cells and enhances levels of naive T cells
Cistanche Antioxidant Protection
Acetoside as an antioxidant is 15x stronger than resveratrol and 5x stronger than Vitamin C
Prevents DNA damage
Enhances superoxide dismutase activity
Prevents lipid peroxidation
Inhibits hepatic apoptosis
Note: Much of the research into cistanche showing these benefits has been done using mice and rats and therefore hasn’t been confirmed for humans.
Depending on someone’s current state of health, cistanche can be useful for men or women, though in general cistanche is more useful to men because of its testosterone boosting properties. Here are the biggest benefits for each sex:
Cistanche Male Benefits
Cistanche increases testosterone production. I have firsthand experience with this, I once supplemented with cistanche for one month and measured my testosterone levels before and after. My multi-variable experiment raised my free testosterone levels by 53%, of which I mostly attribute to the cistanche supplementation! Click the button below to read the full protocol I used and my results.
Further benefits of cistanche for men is that it improves the functions of the testes, increasing sperm count and production of male hormones. Male hormone levels and sperm counts have been on a precipitous decline for decades now and cistanche is a natural supplement that can help reverse this trend.
In the bedroom, cistanche increases the size, strength, and duration of erections and also reduces the latency period in-between erections.
Cistanche Female Benefits
Cistanche reduces chronic fatigue syndrome, otherwise known as adrenal fatigue. Chronic fatigue syndrome is caused most often by a dysregulation of the HPA axis, brought on by excess stress, poor sleep, a bad diet, and other lesser factors. Chronic fatigue syndrome can effect men and women, but typically women are more likely to develop chronic fatigue syndrome for a variety of reasons.
By improving energy metabolism, endurance, and immunity, cistanche is a powerful supplement that can be used to help fix a dysregulated HPA axis and overcome chronic fatigue syndrome. Click the button below to learn more about adrenal fatigue and what steps can be taken to overcome it.
Just as cistanche is a potent aphrodisiac for men, so to is it for women.
How Long does it take for Cistanche to Work?
Cistanche is best used consistently for 2+ weeks in order to fully benefit from its effects. When used acutely for just 1-3 days a larger dose will be required to feel the effects, and even then the effect size will be smaller than if cistanche is dosed consistently for 2+ weeks.
The effects of cistanche build up and really begin to be noticeable at the 10+ day mark depending on how sensitive one is to the herb. Speaking from personal experience in supplementing with cistanche many times now, I notice that the testosterone boosting effects of cistanche really begin to manifest after 1-2 weeks and it continues to increase steadily from there. It takes 1-2 weeks for cistanche supplementation to begin to noticeably improve exercise performance, and it’s around this time as well that the effects of higher testosterone levels are also noticed (increased confidence, stronger, better erections, etc).
Supplementing with cistanche for 1-2 months ensures that its beneficial effects culminate to a point of being relevant and noticeable. Though cistanche has a long history of being used in Traditional Chinese Medicine for extended periods of time without break, since cistanche alters the function of the endocrine system, I recommend cycling off cistanche for as long as it was used for. For example if cistanche is supplemented with for 2 months, it shouldn’t be used for 2 months afterwards.
Cistanche Side Effects
Cistanche tubulosa extract orally administered at 26.4 g/kg to male and female mice and kept for 8 days caused no abnormalities, fatal events, or autopsy abnormalities. No issues were observed when dosing 0.65-1.30 g/kg cistanche daily for 30 days to rats.
Examining potential long term toxicity, Cistanche tubulosa extract was orally administered to male and female rats at 1.65 g/kg per day and kept for 180 days. No abnormalities, fatal events, or autopsy abnormalities were recorded.
Furthermore, no abnomalities, fatal events, or autopsy abnormalities were observed when a Cistanche tubulosa extract was orally administered to male and female beagle dogs at 1.50 g/kg daily and kept for 180 days.
This data was collected by Oryza Oil & Fat Company out of Japan, and when converted to Human Equivalent Doses (HED) based on body surface area we arrive at the following dosages:
2.15 g/kg Cistanche HED - acute toxicity study (mice)
0.85 g/kg Cistanche HED - 180 day toxicity study (dogs)
0.25 g/kg Cistanche HED - 180 day toxicity study (rats)
When multiplied by individual bodyweight, the human equivalent dose for a person is very large at 10+ grams, an amount that far exceeds the typical dosing recommendations, and therefore is not recommended to try but does give confidence that cistanche has a strong safety profile with very little chance of negative side effects occurring at the much lower dosages recommended.
In terms of practical side effects that may be experienced, a large dose may cause digestive discomfort and since cistanche increases testosterone levels, it may cause alterations to mood and aggression. Additionally cistanche as a vaso-relaxant reduces blood pressure and should not be taken if an individual’s blood pressure is already on the low side (<80/60).
Cistanche Dosage
The beneficial health effects of cistanche manifest nicely at dosages of 100 mg - 500 mg of an extracted powder used daily.
For a raw powder, the concentration of active ingredients will be less and therefore a higher dose of 500 mg - 2 grams should be used to achieve the same effect. The dose chosen within that range will depend on an individual’s bodyweight, their individual physiology, and the potency of the effect they desire.
When first using cistanche, start with the lowest dose and only after some time has passed should the dose be increased if desired.
Megadosing Cistanche
I have experimented with megadosing cistanche (400-600 mg of Nootropics Depot Cistanche) which is 2-3x the recommended serving size. I have done this for a few weeks and here are my anecdotal observations:
Rapid strength gains, increases in muscle hardness
Bodyfat around the lower abdominals reduced
Minor confidence boost (and I already wasn’t deficient there)
I went from having just the rare pimple to noticeable acne on the back
The increase in skin acne is a good indicator that testosterone levels are increased in the body, but it’s also undesirable. For this reason I think megadosing cistanche is best done cautiously and only for very limited periods of time (<4 weeks) and for specific reasons (breaking through a strength training plateau, temporary confidence boost for a meeting/event). If megadosing cistanche for the benefits listed above but wish to avoid the possible skin issues, supplement with dandelion at the same time. I discuss this more in more detail in my article on boosting testosterone with cistanche.
Cistanche vs Tongkat Ali
Like cistanche, tongkat ali is another herbal often used by men to increase testosterone levels. I’ve used both herbs extensively and will share my experience of how they compare to each other.
Tongkat ali is a testosterone boosters that works rather quickly, I was able to feel the before and after difference in just 2-3 days, whereas the effects of cistanche build up over weeks and started to became noticeable to me after about a week or so.
Cistanche is much smoother and easier on my body, whereas tongkat ali after a few weeks begins to feel very harsh. This is the main reason I supplement with cistanche much more often than tongkat ali, it just feels safer and less impactful in a negative way on my body.
It’s my experience also that cistanche is a better testosterone booster overall than tongkat ali. Cistanche can be supplemented with for longer periods of time which allows a greater culminative effect to build up, and it’s better at improving overall metabolism. For me tongkat ali gave me more of a raw energy and strength which when focused and utilized to increase exercise performance was useful.
If interested in a quick 1-3 week boost of testosterone, strength, and energy then tongkat ali is a good option, whereas cistanche is a better option for longer term testosterone, strength, and energy improvements.
Where to Buy Cistanche Supplement?
There are many different sellers of cistanche supplements worldwide which can be seen by visiting a marketplace like Amazon.
Cistanche Tubulosa Powder
My favorite supplier of cistanche is Nootropics Depot. Their cistanche product is highly standardized, containing a minimum of 50% echinacosides and 10% acetoside, overall delivering more echinacosides and acetoside per gram than most other cistanche products. I also like Nootropics Depot’s cistanche product because it has a neutral taste and isn’t bitter. The cistanche from Nootropics Depot works very well and is reasonably priced.
If purchasing cistanche from a Chinese pharmacy ask for Rou Cong-Rong, which is how they refer to cistanche.
References:
Li Z, Lin H, Gu L, Gao J, Tzeng CM. Herba cistanche (Rou cong-rong): one of the best pharmaceutical gifts of traditional chinese medicine. Front Pharmacol. 2016;7.
Al-Snafi, Ali Esmail. Bioactive metabolites and pharmacology of Cistanche tubulosa-A review. IOSR Journal of Pharmacy 10.1 (2020): 37-46.
Jiang Y, Tu PF. Analysis of chemical constituents in Cistanche species. Journal of Chromatography A. 2009;1216(11):1970-1979.
Oryza Oil and Fat Chemical Co. Food and cosmetic ingredients with tonics, memory improving, anti-aging, anti-fatigue, anti-sex dysfunction, immune boosting and fat metabolism accelerating properties of Cistanche tubulosa extract-P-25 (Water-soluble Powder, Food Grade). Oryza Oil and Fat Chemical Co., Ltd. 2007
Medical Disclaimer: All information, content, and material of this website is for informational purposes only and is not intended to serve as a substitute for the consultation, diagnosis, and/or medical treatment of a qualified physician or healthcare provider.
Disclosure: Wild Free Organic is a member of various affiliate programs and if a purchase is made through one of our affiliate links a small commission is received. This does not affect your purchase price. Visit our disclosure page for more information.
More Hormone Optimizing Herbs
Black Pepper
Black pepper is the "king of spices" and it's main active ingredient piperine has many attractive heath benefits. Black pepper improves the functioning of the digestive system and stimulates appetite. Piperine is a potent antioxidant and anti-inflammatory with neuroprotective effects. Learn about the herbalism of black pepper with this guide.
Article by Stefan Burns - Updated April 2022. Join the Wild Free Organic email newsletter!
| Name: | Black Pepper, Linnaean - Piper nigrum |
| Color: | Peppercorns are green when unripe and red when ripe on the vine. Dried peppercorns turn a dark brown/black, and if the dark outside skin is removed the peppercorns are white |
| Constituents: | Piperine, terpenes, resins, starches, hydrocyanic acid |
| Effect: | Powerful digestive aid, stimulates appetite, anti-microbial, increases gastric secretions and stimulate mucous membrane, boosts metabolism, antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, cognitive aid |
| Preparation: | Peppercorns are left out to dry in the sun until black. White peppercorns which have the outside skin removed have higher levels of piperine (about double). Ground into a powder for use as a spice. Piperine extracts used as a bioavailibility enhancer for other supplements, as a digestive aid, and as a cognitive aid |
| Dosing: | 1+ grams black pepper powder as a spice. 5-25 mg of 95% standardized piperine. |
| General Notes: | Pepper is one of the most popular spices used worldwide, has a pungency to it that increases appetite and readies the gastrointestinal system for digestion. Piperine is a potent bioavailibility enhancer for other compounds like anti-inflammatory curcuminoids (from turmeric) or psychadelic psilocybin (from magic mushrooms). Piperine is a promising natural supplement to aid in the treatment of neurodegenerative diseases. Has been used for thousands of years. |
What is Black Pepper?
Black pepper is a spice derived from the fruits of Piper nigrum, a perennial climbing shrub with white flowers. After flowering it produces small fruits ~6 mm in diameter which transition from green to yellow to red as they ripen.
The pepper plant is native to the coastal regions of southern India and is now cultivated worldwide in tropical and subtropical regions, requiring shade and high humidity.
Black pepper, the “king of spices”, is produced by drying green unripened peppercorns in the sun. Heat from the sun accelerates natural enzymatic reactions which turn the peppercorns black. Black pepper is used as a spice for flavoring food and as a food preservative.
Is Black Pepper Good for You?
Black pepper is used copiously around the world, being a near ubiquitous food seasoning, and it’s clear that black pepper isn’t harmful when used in reasonable amounts, and it’d be difficult to consume enough pepper to be problematic due to its pungency. Black pepper’s pungent nature is thanks to its main active compound, piperine, and its primarily piperine that gives black pepper its many wonderful health effects.
Piperine regulates gastrointestinal functionality, mediates inflammation, is neuroprotective, and even increases the bioavailability of other nutrients by enhancing their absorption.
Black pepper is an important health food that combines the benefits of being a strong antioxidant with antimicrobial properties. Through its free-radical scavenging ability black pepper is useful against cancer and controls the progression of tumor growth.
Black pepper isn’t just good for you, it’s really good for you, and it’s pepper’s long history of use for health and wellness in Ayurveda and Traditional Chinese Medicine that built the foundation of the worldwide pepper trade from antiquity to today.
Black Pepper Nutrition Facts
It’s first made clear that peppercorns are a health promoting herb by it’s attractive micronutrient profile. Pepper isn’t consumed in large enough amounts for its contribution of micronutrients in the diet to be especially notable for any single meal, but it is rich in a variety of micronutrients on a per gram basis, and when used as a seasoning over time, it’s micronutrient contributions to the diet do add up.
Vitamins (in 1 tbsp, 6 grams)
Vitamin K - 13% DV - 10 mcg
Vitamin A (as beta carotene) - 21 mcg
Vitamin C - 2% DV - 1.3 mg
Minerals (in 1 tbsp, 6 grams)
Potassium - 2% DV - 78.7 mg
Calcium - 3% DV - 27.3 mg
Magnesium 3% DV - 12 mg
Phosphorus - 1% DV - 10.8 mg
Iron - 10% DV - 1.8 mg
Manganese - 18% DV - 0.4 mg
Copper - 4% DV - 0.1 mg
Peppercorns also contain a lot of fiber being 20-45% starch by weight. Flavoring a dish with 1 or more teaspoons of black pepper overtime will help add vitamin K, manganese, iron, and piperine into the body.
As touched upon earlier, black pepper has numerous health benefits, and now we’ll learn more about the health
Black Pepper Health Benefits
Black pepper has a long list of health benefits due to its unique phytochemistry which is made up of a combination of volatile oils, oleoresins, and alkaloids. The main active ingredient in black pepper is piperine.
Black pepper essential oil contributes towards its aroma, and oleoresin contributes towards its taste. Black pepper stimulates appetite, increases the secretion of saliva, and stimulates the release of digestive enzymes. Black pepper enhances HCL production in the stomach and stimulates histamine H2 receptors. In effect even just the aroma of black pepper can stimulate digestive preparedness and thoroughness.
In addition to this black pepper is a diaphoretic and diuretic, capable of stimulating seating and urination. Black pepper and it’s main active ingredient piperine causes a flush of digestive fluids, which is another detoxification pathway. This combined effect is partly responsible for black pepper’s broader anti-inflammatory and anti-growth effect. As an antimicrobial, black pepper and piperine are able to gently balance the digestive system of malfunction, upset, or limited nutrient absorption. Piperine dramatically increases bioavailability for many nutrients, and increasing black pepper intake is one way to easily restore optimal digestive health.
Piperine is responsible for the pungency of black pepper, making up 3-10% of peppercorns by weight. It’s is an alkaloid that is sensitive to light, insoluble in water and acts as a weak base. Piperine is responsible for the main health benefits of black pepper, and when black pepper is consumed whole it has a broader health boosting effect but can’t be as powerfully isolated in effect as 25, 50, or 100 mg of piperine can be.
Piperine Benefits
Increases bio-absorption of vitamins and trace elements
Decreased fat accumulation
Improves digestion
Antimicrobial
Effective against acute inflammation
Piperine ameliorates chronic mild stress
Stimulates anti-cancer pathways
Reduces the extent of toxicity for certain chemicals
Uses for Black Pepper
The properties of black pepper make it useful for ailments of the digestive system. Black pepper tones the muscles of the stomach and stimulates the mucous membranes. Black pepper can be used in constipation and diarrhea.
Black pepper speeds up the metabolic procedures that generate heat in the human body, raising body temperature and burning bodyfat.
As an antimicrobial and anti-parasitic, black pepper can be used to steer the microbiome towards better symbiosis and reduce detrimental vagus nerve inputs. Black pepper can be used for altering neurotransmitter production in the gut. Black pepper and its active ingredients can be supportive in treating disorders of the nervous system which include depression, Alzheimer's, epilepsy, and others.
Black pepper can also simulate the diaphragm (who hasn’t sneezed from black pepper before).
In high doses can be used as a abortifacient and use should be avoided around pregnancy.
Supplementing with Piperine
At higher doses of 25+ mg, piperine exerts its influence on the body strongly. Piperine is an inhibitor of MAO activity, which is a potential treatment path for depression and Parkinson’s disease. Piperine also has the possibility of increasing serotonin and dopamine levels under conditions of stress.
To supplement with piperine use 0.5-1 mg/kg of bodyweight. A good starting dose is 25 mg and increasing from there.
Nootropics Depot Piperine
A standalone piperine supplement allows for piperine to be supplemented alongside other herbs in other to boost their bioavailability. This is useful for a bunch of herbs, namely turmeric, green tea, and medicinal mushrooms.
Nootropics Depot conveniently sells piperine extract in 10mg capsules. Piperine is highly sensitive and will degrade quickly when exposed to light, so supplementing with piperine in capsule form instead of with a powder is not only easier in dosing but also lowers the amount of degradation that will occur due to light exposure.
Black Pepper Ayurveda
In the Ayurveda system of medicine black pepper is an energetically heating spice used to support digestion and assists the flow of qi energy downwards.
Black Pepper vs White Pepper
White pepper differs in its harvest from black pepper. Instead of picking unripe green berries and letting them dry in the sun, as is done with black pepper, the berries are allowed to ripen on the vine and then soaked to remove the skin. Machinery can also be used to remove the outer layer.
Having ripened on the vine and having it’s outer skin removed, white pepper is distinct from black pepper in its aroma and taste. There are differences between black pepper and white pepper as it relates to piperine content. Piperine yield from black pepper was 2.5% - 3.0% and from white pepper 4.0% - 4.5%. The purity of the piperine was found to be up to 98.5% for black pepper and 98.2% for white pepper. White pepper provides about 50% more piperine per weight than black pepper.
Medical Disclaimer: All information, content, and material of this website is for informational purposes only and is not intended to serve as a substitute for the consultation, diagnosis, and/or medical treatment of a qualified physician or healthcare provider.
References:
Malcom Stuart, et al. The Encyclopedia of Herbs and Herbalism. Crescent Books, New York.
Butt MS, Pasha I, Sultan MT, Randhawa MA, Saeed F, Ahmed W. Black pepper and health claims: a comprehensive treatise. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition. 2013;53(9):875-886. https://doi.org/10.1080/10408398.2011.571799
Rahman Khan Z, Moni F, Sharmin S, et al. Isolation of bulk amount of piperine as active pharmaceutical ingredient (Api) from black pepper and white pepper(<i>piper nigrum</i> l.). PP. 2017;08(07):253-262. https://doi.org/10.4236/pp.2017.87018
Disclosure: Wild Free Organic is a member of various affiliate programs and if a purchase is made through one of our affiliate links a small commission is received. This does not affect your purchase price. Visit our disclosure page for more information.
More Digestion Improving Herbs
Green Tea
Green tea is a medicinal beverage that has been consumed and loved by billions of people for thousands of years, and for good reason. Green tea improves cognitive performance, rejuvenates the digestive system and skin, improves cardiovascular and metabolic health, and is also very pleasing! Finding high-quality green tea is very important in order to best enjoy these health benefits and more.
Article by Stefan Burns - Updated April 2022. Join the Wild Free Organic email newsletter!
| Name: | Green Tea, Linnaean - Camellia sinensis |
| Color: | Green leaves, white flowers |
| Constituents: | Chlorophyll, caffeine, L-theanine, catechins (EGCG), flavanols, other phytochemicals |
| Effect: | Cognitive aid, boosts metabolism and fat oxidation, increases 8-12 Hz alpha brainwaves, antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, heals tissues of the digestive system |
| Preparation: | Tea leaves can be prepared in many ways, left dried green or oxidized to create black tea which has a higher caffeine content. Green tea can be powdered for use in supplements and is often extracted to increase the concentration of EGCG, a potent antioxidant |
| Dosing: | 1-5 grams steeped for tea, 250-1000mg EGCG |
| General Notes: | The combination of caffeine, amino acid L-theanine, and green tea catechins make green tea a cognitive aid that increases focus. A few cups a day will increase the bodies metabolic rate. Purported longevity enhancer. Green tea can help heal the lining of the digestive system, but in large quantities or if the tea is brewed incorrectly can cause digestive nausea. One cup of green tea contains about 30mg caffeine, about 1/3 that of a cup of coffee. Green tea has been used for thousands of years throughout Asia and now worldwide. |
What is Green Tea?
Green tea is an ancient beverage that has been brewed for thousands of years. Empires have been created and collapsed around the trade of tea, and for good reason. The leaves of the tea tree when steeped in hot water release an incredible combination of chemicals and nutrients. Specifically green tea contains caffeine, L-theanine, polyphenol catechins like EGCG, among 200 other bioactive compounds. After a cup or two, the entourage effect of all of this are happy taste buds, improved cognitive performance, increased fat oxidation, and rejuvenative effects felt across the body.
A cup of green tea in the morning helps normalize the circadian rhythm, cultivating a productive state of high energy. The unique synergy of caffeine and L-theanine, both found naturally in green tea, is powerful and further supported by the presence of green tea polyphenols known as catechins.
Moc Chau Tea Hills
Is Green Tea Caffeinated?
The leaves of the green tea plant naturally contain caffeine. On a per gram basis green tea leaves contain more caffeine than coffee beans, but the amount of leaves and the way green tea is steeped means a cup of green tea contains less caffeine than an equivalent cup of coffee.
A typical cup of steeped green tea contains 35 mg of caffeine and ~20mg L-theanine.
A cup of match green tea (which is made from powdered green tea leaves) contains ~65 mg of caffeine and ~35 mg L-theanine.
Green Tea vs Black Tea
Green tea is produced from mature green tea leaves which are typically withered, steamed, and then dried for usage. Black tea differs from green tea in how it is produced. Black tea is made from mature green tea leaves that are typically withered, rolled, fermented, fired, and then dried. This process oxidizes the tea leaves turning them a dark brown to black which increases the caffeine content while reducing the L-theanine concentration to near zero.
A typical cup of black tea contains ~60 mg of caffeine and 0-5 mg of L-theanine.
Green Tea Health Benefits
Green tea is a beverage that’s been enjoyed for over 5000 years and possibly longer. Its use is first recorded in ancient China but quickly spread across Asia and later around the world. Green tea leaves are a powerful herbal that have many beneficial health effects on the body due to their unique chemical constituents. The most active of these components are:
Caffeine | Functions: Increases focus, reduces fatigue, improves mental performance, improves fat oxidation and power output
L-theanine (amino acid) | Functions: Activates parasympathetic activity, stabilizes heart rhythms, increases 8-12 Hz alpha brain wave activity, reduces anxiety, reduces stress
Polyphenols (green tea catechins such as EGCG) | Functions: Powerful antioxidants, anti-inflammatory, improves cardiac health, anti-microbial
Together these chemical constituents and others broadly influence the function of the digestive, immune, cardiovascular, metabolic, and cognitive systems providing the following benefits:
Green Tea has Cancer Fighting Properties
Prevents the growth of tumors
Decreases oxidative DNA damage
Reduces the size of cancer already formed.
Green Tea Improves Cardiovascular Health and Increases Metabolism
Reduces systolic and diastolic blood pressure
Improves cholesterol levels by lowering LDL cholesterol and increasing HDL cholesterol
Non-obese people who drink 1-2 cups of green tea everyday lower the risk of developing diabetes by >80%
Equalizes blood glucose levels and increases fat oxidation
Green Tea Improves Gut Health
Green tea polyphenols are anti-microbial and shift the microbiome towards increased symbiotic function
Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties help reduce gut inflammation and aid in gut tissue repair
The increasing fat oxidation and reduction in appetite from green tea makes fasting easier
Polyphenols repair gastrointestinal tight-junctions
Green Tea Improves Skin Health
By improving gut health green tea improves skin health
Topical extracts demonstrate rejuvenating anti-aging effects
Reduces inflammation of skin where green tea extracts like EGCG are applied topically
Note: Green tea has quite a few human studies, observational or otherwise, but much of the research has been done using animal models or with cell cultures. Not all of the health benefits have been directly confirmed for humans.
Green Tea Increases Alpha Brainwaves
What makes green tea so excellent as a natural stimulant is its unique blend of caffeine and L-theanine. L-theanine is an amino acid found mainly in tea leaves, and it has a special ability to increase alpha 8-12 Hz waves in the brain. If you are calm and relaxed, or especially if in a strong flow state, then you are generating alpha waves. You’ll be very productive and clear of mind when synchronous alpha brainwave activity is happening across the brain. A cup of green tea in the morning can increase brainwave power in the 8-12 Hz alpha band, decreasing sleepiness and drowsiness which are common attributes of slower 0-4 Hz delta and 4-8 Hz theta brainwaves. Alpha rhythms promote alert parasympathetic activity throughout the body, and can also normalize non-synchronous higher frequency 12-30 Hz beta brainwave activity to lower frequency but higher total power synchronous rhythms in the alpha band. Alpha brainwaves during the day improve cognitive performance and set the stage for a more restful sleep at night.
Green Tea for Burning Fat
The blend of caffeine, L-theanine, and polyphenols has been shown to increase fat oxidation while reducing appetite, but the effect is minimal in comparison to other factors that influence fat metabolism. That said, in adjunct with a healthy diet and adequate exercise, green tea will will help the weight loss process, especially when consumed consistently over time.
The best way to use green tea for burning fat is as a fasting aid. By not eating for a specified period of time during a fast, the body is eventually forced to burn bodyfat in order to keep normal metabolic processes going. A 16 hour intermittent fast increases fat metabolism noticeably, especially if done for many weeks or months, whereas a 24-48 hour or long fast will dramatically increase fat metabolism. Because green tea reduces appetite, slightly boosts fat metabolism, and increases focus, drinking green tea during a fast makes it noticeably easier to accomplish successfully, and in this way green tea can be a powerful fat burning aid.
Green tea can helps shift the gears towards greater fat oxidation and away from sugar dependent metabolism, for overweight and healthy individuals alike. With body fat oxidation increased, appetite is decreased as the body is coursing with available energy and therefore satiated. Without other lifestyle changes green tea won’t cause anyone to lose significant amounts of weight, but as part of a larger holistic wellness strategy that optimizes diet, exercise, and sleep, green tea can be useful and has a place.
Green Tea Heals the Digestive System
If suffering from serious gut health conditions such as leaky gut, IBS, IBD, celiac, Crohn’s disease, food allergies and intolerances, and other gastrointestinal afflictions, regular green tea consumption can provide symptom relief while also assisting the natural healing process that is working in the background. Poor gut health is closely linked with mental health such as depression or anxiety and it’s not surprising that in addition to its beneficial effects on the gut that consumption of green tea can reduce anxiety and stress.
As partially discussed earlier, the gut healing potential is best amplified during a fast. To best assist the natural gut healing process using green tea, practice 16 hour intermittent or 24 hour one-meal-a-day fasting and during the period of fasting drink 1-3 cups of green tea. Here more cups are better, though timing is also important. Green tea will be most potent when consumed by itself and fairly distanced from other meals. For this reason a cup in the morning works well as the body has been without food for 8+ hours since dinner was eaten. Drink green tea throughout the day around meals can also reduce the inflammatory burden on the gut from each meal.
Green Tea Diversifies the Microbiome
One of the biggest drivers of gut health is how diverse the microbiome is. Food choices, macronutrient ratios, and how food is prepared can all change the microorganism ratios of the microbiome, as well as increase or reduce total diversity (# of species). Green tea as an anti-microbial balances the microbiome and reduces the burden of microbial overgrowth, allowing other beneficial microbes better access to resources and therefore green tea has a microbiome diversifying effect.
Green Tea is a Potent Anti-Inflammatory
When the digestive system and microbiome are in a state of inflammation, the stress placed on the many systems of the body make it possible for many diseases and health conditions to arise, some of which overtime prove deadly. Through its actions in improving the microbiome and also in healing the tight-junctions of the gut, green tea reduces inflammation in the gut and therefore helps reduce chronic inflammation throughout the body.
Just as green tea heals the gut, it can also help improve skin conditions, as skin problems are typically a secondary factor downstream from gut problems. Green tea antioxidants like EGCG are powerful in their anti-inflammatory effect and can even be topically applied for effective treatment of skin conditions such as acne or the aging of skin. Less is known on how green tea can improve other skin issues such as psoriasis or eczema, so careful self experimentation with green tea topicals may prove useful.
Green tea polyphenols that make it past the digestive system enter into the bloodstream where they have an opportunity to exert an effect on the tissues of the cardiovascular system. polyphenols like EGCG are a vasodilator, aiding their circulation and uptake throughout the body, reducing inflammation systemically.
Green tea polyphenols that further make it past the blood-brain barrier will exert their antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects in the brain. Additionally green tea strengthens 8-12 Hz alpha brain wave activity which can perk you up or calm you down depending on your current state on consciousness. Stable brain waves reduce the chance of experiencing mental health problems and in a feedback loop erratic or depressed behavior can lead to poor health decisions like a bad diet which can impact the inflammatory state of the body. The alpha brain wave flow state that a cup or two of green cultivates lasts for several hours.
Green Tea Dosing
Green tea has quite a wide dosing range, from infrequent usage to one cup a day to 5+ cups a day all being fine and safe. When drinking green tea the biggest thing to be aware of is how much caffeine is being consumed in total. Exceeding 300 mg of caffeine a day is not recommended, you can learn more by reading my caffeine usage and tolerance reset guide.
Tea is a very popular beverage, and most tea is grown the same way much of the world’s food supply is, with mass amounts of chemical pesticides. While green tea polyphenols help heal the gut and diversify the microbiome, pesticides like glyphosate do the opposite, degrading the gut barriers and indiscriminately kill the microbiome. It is important for this reason to buy very high-quality tea grown without pesticides, and the more tea that is consumed the more important tea quality becomes.
Drink 1-2 cups of green tea as a cognitive aid, to boost focus, and increase productivity
Drink 1-3 cups of green tea spaced out to help heal the tissues of the gut either during a fast or in-between meals
Drink 5+ cups of green tea daily for the most powerful preventative and longevity enhancing health benefits.
Matcha green tea is about 2x more powerful than regular green tea, so if drinking matcha reduce the amounts above in half.
If taking a green tea extract power or pill like those sold by Nootropics Depot, the recommended dose is 500 - 1000 mg which can be increased if desired after some time has passed to ensure no negatives are experienced. The most likely negative side effect to be encountered when supplementing with a green tea extract, or simply when drinking green tea in general, is digestive discomfort. Green tea polyphenols are great for the digestive system but they are quite astringent and can sometimes cause a minor stomach ache.
Where to Buy Green Tea
There are thousands of sources of green tea and green tea extracts available to purchase and in my search for reputable green tea products I landed on the three following suppliers: Mountain Rose Herbs, Pique Tea, and Nootropics Depot. The green tea products from each supplier have their advantages and which to choose depends on what you want.
Mountain Rose Herbs Tea Products
Rolled Green Tea Pearls
If brewing a cup of green tea in the traditional way (steep for 5-8 minutes with 170F water), then rolled-up pearl tea is typically of the highest quality next to matcha. Mountain Rose Herbs sells
Matcha Green Tea Powder
Mountain Rose Herbs sells a ceremonial grade matcha green tea made from young shade-grown tea leaves from the Kyoto Prefecture, Japan.
Match green tea has the highest caffeine, L-theanine, and polyphenol levels and is one of the strongest ways of consuming green tea.
Green Tea Extract
Mountain Rose Herb’s organic green tea extract is made from sencha green tea which undergoes a dual water and alcohol based extraction process. This dual method of extraction pulls as many beneficial compounds out of the green tea leaves as possible and condenses them into a tincture. Green tea tincture can be taken directly under the tongue or added to a liquid like water or juice.
Pique Tea Crystals
If you’re not in a position to brew tea leaves by steeping due to a lack of materials or time, then cold-brew extracted green tea crystals sold by Pique Tea are a good way to have your green tea and drink it too! Pique Tea is a regenerative organic tea manufacturer who triple-screens their product for heavy metals, pesticides, and mold before cold-brew extracting the main components of green tea leaves into what they call tea crystals. Served in individual packets, Pique Tea crystals are easy to dose and prepare, at home or on the go. Best served with water boiled to 170 F (75 C).
Nootropics Depot Green Tea Extract Products
Nootropics Depot sells a few products derived from green tea, but their main green tea products are their green tea extract powder and their green tea extract + piperine tablets.
Green Tea Extract Powder
The Nootropics Depot green tea extract powder contains a minimum 45% EGCG content. Contains trace amounts of caffeine.
If looking to supplement primarily with green tea catechins like EGCG for their antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects this product is a good choice.
Green Tea + Piperine Tablets
Piperine is a bioavailability enhancer derived from black pepper that when paired with extracted green tea polyphenols aids in their absorption and increase their effect throughout the body.
The tablets are enteric coated so they may pass through the stomach protected to be more effectively absorbed by the intestines.
Each tablet contains 500 mg of green tea extract with a minimum 45% EGCG content alongside 6 mg of piperine.
Medical Disclaimer: All information, content, and material of this website is for informational purposes only and is not intended to serve as a substitute for the consultation, diagnosis, and/or medical treatment of a qualified physician or healthcare provider.
References:
Jankun J, Selman SH, Swiercz R, Skrzypczak-Jankun E. Why drinking green tea could prevent cancer. Nature. 1997;387(6633):561-561.
Wolfram S. Effects of green tea and egcg on cardiovascular and metabolic health. Journal of the American College of Nutrition. 2007;26(4):373S-388S.
Hara, Y. Influence of tea catechins on the digestive tract. J. Cell. Biochem. 1997, 67: 52-58.
Katiyar S, Elmets C. Green tea polyphenolic antioxidants and skin photoprotection (Review). Int J Oncol. Published online June 1, 2001.
Cooper R. Green tea and theanine: health benefits. International Journal of Food Sciences and Nutrition. 2012;63(sup1):90-97.
Disclosure: Wild Free Organic is a member of various affiliate programs and if a purchase is made through one of our affiliate links a small commission is received. This does not affect your purchase price. Visit our disclosure page for more information.
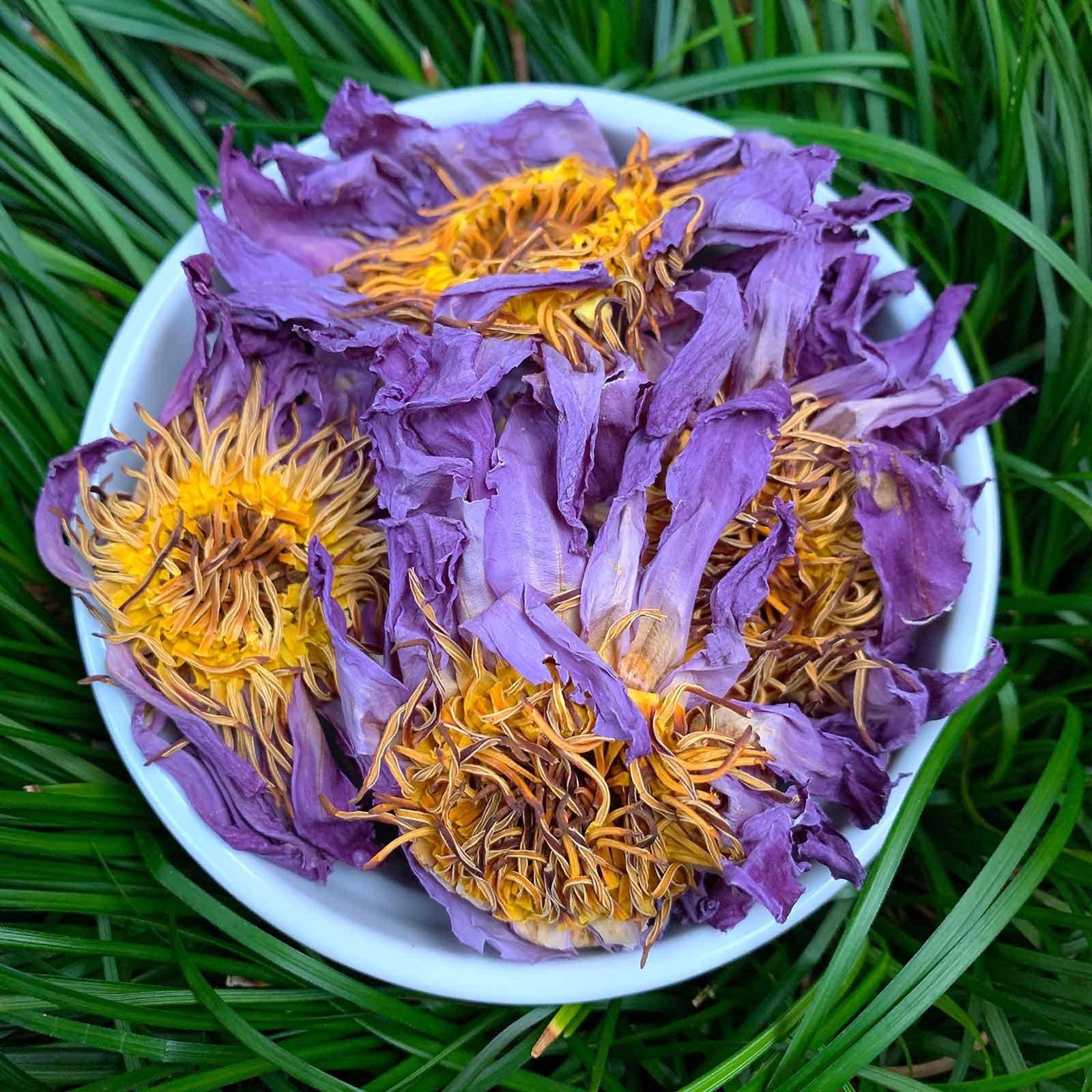
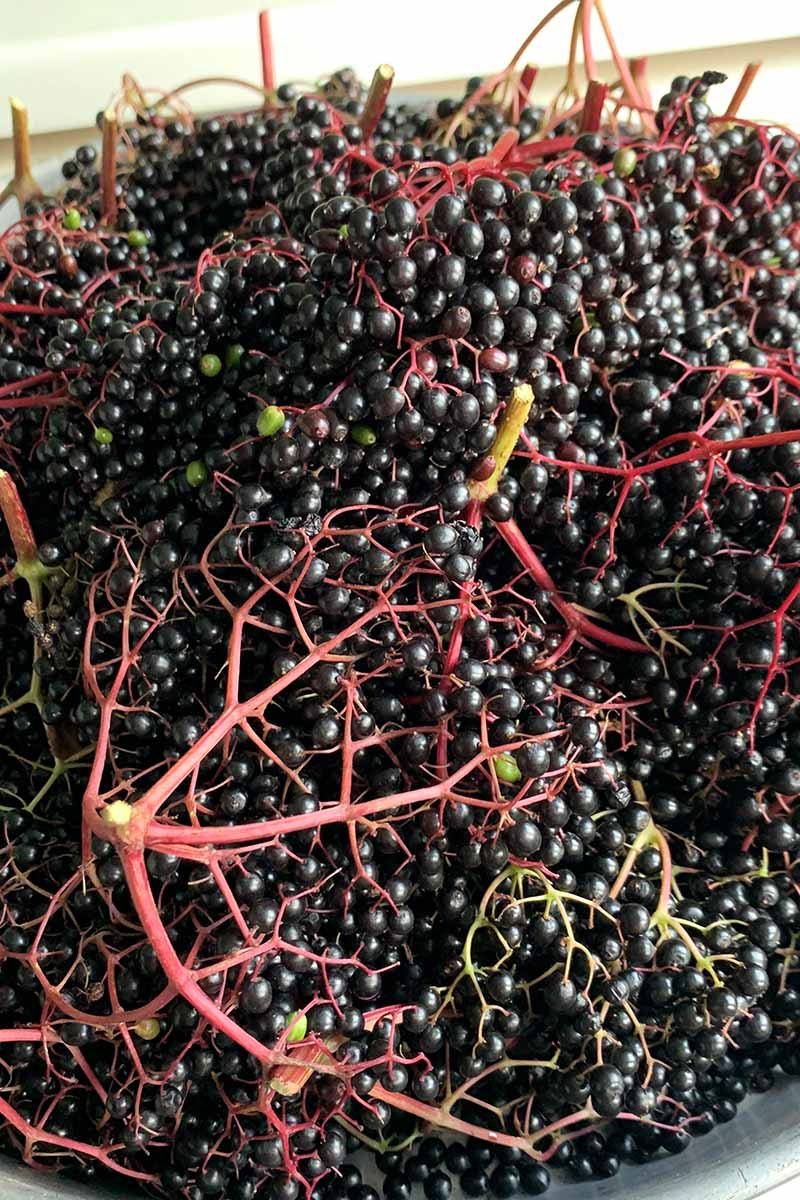




















































































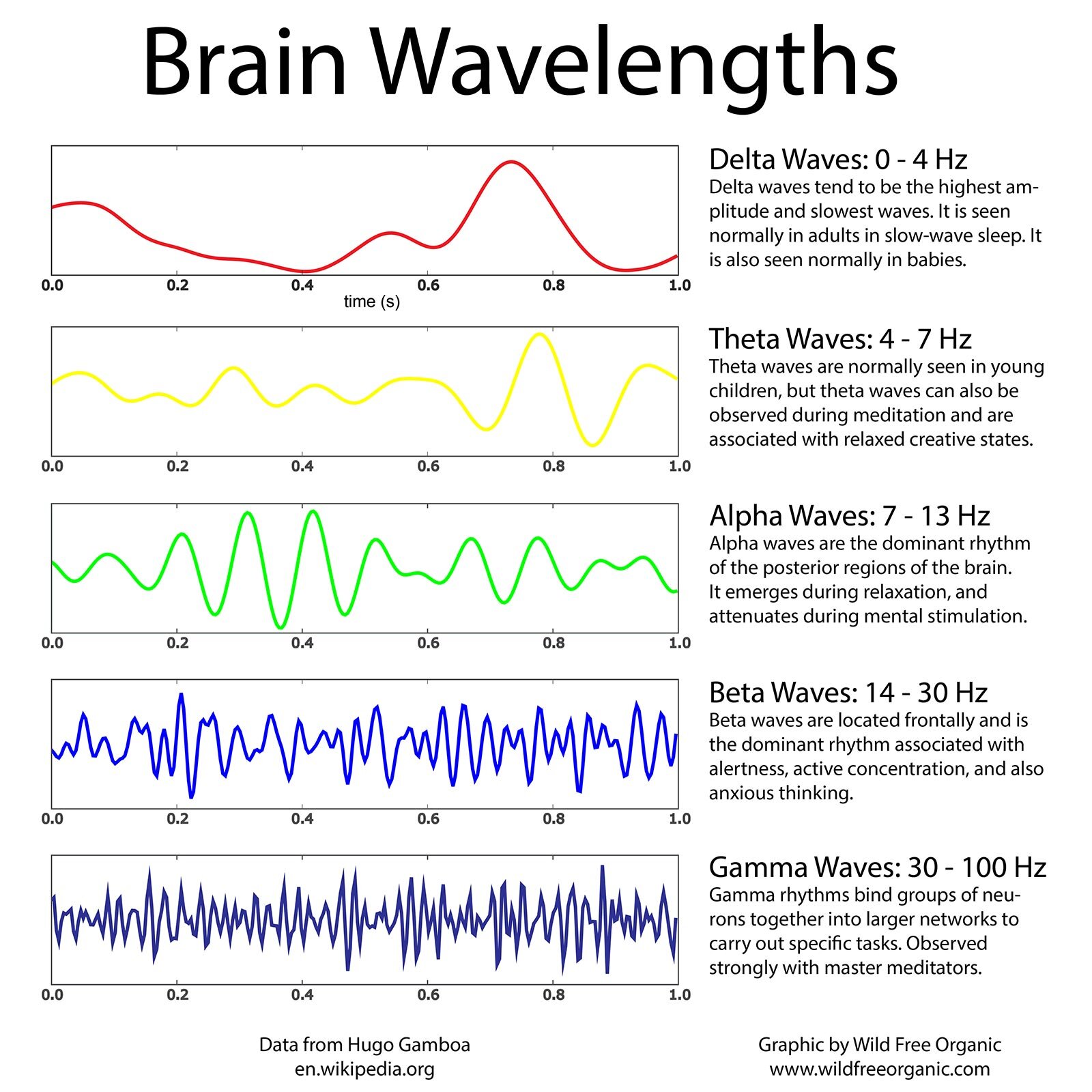









Tongkat ali is a potent testosterone booster through its interactions with SHBG and aromatase. Tongkat ali is also a cognitive enhancer, has anti-cancer properties, and has shown promise as an herbal supplement for athletic enhancement. Tongkat is popular for its aphrodisiac and libido enhancing effects which can help with sexual dysfunction and infertility. Learn more about Eurycoma longifolia.