Wellness
Body + Mind + Energy + Emotion
When the elements of life are in balance, wellness happens naturally. It is normal to have an affinity towards some but not all of the elements of wellness. Wild Free Organic is here to guide you on your journey towards a balanced healthy lifestyle and provide new paths of exploration.
Categories
Join the Wild Free Organic email newsletter!
Best Supplements for Brain Fog
Brain fog and overall mental fatigue is a serious health concern that effects executive decision making, focus and memory, and also emotional status. The symptoms of brain fog itself make it difficult to treat, so the use of natural supplements like herbs is a great strategy for quickly making in-roads into the treatment of the condition.
and for Optimizing Cognitive Performance
Article by Stefan Burns - Updated September. Join the Wild Free Organic email newsletter!
If you have brain fog you know how helpless it can feel at times to remedy the problem, as the very symptoms of brain fog like an inability to concentrate and focus limit your ability, energy, and drive to find and implement useful helpful solutions.
When this is the case, using the best supplements for focus and concentration can provide some relief from brain fog and mental fatigue and help bring in enough energy and clarity of mind to kickstart the lifestyle changes that need to be made to permanently solve the problem.
Brain fog can be experienced all on its own, or it can be part of a larger health problem like chronic fatigue syndrome. The best supplements that help with mental fatigue aren’t ones that simply stimulate the brain but instead are ones that beneficially target the stressed and dysfunctional parts of the body that are creating the mental fatigue in the first place.
There is no perfect brain fog cure, but with the right supplemental support and then the corresponding necessary lifestyle changes, mental fatigue can be recovered from and brain function can be returned to normal. In this article I share with you my favorite remedies for combatting brain fog and why they work.
Chronic vs Acute Mental Fatigue
There are two types of mental fatigue, chronic and acute. Temporary mental fatigue that is the result of one night’s bad sleep is quite different in effect and in its treatment from daily mental fatigue brought on from excessive stress, constant sleep deprivation, or neurocognitive conditions. When people ask for solutions that help alleviate their brain fog and mental sluggishness, most often they are seeking help for chronic mental fatigue.
Symptoms of Brain Fog
A term commonly used to describe mental fatigue is brain fog. Just like with sleep deprivation, where after a few continuous days of insufficient sleep you begin to not notice your symptoms of sleep deprivation (though they still exist), brain fog has a similar desensitizing effect. A lot of people who have mental fatigue do not realize they have it as they have become used to their chronically sluggish mental processes. It’s usually only when brain fog lifts temporarily for some reason, and clear lucid awareness is experienced before the brain fog returns, that people realize that they’re not functioning at their best. The symptoms of brain fog are subtle, especially when desensitized to the effect, so if you have any of the symptoms below, especially more than one, then it’s worth closely examining the functioning of your brain, your lifestyle, and perhaps taking one or more of the supplements below to see if you experience a noticeable before and after improvement.
Common symptoms of mental fatigue and brain fog:
You have difficulty focusing and concentrating on one task. High distractibility
You get lost in unconscious behavioral patterns (like endlessly scrolling on social media)
Its a struggle for you to hold onto multiple thoughts/ideas at once in order to understand a greater concept, follow a conversation, etc.
You get tired easily, especially with a cognitively demanding task like studying, learning a language, etc.
You experience frequent mood swings, and these mood swings can be triggered from small relatively insignificant events
Your short and/or long term memory isn’t good
You don’t have much patience
You get triggered and angered easily
If mental performance needs to be raised while experiencing acute mental fatigue, like from a poor night’s sleep, then it can usually be treated successfully with a stimulant like caffeine. Chronic mental fatigue is quite different though, and treating chronic brain fog with a stimulant like caffeine can further exacerbate the problem.
Treating long-term brain fog is best done with things that activate the parasympathetic “rest and digest” nervous system. Resting more often, improving sleep, engaging in restorative exercise like yoga, grounding, meditation, breath work, and more are all things that activate the parasympathetic nervous system and help reduce chronic mental fatigue. This article will mostly stick to supplemental measures that help with mental fatigue, so if you wish to examine and treat the very important lifestyle component of the problem, then I suggest you read my article How to Balance Sympathetic and Parasympathetic States.
Sometimes brain fog and mental fatigue is so severe that it can be difficult to even think about let alone implement lifestyle changes that will help and reverse the issue, and when this is the case supplements are a convenient and useful way to jumpstart the turnaround process.
Chamomile for Brain Fog
One of the best things for treating chronic brain fog and mental fatigue is also a very well-known herb, and that’s chamomile!
Chamomile is one of the most ancient and well-known medicinal herbs known to mankind, the two most common varieties being Roman chamomile and German chamomile. Chamomile is identified by its small white flower petals that surround its yellow center, and it’s the chamomile flower that’s used in herbal practices because the flowers contain a wide range of biologically active chemicals such as terpenes, flavonoids, and azulenes that have been shown to be health promotive.
Chamomile is so useful in treating chronic mental fatigue because it provides multi-targeted treatment to the systems which are under the most stress and are causing the symptoms of brain fog as described above.
Chamomile Increases Parasympathetic Activity
First, chamomile helps promote more balanced autonomic nervous system by increasing parasympathetic activity throughout the body, and this helps reduce systemic stress and regenerate the bodily systems that are most worn down, like the adrenal glands.
Chamomile does this by improving heart rate variability (HRV), reducing erratic heart rhythms and instead shifting heart rhythms to be more sinusoidal and coherent in nature (see right half of figure 1). Heart rate variability is the measure of the time interval between heartbeats, and HRV is a key measure of cardiac health, stress, and sudden mortality risk.
Figure 1 - Change in heart rate when emotionally reframing from feelings of frustration to appreciation
CC - McCraty R. The Energetic Heart. HeartMath Institute; 2003
Chamomile’s ability to improve HRV and overall cardiac function is more important than most people realize, because the functioning of the brain is determined to a large degree by the health and functioning of the heart.
Chamomile Increases Alpha Brainwaves
Every heartbeat creates a pressure wave that travels through the circulatory system, and it has been shown that when this blood pressure pulse reaches the brain it generates 8-12 Hz alpha brainwaves. Put another way, the change in blood pressure 1-2 times every second (depending on heart rate) in the brain is the timing signal the brain uses to generate and synchronize alpha brainwaves that cycle 8-12 times per second.
Alpha brainwaves are so important because they are the middle frequency brainwave that sit in-between slow rhythm 0-4 Hz delta and 4-8 Hz theta brainwaves and 12-30 Hz beta and 30+ Hz gamma brainwaves. How well your brain is functioning can be measured quite clearly via brainwave patterns across the head, with the most important factors being brainwave frequency, power, and synchronicity.
There aren’t many (if any) studies that directly show this, but enough evidence exists to greatly suggest that those suffering from mental fatigue and brain fog have weak non-synchronous brainwave activity without clear frequency bands of activity. Chamomile’s ability to increase alpha brainwaves is so important because alpha rhythms are the dominant brain rhythm from which other brainwaves can then be switched to. When alpha brain rhythms are propagating strongly throughout the brain, there’s sense of calm, patience, creativity, and a feeling of relaxed alertness. Sounds like a good resting state of mind eh?
If alpha rhythms are propagating strongly throughout the brain, then it’s easier for the brain to rev up and begin propagating higher frequency beta and gamma brainwaves, which are associated with focus, productivity, and ingenuity. By supporting the stable functioning of the heart and the overall cardiovascular system, chamomile also improves brainwave activity and overtime trains the brain to establish these patterns of activity on its own.
How to Use Chamomile for Brain Fog
There are a few ways chamomile can be used in the treatment of mental fatigue, an important factor to known is that chamomile in my experience acts like an adaptogen for this purpose. If you’re overly tired then chamomile will help to stimulate and gently pick you up because it’s increasing your brainwave frequencies and their coherence of propagation, whereas if you’re overly stimulated and scattered then chamomile will help calm you down by increasing the power of lower frequency brainwaves. In many ways alpha brainwaves are the base from which all brain activity shifts up or down from, and building a strong base of alpha brainwave activity is incredibly useful in coping with stress and for clearing the haze of brain fog.
The three main ways chamomile can be used are as a tea, as an essential oil in aromatherapy, and by dry vaporizing or smoking the herb.
Chamomile Tea: This is the most common way to use chamomile as brewing chamomile tea is simple and very effective. Chamomile tea is also really helpful for gut health, and we’ll discuss further down why the gut-brain axis and the microbiome are really important to address when combating mental fatigue. Bring water to a temperature of 75-100 C (170 - 212 F) and steep dried chamomile flowers for 5-15+ minutes. Chamomile is a pleasantly sweet herb and it can be steeped for hours without the resultant tea becoming bitter. Chamomile makes for a great iced tea, and when endeavoring to remedy brain fog, drinking chamomile tea throughout the day is one of the best things you can do, and it’s so simple! Just brew a large batch of the tea once everyday and drink it often. I usually make 1 liter of chamomile tea (often with other herbs, more on that at the end) at night by bringing water to a boil and then letting the herb steep overnight in the fridge. When I wake up delicious iced tea is waiting for me every morning!
Chamomile Essential Oil: Chamomile essential oil is an ultra convenient and effective way to enjoy the beneficial parasympathetic effects of chamomile. You can simply smell the essential oil from the bottle, place a few drops into a diffuser, or apply it directly to parts of your body like your temples, forehead, the back of the neck, and your chest. I find chamomile essential oil if applied directly to the body to be more sedative in effect than chamomile tea, so it’s best used at night or when you quickly need to calm down and relax.
Chamomile Herb for Vaporizing or Smoking: Dried chamomile flower can also be shredded by hand or with a herb grinder and vaporized or smoked for a relaxant effect. I recommend dry herb vaporization because no carcinogenic smoke is produced in the process, but if you’re already a smoker then incorporating chamomile into your tobacco cigarettes, cannabis joints/bowls, or herbal smoking blend is really simple. Vaped or smoked cannabis has a pleasant sweet taste and has an nice overall calming effect that lasts quite a while.
For those who are struggling with chronic mental fatigue and the symptoms of brain fog, chamomile is my top recommendation for helping with the problem. Chamomile is an amazing herb for overall health and wellness, and while it won’t fix brain fog in one day, if chamomile is used consistently then it will almost certainly have a large positive effect.
Chronic mental fatigue takes time to develop, it sometimes develops over many years, and it’s the beneficial habits that can be done daily for long periods of time that will prove the most useful in reversing brain fog, and chamomile is one of the best herbs for this.
Organic dried chamomile flower and blue chamomile essential oil can be purchased from Mountain Rose Herbs. I like to use and combine both in my self-care practices, and if you pick up one then I recommend you purchase the other too.
Medicinal Mushrooms for Brain Fog
Not all mushrooms are poisonous or cause psychedelic effects, and the medicinal mushrooms I have listed below are safe and have a bunch of great wellness benefits. Every medicinal mushrooms varies in their chemical composition, but in general they contain phytochemicals like polysaccharides, beta-glucans, and triterpenoids which benefit your brain as well as other parts of the body.
Reishi Mushroom
Reishi mushroom is one of my favorite “herbs” for helping with brain fog not only because it’s very effective in doing this but also because in my neighborhood Ganoderma sessile, a type of reishi mushroom, grows everywhere and I have a lot of personal experience in using this mushroom.
Reishi mushroom is polypore mushroom nearly impossible to misidentify once its distinguishing features are known, and it has broad effects throughout the body. One of the main benefits of reishi is that it activates the parasympathetic nervous system, just like chamomile, thereby promoting rest and relaxation after use. In fact you can brew reishi and chamomile together into a tea and just like as described above and drink this tea throughout the day to help remedy long-term brain fog.
Reishi mushroom can be purchased from Mountain Rose Herbs in a variety of formats from whole cap to slices to powder to extract, and 1:1 reishi mushroom supplement capsules and 8:1 reishi mushroom supplement capsules that are more concentrated in active ingredients can be purchased from Nootropics Depot.
I wrote a full article on using reishi mushroom for stress, chronic fatigue, and anxiety, and if you’d like to learn more about the many other health benefits of reishi mushroom then you can read the reishi mushroom herbal page. You can also watch my video below!
Chaga Mushroom
Chaga mushroom is very useful in the treatment of mental fatigue and brain fog because it contains many powerful antioxidants, is anti-inflammatory, and optimizes the cardiovascular and nervous systems by calming erratic heart rhythms and increasing the contractile power of the heart. Chaga also contains antimicrobial compounds which benefit the microbiome of the gut by selecting against harmful pathogens while simultaneously supporting good symbiotic bacteria.
As you can see, these natural products are all similar in their ability to help treat mental fatigue because they target not only the brain, but also the heart and gut . Stress destabilizes the proper functioning of the heart, nervous system, and digestive system, and the herbs that support the actions of these parts of the body, in addition to any direct cognitive benefits they have, improve the functioning of the brain.
Chaga mushroom can be purchased from Mountain Rose Herbs as a course powder which can easily be brewed alongside coffee to create a chaga coffee. Nootropics Depot also sells a 1:1 chaga extract powder which is more concentrated in active ingredients and mixes very easily into any beverage.
Chaga is an ingredient that’s part of a nootropic coffee blend that I absolutely love, and if you’re a regular coffee drinker then I recommend you learn more about the best nootropic coffee, as that provides an easy route to creating a daily habit which will help reduce your brain fog and also dependence on coffee. One cup of this nootropic coffee is enough to power you throughout the day without any need for additional cups of coffee, which helps to reduce the possibility of a caffeine tolerance building up, something which commonly occurs with people who are trying to stimulate away their brain fog. More on that below.
Cordyceps Mushroom
Cordyceps mushroom is another medicinal mushroom that has broad health benefits, it’s especially well-known for its physical endurance and stamina promoting effects. The exact mechanisms for how cordyceps improves energy metabolism isn’t known, but its thought to interact and improve the functioning of mitochondria, the energy powerhouses of our cells. By improving mitochondrial function, cordyceps not only improves physical energy levels but also mental energy levels, especially if taken daily.
I supplemented with cordyceps mushrooms extensively to aid in my weight training a few years back, and I could tell one of the reasons it improves physical endurance is by increasing mental focus. It’s easier to push through something when you’re more focused on your desired outcome, and if chronic mental fatigue is a problem during work or any other time of the day where focus is required, then cordyceps will help. Cordyceps can also be used to help treat acute fatigue, it’s a supplement that can be used for both acute and chronic tiredness and brain fog.
I share my full experience with cordyceps mushroom and talk about it more with my friend Rob in this video interview.
Cordyceps mushroom can be purchased from Mountain Rose Herbs, and Nootropics Depot also sells a 1:1 cordyceps mushroom powder as well as a 10:1 cordyceps mushroom powde, both of which are concentrated in cordyceps’s main active ingredients.
Lion’s Mane Mushroom
Lion’s mane mushroom is another medicinal mushroom useful in improving the functioning of the brain, but it’s a bit different than the others because it has been well shown that lion’s mane promotes neurogenesis! Neurogenesis is the growth of new neurons, and any brain under stress and experiencing chronic fatigue is a brain that is losing brain cells due to increased inflammation and apoptosis. One way to turn around overall neurocognitive conditions, either minor like brain fog or more major like dementia, is to increase neurogenesis in the brain.
Supplementing with lion’s mane mushroom, either with a lion’s mane extract like the one sold by Mountain Rose Herbs, or with more condensed supplements like the 1:1 lion’s mane mushroom powder or the 8:1 lion’s mane mushroom powder sold by Nootropics Depot, is an excellent way to incorporate the neurogenesis benefits of lion’s mane into your everyday life.
My friend Rob from Secrets of the Underground made a good video which explores the benefits of these four medicinal mushrooms along with turkey tail (another good one), and you’ll see a cameo of me starting at 07:44 ;)
Note - Yes lots of YouTube videos in this article from myself or my friend Rob, and if you want to reinforce what you’ve learned in this article then I suggest you add these videos to your watch later playlist and enjoy them at some future point in time.
Gut Health for Brain Fog
While this recommendation isn’t a supplement, for your best success in overcoming mental fatigue it’s necessary to mention the very important role gut health has in the development of mental fatigue and mental health problems. The gut and brain are linked via what’s known as the Gut-Brain Axis, and when the digestive system is functioning poorly and microbiome is pathogenic in nature, then the functioning of the brain suffers. Once you learn of how this connection works, then it becomes much easier to consciously make choices which improve the functioning of your gut-brain axis and therefore your mental health and overall wellness.
Gut-Brain Axis
The gut-brain axis is a bidirectional connection pathway that exists between the gut microbiome and nervous system + brain, and not only does the microbiome effect the functioning of the brain, but conditions of the nervous system and brain like stress, anxiety, depression, insomnia, and more in-turn effect the microbiome and gut.
Put simply, if you want your brain to work optimally, then attention must be given to gut health and the condition of the microbiome. The gut and brain are connected together via four main pathways:
Neurologic - Neurologic signals are sent between the gut and brain via the vagus nerve, with neurologic signals being the fastest mode of information transfer between the gut and brain.
Endocrine - The digestive system is a key component of the endocrine (hormone) system, and changes in the functioning and expression of the gut alter the overall status of the endocrine system and hormonal secretion as a result.
Metabolic - Compounds with metabolic functions that the microbiome produce like short-chain fatty acids influence overall metabolism which then affects cognitive ability. Having unstable blood sugar levels for example can result in periods of focus-scattered hyperactivity followed by energy crashes and brain fog.
Immune - The immune system protects the body from foreign microorganisms and unwanted compounds, and in the cleanup process they produce inflammatory cytokines. If the immune system is overly stressed then inflammation becomes rampant throughout the body and brain, which effects physical, mental, and emotional status.
Cultivate a Healthy Microbiome
Humans have co-evolved with microorganisms for millions of years, and having a healthy microbiome is so important for overall health and wellness in many different ways. The types of microorganisms that inhabit the gut have a big impact on general brain health, neurocognitive and neurodegenerative disorders, and brain performance.
To explain the relationship in more detail, microorganisms produce chemicals that are either useful or harmful to the body. In the large intestine where most of the gut microbiome resides, symbiotic (helpful) and pathogenic (harmful) microorganisms reside. Symbiotic and pathogenic microorganisms compete against each other for resources and space, and to survive pathogens produce and release toxins into their immediate environment. These toxins hurt symbionts, degrade gut tissues, reduce overall digestive function, and if absorbed into the bloodstream create inflammation throughout the body and brain. Symbiotic microorganisms on the other hand produce natural antimicrobial compounds which keep pathogens in check, and if symbiotic microorganisms are fed with fiber and flavonoids, they respectively produce short-chain fatty acids and beneficial secondary metabolites which are biologically beneficial for metabolism, cognitive health, and gut health.
A microbiome with too many pathogens exposes you to greater levels of toxins than your body can normally cope with and handle without much fuss, and a common result of having this type of microbiome is poor gut health, chronic inflammation, and brain fog.
Luckily shifting the microbiome towards greater symbiotic function is relatively simple! It’s outside the scope of this article but if you’d like to learn how you can do this you can read my article How to Restore Healthy Gut Flora or purchase the Holistic Gut Health Guide which covers how to improve gut naturally in-depth.
Together the digestive system and microbiome are the foundation of health from which everything else is dependent on.
The Holistic Gut Health Guide contains all the information you need to identify and understand the gastrointestinal and microbiome problems you may have while also providing you the most effective natural methods you can use to heal your gut. No gut health problems are unsolvable, give yourself every possible advantage along your gut health journey by reading an implementing the advice shared in the Holistic Gut Health Guide.
Ashwagandha for Brain Fog
Ashwagandha is a powerful adaptogenic herb well-known in the ayurvedic system of medicine that contains many beneficial compounds such as alkaloids, lactones, and saponins. Ashwagandha is an herb that can be used to treat both acute or chronic mental fatigue. Ashwagandha has the following cognitive benefits:
Ashwagandha leaf and root extracts reduce symptoms of anxiety, comparable to pharmaceutical drugs
Ashwagandha inhibits nerve cells from over firing
Slows, stops, and even reverses neural decay by promoting the growth of new neurons and by creating new synaptic connections
Comparable to pharmaceutical drugs in reducing symptoms of depression, stabilizes mood
Normalizes dopamine levels to normal, increasing dopamine levels in those suffering from Parkinson’s disease
Intensifies acetylcholine, glutathione, and secretase enzyme activity
Inhibits the production of amyloid beta plaques in those suffering from Alzheimer’s disease
Helps to reverse addiction through its balancing actions on neurotransmitters GABA and serotonin
All of these cognitive benefits help with mental stress, and ashwagandha further helps with mental fatigue through how it supports the functioning of the adrenal glands. An interesting effect of ashwagandha is if it is supplemented before a stressful event/task, the stress response and the amount of cortisol that is secreted after the stressor is greatly blunted, allowing for faster recovery.
Mental fatigue and the corresponding brain fog is often a result of a dysfunctional Hypothalamic-Pituitary-Adrenal (HPA) Axis. the endocrine glands of the HPA-axis influence a lot of biologic functions throughout the body and one’s physiological status, and when the HPA-axis is constantly loaded with greater demands due to stress, it becomes deficient in necessary nutrients and changes its secretion of hormones in response to the demands placed upon it. By stopping the adrenal glands, and the HPA-axis in general, from generating a strong reaction to a stressful event, it provides an opportunity to the body to recharge and begin returning to normal physiological function.
For treating acute bouts of mental fatigue, ashwagandha is best used before the stressful event is to occur, or as soon as possible after it’s happened, and for helping with chronic brain fog ashwagandha should be used daily at a lesser dose.
Various ashwagandha products can be purchased from Mountain Rose Herbs, and ashwagandha can also be purchased form Nootropics Depot in a variety of formulations, the two I recommend being the standard ashwagandha powder and the other being the shoden ashwagandha powder.
Caffeine for Brain Fog
Lastly we arrive at caffeine, probably the most well-known and abused compound used to help with brain fog and mental fatigue. Caffeine has been well-studied in how it affects the brain and how it improves certain measures of mental performance like focus, attention span, reaction speed, and more, and caffeine also helps reduce sleepiness. For these reasons caffeine is very effective in ameliorating some of the effects of acute mental fatigue if a preexisting caffeine tolerance doesn’t exist, and what’s common is after people first notice some success with caffeine they begin to consume too much caffeine too often in hope of treating not the acute but the chronic brain fog they have. Caffeine is not useful in treating chronic mental fatigue because its stimulatory, and if overused in this manner it’ll usually make the situation worse.
If you have chronic daily brain fog and mental sluggishness, then I recommend you reduce your caffeine intake (if you’re consuming it) to under 100 mg a day, the equivalent of 1 cup of coffee or a couple cups of tea. To learn more on the science behind how caffeine works and how to do, this read my Caffeine Usage and Tolerance Reset Guide.
With that disclaimer said, caffeine is very effective for helping alleviate an acute bout of brain fog brought on from one-off events like a poor night’s sleep or temporarily increased mental and/or emotional stress. The feeling of brain fog can also sometimes descend when dealing with/studying a very mentally complex and demanding subject, and caffeine can also be used in these situations to assist with the increased information processing demands.
One important note with caffeine is that it blocks the binding of adenosine to adenosine receptors in the brain. If caffeine is consumed too early after waking up, adenosine builds up in the brain, and then when the caffeine wears off the flood of adenosine then causes an energy crash. A better method of using caffeine is to wait 90+ minutes after waking up to consume it, which allows the brain to process a lot of the adenosine in that first 90 minutes, and then when the caffeine wears off later, not as much adenosine is pooled up and ready to activate adenosine receptors.
The most common ways to ingest caffeine are by drinking tea or coffee, though caffeine pills are also a viable alternative.
Green Tea
Green tea is my favorite way to consuming caffeine because each cup of green tea only contains about 30-45 mg of caffeine versus 95 mg per cup of coffee, and green tea also contains plant polyphenols known as green tea catechins which have many beneficial health effects. Green tea also naturally contains L-theanine, an amino acid that helps to stabilize the energy increasing effect of caffeine while simultaneously promoting better sleep. Green tea is a wonderful beverage with a broad holistic effect for treating acute mental fatigue, and with each cup of caffeine containing much less caffeine than a cup of coffee, it’s easier to carefully dose caffeine upwards in a sequential manner with green tea to avoid a caffeine overload and subsequent energy crash.
A variety of green teas can be purchased from Mountain Rose Herbs, Nootropics Depot sells a green tea extract powder and a green tea extract + piperine supplement (piperine is another cognitive boosting compound), and Pique Tea sells green tea crystals that are super convenient and dissolve easily in both hot and cold water.
Coffee
Coffee is the classic beverage of choice fueling millions of people around the world day in and day out, and for good reason! Coffee contains a bunch of beneficial plant phytochemicals, and at ~95 mg of caffeine per cup, one cup of coffee is a significant pick-me-up which can reduce brain fog and the feelings of mental fatigue. Since coffee contains more caffeine than tea, it’s best to stop coffee consumption after 4pm in order to not deviate the circadian rhythm and cortisol secretion (remember caffeine simulates cortisol) too far off normal. The beneficial effects of caffeine greatly taper off after 300 mg, so if you are going to drink more than one cup of coffee, stick to a maximum of three cups in the ideal 90 minutes after waking up to 4pm drinking window.
Other nootropics mix well with coffee, and if you want to experiment with boosting the beneficial mental effects of coffee, then read my article on the best nootropic coffee.
Brain Fog Treatment
How you treat brain fog and mental fatigue is dependent on whether the effect is acute or chronic in nature. Chronic mental fatigue is best treated supplementally with herbs and medicinal mushrooms that activate the parasympathetic nervous system and support the HPA-axis, whereas acute brain fog can be treated preventatively by supplementing with ashwagandha or by using a stimulant like caffeine.
Each of the herbs and mushrooms listed above can be used independently for the treatment of chronic brain fog, but my recommendation would be to brew a tea from a combination of these herbs, for example a 1:1:1 blend of equal parts chamomile:reishi mushroom:green tea would be broadly supportive to the body and brain and overtime will help greatly in reducing chronic fatigue.
If you suspect your mental fatigue is just a symptom of a larger problem like chronic fatigue syndrome, also known as adrenal fatigue, then I suggest you read my article on adrenal fatigue to learn more about the condition and what you can holistically do to turn the issue around.
Medical Disclaimer: All information, content, and material of this website is for informational purposes only and is not intended to serve as a substitute for the consultation, diagnosis, and/or medical treatment of a qualified physician or healthcare provider.
Disclosure: Wild Free Organic is a member of various affiliate programs and if a purchase is made through one of our affiliate links a small commission is received. This does not affect your purchase price. Visit our disclosure page for more information.
References:
Miraj S, Alesaeidi S. A systematic review study of therapeutic effects of Matricaria recuitta chamomile (Chamomile). Electron physician. 2016;8(9):3024-3031.
McCraty R. The Energetic Heart. HeartMath Institute; 2003
Batra P, Sharma AK, Khajuria R. Probing lingzhi or reishi medicinal mushroom ganoderma lucidum (Higher basidiomycetes): a bitter mushroom with amazing health benefits. Int J Med Mushr. 2013;15(2):127-143.
Shashkina MYa, Shashkin PN, Sergeev AV. Chemical and medicobiological properties of chaga (Review). Pharm Chem J. 2006;40(10):560-568.
Das SK, Masuda M, Sakurai A, Sakakibara M. Medicinal uses of the mushroom Cordyceps militaris: Current state and prospects. Fitoterapia. 2010;81(8):961-968.
Ryu S, Kim HG, Kim JY, Kim SY, Cho KO. hericium erinaceus extract reduces anxiety and depressive behaviors by promoting hippocampal neurogenesis in the adult mouse brain. Journal of Medicinal Food. 2018;21(2):174-180.
Zahiruddin S, Basist P, Parveen A, et al. Ashwagandha in brain disorders: A review of recent developments. Journal of Ethnopharmacology. 2020;257:112876.
Cooper R. Green tea and theanine: health benefits. International Journal of Food Sciences and Nutrition. 2012;63(sup1):90-97.
Smith A. Effects of caffeine on human behavior. Food and Chemical Toxicology. 2002;40(9):1243-1255.
Papadopoulos, A., Cleare, A. Hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal axis dysfunction in chronic fatigue syndrome. Nat Rev Endocrinol 8, 22–32 (2012).
Apigenin is Nature's most Powerful Flavonoid
When it comes to fighting cancer few other phytochemicals if any can match the effects of apigenin. Apigenin is a flavonoid most notably found in parsley and chamomile flowers that in addition to its powerful anticancer effects also improves mental health disorders, heals the gut and microbiome, is neuroprotective, and so much more! Learn more about apigenin and the best way to supplement with it.
Article by Stefan Burns - Updated May 2022. Join the Wild Free Organic email newsletter!
In the English Ballad Scarborough Fair, most well-known as sung by Simon and Garfunkel in their album Parsley, Sage, Rosemary, and Thyme, a man and women ask of each other impossible tasks so the other may demonstrate their true love, and sprinkled throughout the song is the refrain of “parsley, sage, rosemary, and thyme”.
To many curing cancer and other chronic inflammation-based diseases likewise seems an impossible task, but if the herbs of the ballad are sprinkled liberally throughout life then true healing is no longer out of reach thanks to the presence of a unique and very powerful anti-cancer phytochemical contained in all those herbs known as apigenin.
In this article we discuss the health benefits of apigenin, what foods to eat to receive more apigenin into the diet, and other high-density ways of supplementing apigenin so you can enjoy all the amazing health benefits of this unique flavonoid phytochemical.
Curly parsley from my 2021 summer garden, zone 7a. Yum!
Pharmacology of Apigenin
Apigenin is a phytochemical flavonoid (more specifically a flavone) naturally produced by plants shown to exhibit several biologic activities such as being an antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial, anti-cancer, neuroprotective, and cardioprotective.
Apigenin is synthesized in a number of plants as secondary metabolite via the shikimate pathway* (how all flavonoids are synthesized). Once apigenin has been produced by a plant it’s bound to sugar molecules in various ways creating what are known as glycosides which are another class of powerful health-promoting phytochemicals. Flavonoids like apigenin are produced by plants for functions like protection against ultraviolet light, defense against insects, fungi, and microorganisms, as antioxidants, and as plant hormone controllers. Just as plants use flavonoids to improve their lot in life, so too can we, with flavonoids like apigenin and quercetin (among many others) raising the efficiency and stable functioning of biologic systems.
Note* - The reason pesticides like glyphosate are so effective at killing bacteria, fungi, and plants is because they turn off the shikimate pathway. Non-organic produce having been grown with disrupted shikimate metabolism will therefore contain much less of the valuable phytochemicals that our bodies crave! Something to consider next time you’re purchasing vegetables and are wondering whether to buy conventional (sprayed with glyphosate) or organic (not sprayed with glyphosate) fruits and vegetables.
Apigenin Bioavailability
Apigenin glycosides are more bioavailable than free apigenin as free apigenin has very poor water solubility.
In the intestines, apigenin is extensively metabolized into forms more readily transported to the liver before being distributed out to tissues of the body. Any apigenin that makes it past the small intestine transits to the colon where it also has biologic effects before eventually being eliminated from the body. Remaining apigenin from the tissues (and some from the liver) are eventually processed by the kidneys and excreted via urine.
From the whole-food source of parsley (the densest source of apigenin known), the excretion half-life for apigenin was observed to be about 12 hours. There exist significant individual variation in the bioavailability and excretion of apigenin, but in general apigenin is absorbed slowly by the body and eliminated slowly by the body (important to discuss further, see side effects section below). No difference in the mean excretion of apigenin has been observed between men and women.
If apigenin is taken in reasonable amounts the long half-life of apigenin proves to be one of its main benefits as a wellness promoting phytochemical. The longer a chemical can stay in the body, the more time it has to exert biologically-relevant effects, and by eating a diet high in apigenin, over time the body builds up consistent levels of apigenin in the bloodstream that keep inflammation low, among many other health improvements.
Apigenin Benefits and Uses
If you’ve read through the herb section of Wild Free Organic, you’ll have found that the theme of many health-promoting herbs is that they are always possess antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and antimicrobial properties. Antioxidants help neutralize free radicals in the body which otherwise would cause oxidative stress and DNA damage. Inflammation isn’t bad per-say as it is vitally important in the healing process, but the out-of-balance modern lifestyle has inflammation elevated way beyond normal levels chronically for many people. And the natural antimicrobial properties of herbs keep the gut’s microbiome healthy and in-check while also sweeping the bloodstream clear of pathogens which increases immunity.
When antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and anti-microbial properties are combined together thanks to flavonoids like apigenin, and biologically relevant amounts are consumed consistently, beneficial actions at the cellular scale are felt at the human scale for example as reductions in cancer, improved sleep and less anxiety, better gut health, and optimized hormone levels for men and women. Apigenin is most popularly known for its anti-cancer, anti-mutagenic, and chemoprotective effects so we’ll start there when discussing the health benefits of apigenin.
Apigenin for Cancer
In most situations when a cell undergoes a genotoxic mutation DNA repair mechanisms kick in and repair the damage or the cell undergoes apoptosis (programmed cell death) and is terminated. If the DNA damage isn’t fixed and the cell doesn’t undergo apoptosis then the mutated cell begins to deviate from its normal behaviors and becomes cancerous.
Apigenin plays an important role in cancer prevention by inducing apoptosis and inhibiting cell proliferation in mutated cells. Apigenin triggers various anti-cancer pathways and activates tumor suppressive genes. Apigenin also further combats the rise and spread of cancer through its binding action to certain proteins and also in how it adjusts certain cellular receptors in their expression and density. Apigenin bolsters all of these anti-cancer effects but also inhibiting excessive platelet adhesion thereby improving the transport of oxygen, nutrients, and immune cells throughout the body.
One special trait of apigenin is that it is able to overcome the multi-drug resistance some tumor cells have by inhibiting the viability of the mutated cells while increasing their cellular uptake of doxorubicin (a chemotherapy medication).
Apigenin is one of the most powerful anti-cancer phytochemicals currently known and for anyone who has cancer reading this I would suggest you read the full research paper linked as the sixth reference for this article (see end).
Apigenin for Sleep
Apigenin binds to benzodiazepine receptors in the brain which, if taken in high enough doses, can trigger muscle relaxation and sedation.
Chamomile is a common source of apigenin, and chamomile is well-known for it’s relaxation and sleep benefits, which can be partly ascribed to apigenin’s neurochemical interactions. Not only does chamomile activate the "rest and digest” parasympathetic nervous system, it also improves day-time functioning because 8-12 Hz alpha brainwaves are increased in power. Alpha brainwaves are the gateway between wakefulness and sleep, and strong alpha brainwave activity in general is correlated with higher levels of consciousness.
Apigenin for Anxiety and Depression
Anxiety, depression, insomnia, and other mental health issues are central nervous system (CNS) related disorders, and apigenin’s influence over the CNS is beneficial in reducing these mental health issues. There is increasing awareness surrounding the effectiveness of phytochemicals like apigenin or sulforaphane in treating mental health issues, and an important thing to know then if seeking to use natural alternatives for mental health treatment is the effectiveness of a bioactive compound is determined in part by its ability to pass through the blood-brain barrier. Of the many flavonoids that exist, apigenin is near the top of the list in its ease of penetration of the blood brain barrier.
Apigenin reduces anxiety, depression, and other central nervous system disorders through a few different factors. Apigenin upregulates the production of brain-derived neurotropic factor, an important protein for nerve cell growth and survival. Apigenin lowers stress-induced alterations in the brain and it reverses mild stress-induced increases in corticosteroid hormones. Apigenin possibly has a role in modulating the neurotransmission activity of noradrenalin, dopamine, and serotonin, and by doing this apigenin helps to prevent abnormal behavior.
The beneficial neuroprotective effects of apigenin listed in the next section are also applicable to this section.
Apigenin is Neuroprotective
As a neuroprotective agent, apigenin reduces oxidative damage, neural inflammation, and activation of the central nervous system’s immune microglial cells. Apigenin has been shown to cause a reduction in amyloid deposits in the brain and it has an ameliorating effect on Alzheimer’s disease. Apigenin causes improvements in memory, most notably spatial learning and memory.
Possibly one of apigenin’s most important effects is that is has a neurovascular protective effect, helping to keep the brain well supplied with oxygen and nutrient-rich blood. Not only does apigenin have an easy time passing through the blood-brain barrier, its presence also maintains the healthy status of the brain’s vascular network, which is a win-win.
Apigenin for Gut Health
Not all flavonoids will be absorbed in the small intestine, and any flavonoids (like apigenin) that reach the colon beneficially interact with the microbiome there. Flavonoids and their metabolites alter the microbiome by inhibiting the growth of various pathogens while increasing the beneficial genera such as Bifidobacterium and Lactobacillus. Through these actions gut health is improved because endotoxin production is reduced, the conversion of primary into secondary bile acids is increased, and overall nutrient absorption increases. Flavonoids are one of the best things to ensure you’re getting adequate amounts of in your diet if looking to heal gastrointestinal issues or maintain good gut health. Flavonoids improve intestinal barrier function by strengthening epithelial tight-junctions which has a big impact on reducing gut inflammation.
If you are experiencing gut health problems then the Holistic Gut Health Guide is the all-in-one-guide you need to begin healing your digestive system and microbiome.
Apigenin for Women
As women age hormone levels decline, notably progesterone which affects the functioning of various neurotransmitters like GABA. Women with lower progesterone levels at any age have a greater likelihood of experiencing depression, anxiety, irritability, and insomnia. Headaches, migraines, and mood changes are more common, as is irregularity in the menstrual cycle. Apigenin has some effect in improving progesterone levels and thus can help mitigate the effects of low progesterone levels in women of all ages.
Apigenin for Men
The two main ways apigenin specifically helps men is in regards to their hormonal and prostate health.
Apigenin and Testosterone
Apigenin broadly improves the function of Leydig cells, the cells responsible for testosterone production in the testes. Apigenin also reduces heat-induced damage to the extremely heat sensitive Leydig cells. Apigenin enhances steroidogenesis by increasing the sensitivity of Leydig cells to cAMP stimulation.
In addition to improving steroidogenesis, apigenin can promote skeletal muscle hypertrophy and myogenic differentiation of muscle cells through its actions as a potent aromatase inhibitor (like most plant flavonoids). Aromatase is an enzyme that converts androgens like testosterone into estrogenic hormones like estradiol, and by inhibiting the action of aromatase enzymes throughout the body more androgenic hormone levels can be maintained.
Apigenin for Prostate Health
Plant flavonoids like apigenin induce apoptosis in prostate carcinoma (epithelial cancer) cells by inhibiting fatty acid synthase, a long chain fatty-acid synthesis enzyme that is over-expressed in prostate cancer cells. Apigenin also changes various cellular pathways the inhibits the growth of prostate cancer. One of these pathways is the uptake and accumulation of apigenin in the nuclear matrix of a cell, binding apigenin to DNA which reduces oxidative DNA damage and apoptosis in healthy prostate epithelial cells.
One of the main concerns regarding any chemotherapy treatment is how it also damages and kills healthy cells alongside mutated ones. By protecting healthy cells and by fighting cancer in its own way apigenin is truly a miracle flavonoid that is easily and safely added alongside existing cancer treatment options.
What is Apigenin Found In?
As a plant-created flavonoid apigenin is found in a variety of herbs, fruits, and vegetables. Most commonly apigenin isn’t found in its free form but bound as one of its various glycosides. For example apigenin does not occur in living chamomile flowers, instead residing in the plant as apigenin 7-glycoside and its derivatives. Once harvested some of the apigenin glycosides convert into free apigenin.
Whether an apigenin containing food is eaten fresh or dried (a denser source), the apigenin will be absorbable.
Herbs High in Apigenin
Parsley is the richest known source of apigenin and there is nothing else that comes close. Fresh parsley contains ~2.2 mg of apigenin per gram of fresh parsley. With its water content removed dried parsley is an even denser source of apigenin coming in at ~45 mg/g.
Chamomile (Matricaria recutita) is another source of apigenin that’s well-known, with dried chamomile flower containing 3-5 mg/g.
Peppermint contains 0.055 mg of apigenin per gram of fresh leaves, and the apigenin density is higher in dried peppermint.
Thyme contains ~0.025 mg of apigenin per gram of fresh leaves, and dried thyme has a higher apigenin density.
Oregano contains ~0.025 mg of apigenin per gram of fresh leaves, and dried oregano is an even denser source of apigenin.
Sage, rosemary, and tea leaves are other sources of apigenin. Lastly one important thing to note regarding the apigenin content of herbs, and this also applies more broadly to all polyphenols found in herbs, is that there typically is a significant increase in total polyphenols from April to September, so the apigenin content of food does vary with the seasons.
Fruits and Vegetables High in Apigenin
Since apigenin is a common flavonoid it’s found in some concentration in most fruits and vegetables.
Celery is a vegetable known for its high apigenin content, and all parts of the celery plant contain apigenin in different ratios. Celery seed has the densest concentration of apigenin at 0.8 mg/g, whereas celery hearts have a lower density of 0.02 mg/g, and celery stalk is even lower still at only 0.003 mg/g.
Other fruits and vegetables known for their apigenin content are rutabaga, green chili peppers, onions, and oranges.
Liposomal Apigenin
The health benefits of apigenin are becoming more well-known in the medical field and it’s common to be recommended liposomal apigenin for a variety of health reasons. A liposome is a spherical drug delivery vehicle made of a lipid bi-layer that increases bioavailability of the nutrient encapsulated within it into the bloodstream. Apigenin is already very bioavailable and liposomal apigenin is only really useful in the context of shuttling the majority of the apigenin into the bloodstream, whereas normally the tissues of the digestive system will absorb and use some apigenin themselves, some apigenin will make it into the bloodstream, and some apigenin will also make its way to the microbiome of the large intestine.
There are benefits to letting apigenin naturally be distributed throughout the body, specifically having apigenin make it to the microbiome is very valuable for the gut-brain axis, metabolic health, and the cardiovascular system. The microbiome produces biologically useful secondary metabolites from flavonoids like apigenin, and for this reason supplementing with a natural source of apigenin like dried parsley is preferred.
Apigenin Side Effects
There is some concern that exist regarding apigenin and its potential to build up in the body based on its half-life in rats, which is 92 hours. The half life of apigenin in humans though is 12 hours, and there is little evidence to suggest that apigenin builds up to dangerous levels or promotes adverse metabolic reactions when consumed as part of a normal diet.
Direct supplementation of high doses of isolated apigenin can result in liver toxicity over time, and its for this reason that I believe its best that those who wish to supplement with apigenin capsules don’t supplement with them daily and instead follow a more holistic approach, sticking with whole foods and herbal teas. Information for those interested in supplementing with high doses of apigenin and for others who want to follow the holistic approach is below.
Supplement Apigenin
There are two main methods to follow when supplementing with any compound or chemical. The first method is to supplement with the desired chemical just 1-3x at a high dose for an acute effect. The second method is to incorporate into the diet natural sources of the desired chemical for much broader long term health benefits. With good understanding of what a chemical does and its safety profile methods 1 and 2 can be combined. We’ll start with the low-dose daily way to add apigenin into the diet and then progress upwards towards the most potent forms available.
Chamomile, Dandelion, Peppermint Tea for Apigenin
An excellent way to add extra apigenin to the diet is to drink a 1:1:1 chamomile, dandelion, and peppermint herbal tea. This herbal tea blend is so powerfully healthy for you because of the presence of flavonoids like apigenin, quercetin, and hundreds of other health-promoting phytochemicals.
All three of these herbs are powerful antioxidants, anti-inflammatories, and natural antimicrobials. Drinking this tea will boost your immune system and help you get over a cold/flu/covid faster, will reduce symptoms associated with inflammation-based and autoimmune diseases, and is excellent for healing the digestive system and keeping it functioning at a high level. I’ve writen more about the benefits of drinking herbal teas for improving gut health and for use during fasting, and if you’re currently facing gut health problems I highly encourage you to learn more.
Drinking herbal teas is one of the best preventative health strategies that exists. Each cup is packed with biologically useful phytonutrients that the body craves, and with so many different herbs that exist it never gets boring. Drink a cup or two of chamomile/dandelion/peppermint tea a day and with the 12 hour half life of apigenin it’s not an issue if a few days are missed every now and then. All three of these herbs are extremely safe with no known toxicity concerns.
Mountain Rose herbs sells organic dandelion root, chamomile flowers, and dried peppermint leaves.
Dried parsley for Apigenin
Dried parsley is a ridiculously dense source of apigenin coming in at ~45 mg/g. While pure apigenin supplements do exist as you’ll see below, dried parsley is the best way to supplement with high amounts of apigenin because in addition to receiving the apigenin you also receive all the other useful vitamins, nutrients, and phytochemicals that parsley has to offer. Parsley is a dense source of vitamin C, vitamin A, vitamin K, calcium, and iron. All of the components that make up parsley aid in the bioavailability and health effects of the other components in what’s known as the entourage effect. So when using dried parsley to intake higher levels of apigenin (for example to aid in the fight against cancer), you not only receive abundant apigenin but lots of other health promoting goodies that would not come when supplementing with apigenin in a standardized pill form.
You can purchase dried parsley in the spice section at the local supermarket or save some money by buying dried parsley online. You can purchase dried parsley on amazon, where it’s usually sold in greater quantities and cheaper in price than the supermarket, or from my favorite supplier of herbs, essential oils, and other health and wellness products Mountain Rose Herbs who also sells organic dried parsley leaf.
Easy ways to incorporate dried parsley into your diet is to mix it into different spreads like cream cheese and hummus, to sprinkle it liberally on top of meals like a grain bowl, mix it into soup or paste-type dishes, you get the idea.
Pure Apigenin Supplements
Highly standardized apigenin supplements can be useful under certain circumstances. For example if someone is having severe gut health issues and even dried parsley is likely to cause too much gastrointestinal upset, then a pure apigenin supplement can be useful combined alongside herbal teas. Nootropics Depot sells a few different supplements that contain apigenin, most notably they sell a raw 98% apigenin powder that’s also available as 98% apigenin capsules.
Try Herbalism
A final message to leave you with is to never underestimate the healing power of natural remedies, a great introduction being herbal teas. A lot of supplements are very expensive and have poor safety and quality testing. For the same price or less as a few different health supplements an entire assortment of health-promoting herbs can be acquired through a supplier like Mountain Rose Herbs. Try natural herbal remedies at least once and see if they can help you. A good place to start learning more about herbs is on the herbs section of this website.
References:
Ali F, Rahul, Naz F, Jyoti S, Siddique YH. Health functionality of apigenin: A review. International Journal of Food Properties. 2017;20(6):1197-1238.
Nielsen SE, Young JF, Daneshvar B, et al. Effect of parsley (petroselinum crispum) intake on urinary apigenin excretion, blood antioxidant enzymes and biomarkers for oxidative stress in human subjects. Br J Nutr. 1999;81(6):447-455.
Salehi B, Venditti A, Sharifi-Rad M, et al. The therapeutic potential of apigenin. IJMS. 2019;20(6):1305.
Pei R, Liu X, Bolling B. Flavonoids and gut health. Current Opinion in Biotechnology. 2020;61:153-159.
Higdon J. Flavonoids. Micronutrient Information Center, Linus Pauling Institute, Oregon State University. https://lpi.oregonstate.edu/mic/dietary-factors/phytochemicals/flavonoids
Shankar E, Goel A, Gupta K, Gupta S. Plant flavone apigenin: an emerging anticancer agent. Curr Pharmacol Rep. 2017;3(6):423-446.
Medical Disclaimer: All information, content, and material of this website is for informational purposes only and is not intended to serve as a substitute for the consultation, diagnosis, and/or medical treatment of a qualified physician or healthcare provider.
Disclosure: Wild Free Organic is a member of various affiliate programs and if a purchase is made through one of our affiliate links a small commission is received. This does not affect your purchase price. Visit our disclosure page for more information.
Articles on Herbalism and Nutrition
Heal Adrenal Fatigue
Adrenal fatigue (also known as chronic fatigue) is a dysregulation of the HPA-axis and the hormone cortisol. The condition is characterized by extreme fatigue and out-of-whack hormones. Lifestyle issues and accumulated stress are how adrenal fatigue develops, and changes to lifestyle and diet along with the use of certain herbs and supplements can reverse the condition naturally.
Article by Stefan Burns - Updated June 2022. Join the Wild Free Organic email newsletter!
Small adrenal glands are found above the kidneys which produce a variety of hormones as part of the endocrine system. A common health complaint often heard of is adrenal fatigue. Adrenal fatigue is characterized by the abnormal production of cortisol, an important stress hormone connected to the circadian rhythm and metabolism. The timing and release of cortisol is the last component of a complex pathway of hormones governed by the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis (HPA axis). Cortisol influences other body systems to alter their energy metabolism. Cortisol production is downstream of many hormones so many variables have the potential of affecting cortisol levels, with light being one of the main causal factors.
Because of the complicated pathway that leads to cortisol production, it has been argued that adrenal fatigue is a myth and that no evidence points to adrenal insufficiency in people who suffer from chronic fatigue syndrome (CFS). In this article we examine the evidence for adrenal fatigue, better known as chronic fatigue syndrome, and explore natural treatment options that may help restore balance to the HPA axis.
Note - This article does not constitute as medical advice, it is presented for informational purposes only. For medical conditions please consult a medical professional.
Is Adrenal Fatigue Real?
Before a discussion of treatment options to help heal adrenal fatigue, we must first determine if it actually exists or whether the symptoms of adrenal fatigue are due to an unidentified state of disease elsewhere in the body.
Common Symptoms of Adrenal Fatigue
Poor metabolism, weight gain
Low energy, generalized fatigue
Difficulty waking up, unrefreshing sleep
Impairment in short-term memory and concentration (brain fog)
Low stress tolerance
Overuse of stimulants
Lesser Symptoms of Adrenal Fatigue
Anxiety
Tender lymph nodes
Muscle and joint pain
Sore throat
Headache
Low libido
Examining the symptoms, we can see that they are quite broad in scope but generally deal with the metabolism, disrupted circadian rhythms, degraded cognitive function, and tender/painful body parts. The hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis is responsible for governing many of the systems that could exhibit the above symptoms, especially when immune dysfunction and neurochemical alterations are taken into effect.
Adrenal fatigue and chronic fatigue syndrome are different terms that describe the same issue, and the causal factors for these fatigue problems aren’t strictly defined yet because the system has proven complex to understand. That said, there are a few known factors that are well associated with adrenal fatigue which will be discussed below.
Main Factors of Adrenal Fatigue
Across the many studies that have been done on those with chronic fatigue syndrome and health controls, the most commonly observed changes are (1):
Mild hypocortisolism (low cortisol)
Attenuated diurnal variation of cortisol (less cortisol variation)
Blunted HPA axis responsiveness
Enhanced negative feedback by cortisol on the production of certain hormones by the hippocampus, hypothalamus, and pituitary glands.
Women are more likely to show hypocortisolism than men, and experiencing the abnormalities above is more probable for people who are inactive and/or depressed.
Examined biologically, adrenal fatigue is characterized by low cortisol levels and blunted cortisol plasma variation across the diurnal (24 hr) cycle (which governs in large part the wake/sleep cycle and energy levels throughout the day). In addition to hypocortisolism, HPA axis responsiveness is blunted by enhanced negative feedback.
Hypothalamic-Pituitary-Adrenal Axis (HPA Axis)
Cortisol hormone is one of the end products of the HPA axis, and cortisol also cyclically regulates the functions of the HPA axis through its actions on glucocorticoid and mineralocorticoid receptors. Glucocorticoid receptors are found in the hypothalamus and anterior pituitary gland. Mineralocorticoid receptors are found primarily in the hippocampus.
CC Sandi, C. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 5, 917–930 (2004).
Hippocampus
The hippocampus is a major component of the brain consisting of two hippocampi, one of each side of the brain. As part of the limbic system, the hippocampus is important for the consolidation of information from short-term memory to long-term memory, as well as in spatial memory used for navigation. The hippocampus is one of the first regions of the brain to suffer damage with Alzheimer's disease and other forms of dementia.
Hypothalamus
The hypothalamus is part of the limbic system and regulates certain metabolic processes and activities of the autonomic nervous system. Hormones are synthesized in the hypothalamus that stimulate or inhibit the secretion of hormones from the pituitary gland. The hypothalamus controls circadian rhythms, body temperature, sleep, fatigue, thirst, hunger, and attachment behaviors.
Pituitary Gland
The pituitary gland regulates hormone activity in other endocrine glands and organs. The pituitary has an anterior and posterior lobe. Hormones produced by the anterior pituitary include growth hormone, thyroid-stimulating hormone, adrenocorticotropin hormones, luteinizing hormone, follicle-stimulating hormone, and prolactin. Hormones produced by the posterior pituitary lobe include oxytocin and vasopressin.
How Adrenal Fatigue Develops
Cortisol is one of the bodies main stress related hormones, and it is release in a diurnal cycle in response to stress and low blood-glucose levels. Cortisol increases blood sugar through gluconeogenesis and aids in the metabolism of fatty acids, proteins, and carbohydrates. Cortisol also suppresses the immune system and decreases bone formation.
When engaging in acutely stressful activities such as strength training or cardiovascular exercise, cortisol is released from the adrenal glands to increase metabolism, blunt pain, and improve performance. Social stressors at work or home can also increase cortisol production, and cognitive behavioral therapy is able to reverse some HPA axis changes associated with adrenal fatigue.
Many of the activities that benefit from the increased stimulation of cortisol by the adrenal glands are health promoting when done in moderation against the backdrop of a low-stress lifestyle. Adrenal fatigue develops when increased cortisol stimulation is abused by excessive exercise and activity, social stressors, a poor diet, abuse of psychedelics, and poor sleep. Adrenal fatigue can also result from inactivity, a factor which highlights the importance of exercising in moderation for optimal wellness. Cortisol is a feel good hormone which can ease the feeling of pain and promote feelings of euphoria. One of the ways adrenal fatigue can develop in the first place is because its overstimulation overtime can be slightly addicting, and that encourages repeat behavior.
Adrenal fatigue is commonly observed in a few subsets of people. One group has a high-stress job and also excessively works out while restricting their calories to lose weight. Adrenal fatigue is also observed in overweight individuals who are extremely inactive. Adrenal fatigue is a widespread problem that affects people from a variety of lifestyles because the HPA axis can become deregulated in a variety of ways. Women are more susceptible to developing chronic fatigue then men.
Abuse of the metabolic pathways governed by cortisol dampens the parasympathetic (rest and digest) nervous system and overstimulates the sympathetic (fight or flight) nervous system. Left unchecked, excessive cortisol stimulation overtime makes it harder to go parasympathetic, compromising the bodies recovery and healing mechanisms. Muscle and joint inflammation increases, bone strength decreases, the endocrine system is altered in function, libido lowers, and chronic stress and fatigue accumulate eventually resulting in even larger health problems if left untreated.
My Experience with Adrenal Fatigue
I first realized I was experiencing some level of adrenal fatigue after I recovered from SARS-CoV-2 early in 2020. My immune system was suppressed from an overindulgence in strength training while stress at work was increasing steadily. I was also dry-vaporizing cannabis regularly which had an effect on my metabolism and endocrine system.
While I was knocked out for 7-10 days because of the coronavirus, I realized that I had been placing too much stress on myself and on my adrenal glands, dysregulating my HPA axis. Afterwards I took a step back from lifting weights and shifted my exercise to calisthenics, walking, and yoga. A few months later I transitioned to a plant-based diet which further helped me recover from the mild chronic fatigue I had.
Now with a properly functioning HPA axis, my blood pressure is lower, my digestive system is healthy, I’m calmer and more emotionally stable, and I make better food choices. I’m more focused, no longer have any anxiety, and I enjoy restful sleep.
When plagued with chronic fatigue, it’s difficult to see how to get out of it because the energy to do anything is so low. Motivation feels ethereal, willpower is seemingly nonexistent, and depression may also be a factor. For these reasons it’s important to keep the treatment for chronic fatigue simple and to slowly build on the success first gained by various methods available.
Treatment for Adrenal Fatigue
When it come to treating adrenal fatigue, it’s suggested to start with the “low hanging fruits” that will provide quick and immediate improvements to one’s condition. Remember cortisol is a stress hormone connected to the circadian rhythm and metabolism, and by manipulating these variables fatigue can be reduced.
Diurnal cortisol variation averaged across 28 individuals. CC Whitaker, Martin et al Clinical endocrinology 2014;80554-61
Adrenal fatigue occurs when there is an accumulation of chronic stress that hasn’t been properly recovered from yet. Focusing first and foremost on restful activities will help to reduce and eliminate built-up chronic stress an inflammation while also resensitizing the HPA axis to normal function.
Prioritizing SLEEP is the first thing that should be done. Everyone receives the same 24 hours in a day, and setting aside a quality 8 hours a night for sleep is foundational to reducing and eliminating adrenal fatigue. There will be times where sleeping for the normal 7-9 hours isn’t possible, so when those variations are unavoidable, keep in mind the overall number of 56 weekly hours of sleep and catch up when possible. Catching up on sleep has the best success on the day following a shortened sleep cycle. Some simple advice is to listen to your body and to enjoy a nap if feeling tired.
Have time to REST and decompress every day. This doesn’t have to involve closing the eyes and can instead be performing some self-care, enjoying a peaceful walk through nature, or simply reading a book. When dealing with excessive muscle and joint inflammation and fatigue, Yin Yoga is great way to facilitate the recovery process while keeping energy expenditure low.
ESTABLISHING A ROUTINE and making a habit out of following a normal sleep cycle and resting when needed makes it easy to begin enabling positive incremental changes day by day without having to rely solely on motivation or willpower (which fluctuate). How each day is started determines in large part one’s physical, mental, and emotional status throughout the entire day. Simple movement, meditation, and BREATHING EXERCISES gently activate the metabolism and bring balance to the body and mind.
While making these lifestyle adjustments, the following herbs, supplements, and dietary changes can be made in tandem to facilitate the healing of chronic fatigue and the return to normal cortisol function.
Herbs for Adrenal Fatigue
There are many herbs that effect the energetic systems of the body and there are many ways the HPA axis can become dysregulated, therefore it is best to use adaptogenic herbs which help bring the systems of the body into balance irrespective of the starting conditions.
Ashwagandha for Adrenal Fatigue
Ashwagandha is a grounding and nourishing herb found in India. Popular in Aryuveda.
Helps to cope with stress and enhances sleep
Increases vital energy and balances hormones
Supports overall cognitive health
Ashwagandha - from Mountain Rose Herbs
Siberian Ginseng for Adrenal Fatigue
Siberian Ginseng is also known as eleuthero root and is native to Siberia (Asia). Eleuthero root is mildly stimulating.
Supports the adrenals, boosts the immune system, and fights fatigue
Reduces inflammation, improves sleep, and helps with depression
Improves vital energy, sexual energy, and enhances digestion
Siberian Ginseng - from Mountain Rose Herbs
Reishi Mushroom for Adrenal Fatigue
Known as the mushroom of immortality and found worldwide. Reishi is highly rejuvenating and a potent immune booster.
Has powerful immune strengthening, antiviral, and antitumor properties
Regulates blood sugar and lowers cholesterol by fighting free radicals
Reduces fatigue and fights depression through its strong neuroprotective effects
Reishi mushroom can be eaten raw, brewed into a tea, tinctured, or made into a herbal broth for soup.
Reishi Mushroom - from Mountain Rose Herbs
Chamomile Flower for Adrenal Fatigue
A gentle herb used worldwide to promote relaxation and calm.
Relaxant, relieves stress and tension, and improves sleep
Promotes the production of alpha brainwaves which increase sense of calm alertness
Supports digestive health, helps with stomach ulcers, and improves regularity
Chamomile Flowers - from Mountain Rose Herbs
Preparation: All of these herbs can be brewed into a tea individually or together in equal parts. Steep at 170 F (75 C) water for 5-15 minutes. These herbs can also be decocted into a tincture.
Supplements for Adrenal Fatigue
The herbs above can also be purchased as supplement pills for use in resolving adrenal fatigue. With a tea or tincture it’s more effective and costs less, but if the ease of use of pills is preferred that option exists.
Other supplements that are useful in healing chronic fatigue include key vitamins and minerals which are used by the endocrine and energy systems of the body.
Vitamins for Adrenal Fatigue
The main vitamins that are useful in the context of adrenal fatigue are the B vitamins, vitamin C, and vitamin D.
B vitamins help with energy metabolism, detoxification, and can have mood-elevating effects. For adrenal fatigue getting enough B vitamins through a food like nutritional yeast or by taking a B vitamin complex can help. I recommend the following vitamin B supplement.
The adrenal gland is one of the organs with the highest concentration of vitamin C in the body because it uses it in the production of all adrenal hormones including cortisol. Adrenal fatigue is marked by chronically reduced cortisol levels, and providing the body more vitamin C ensures that vitamin C is not a limiting factor in the production of normal levels of adrenal hormones. I don’t recommend vitamin C supplements because getting enough vitamin C is easy enough by eating fruits and vegetables, for example one orange contains 90% DV of vitamin C.
Vitamin D is important for the healthy functioning of the endocrine system, and most people are deficient in vitamin D. Vitamin D can be synthesized endogenously by the skin through sun exposure. Depending on skin color and the weather, bathe some or all parts of skin for 10-60 minutes to produce the vitamin D needed for 1-3 days. Limit sun exposure in order to not get sunburnt. If healthy sun exposure is not possible or problematic I recommend Nootropic Depots Vitamin D3 + K2 + C supplement.
Minerals for Adrenal Fatigue
Magnesium and boron are two important minerals which are used extensively throughout the body and supplementation with each is helpful in the context of adrenal fatigue.
Magnesium is the second most common micronutrient deficiency, and getting enough magnesium ensures the bodies hormonal systems, metabolism, and circadian rhythm function properly. Magnesium supplementation in the evening aids in relaxation and improves sleep quality. I recommend the following magnesium supplement.
Boron is a trace mineral which assists the actions of vitamin D and magnesium. Boron has also been shown to have anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects, improving healing from tissues wounds and injuries. Boron improves the brain’s electrical activity, cognitive performance, and short-term memory for elders. Learn more about supplementing with boron.
Herbs for Adrenal Fatigue
There are two herbs that readily come to mind, chamomile and ashwagandha, that help mitigate the symptoms of adrenal fatigue and provide the body the support it requires to overcome and heal the issue.
Tea brewed from chamomile flowers has relaxing and sleep benefiting properties while also having the benefit of improving daytime functioning. Chamomile increases 8-12 Hz alpha brainwaves which provide a sense of stability and calm, and chamomile contains many flavonoids like apigenin which help the brain to repair itself and maintain proper function, important for HPA axis dysfunctions. Mountain Rose Herbs sells organic chamomile flowers which are easy to brew into a tea and can be used for a variety of other purposes.
Ashwagandha is one of the premiere herbs known for its ability to reduce the amount of stress experienced from a stressful event. For example ashwagandha taken before an endurance activity greatly lessens the depletion of cortisol from the adrenal glands in response to the stress experienced, thereby reducing the demand for nutrients like vitamin C for the production of new cortisol. Taking ashwagandha before a stressful event, whether physical, mental, or emotional will help reduce the stress burden that results from after the event which is super useful for those who already have chronic fatigue. Taking ashwagandha daily also is helpful. Mountain Rose Herbs sells organic ashwagandha root powder (recommended), ashwagandha root, ashwagandha root capsules, and ashwagandha extract.
Nootropics Depot also sells a variety of ashwagandha products that have been standardized to contain a certain minimum percentage of withanolides (the main active component of ashwagandha) and I recommend their Shoden Ashwagandha Capsules which has a minimum of 35% withanolides for those looking for a more potent ashwagandha supplement.
Diet for Adrenal Fatigue
There are two aspects of diet that are important in the context of healing adrenal fatigue, or really any health issue.
First is to eat foods that contain the micronutrients the body is currently deficient in. For the nutrients listed above, the following foods can be eaten:
B Vitamins - Nutritional yeast, leafy greens, sunflower seeds, fish, meat, dairy, and fortified grains
Vitamin C - Citrus fruits, parsley, rose hips, peppers, cruciferous vegetables (broccoli, kale, brussels sprouts)
Vitamin D - Fish, eggs, mushrooms (exposed to sunlight), fortified milk
Magnesium - Pumpkin seeds, nuts, avocado, dark chocolate, beans
Second is simply to eat a healthy well-rounded diet full of unprocessed foods which contain enough fiber and protein. This means eating fruits, vegetables, grains, nuts, seeds, and pulses if vegan. If vegetarian eggs and dairy can be added if easily digestible, and if a meat eater then pasture-raised meats and seafood can be further added to the diet. The main takeaway is to avoid sugary and ultra-processed foods is important to make sure cortisol secretion returns to normal because cortisol is released in response to blood glucose levels.
Adrenal Fatigue and Caffeine
Caffeine has an effect on cortisol levels. When caffeine isn’t used regularly, then caffeine will cause a robust increase in cortisol during morning, afternoon, or evening usage. When consuming caffeine on a daily basis, then morning caffeine usage doesn’t impact cortisol significantly but afternoon caffeine usage will elevate cortisol blood concentrations for up to six hours. Even if caffeine creates an afternoon cortisol increase, cortisol levels will drop to normal levels by nighttime.
Since it is the circadian rhythm and cortisol which plays a large part in the wake and sleep cycles of the body, it is important to be mindful of caffeine usage throughout the day and to limit usage of caffeine to time windows that won’t affect normal sleep, unless that is the desired goal. A good rule of thumb to follow is to not have any caffeine after 2 pm.
In the context of adrenal fatigue, it is best to not have any caffeine until the problem is well on its way to being resolved. An abuse of caffeine through heavily caffeinated drinks or excessive coffee usage often is a main factor that led to chronic fatigue syndrome in the first place. For help in quitting caffeine or in resetting a caffeine tolerance, read my caffeine guide:
Reset the Adrenal Glands
Incorporating wellness practices that promote balance into one’s lifestyle has a tremendous impact on health and wellness over the long term. Learning to evenly balance mind, body, and emotions takes time but the effort is well worth the reward. Healing occurs when the body is in a state of balance, so consider adding a morning routine that functions as a “balancing gyroscope”, bringing consistency and balance to day to day life. Establishing a grounding practice outside in nature is a great way to bioelectrically balance the various systems of the body
The human circadian rhythm is driven in large part by the cycles of light and temperature on our planet. Rising with the light and not going to sleep too long after the sun sets is the best way to stay aligned with these natural cycles. If experiencing insomnia and falling asleep is difficult, simply resting at the appropriate times when sleep normally should occur will create the habit of rest during that time window, and with consistency that habit will make falling asleep at regular hours easier.
Healing the adrenal glands and restoring normal function to the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis can take a long time, sometimes months to years. One step in front of the other will lead to eventual success.
As a holistic wellness practitioner I offer coaching services, contact me to learn more.
References:
Papadopoulos, A., Cleare, A. Hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal axis dysfunction in chronic fatigue syndrome. Nat Rev Endocrinol 8, 22–32 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/nrendo.2011.153
Medical Disclaimer: All information, content, and material of this website is for informational purposes only and is not intended to serve as a substitute for the consultation, diagnosis, and/or medical treatment of a qualified physician or healthcare provider.
Disclosure: Wild Free Organic is a member of various affiliate programs and if a purchase is made through one of our affiliate links a small commission is received. This does not affect your purchase price. Visit our disclosure page for more information.
Other Articles on Recovery
What are Hypnagogic Naps?
Hypnagogic naps are quick, just the time it takes to transition from wakefulness to stage 1 of sleep, everyone has done them whether they realize it or not. Hypnagogic naps are easy to perform and are great at boosting creativity, generating ideas, and enhancing lucid dreaming. Learn everything you need to know about hypnagogic naps and how to do them here.
Article by Stefan Burns - Updated November 2021. Join the Wild Free Organic email newsletter!
Hypnagogic naps are a prime example of the power of theta brainwaves.
A hypnagogic nap is one where you fall asleep and then through some loud stimulation immediately wake back up.
The classic method is to fall asleep in a chair with a steel ball in one hand and a wide metal pan placed below it. When the transition from wakefulness to stage 1 sleep occurs, the hand relaxes and the ball hits the pan, making a loud sound which wakes the user up.
The red dashed line at about the five minute mark is when a hypnagogic nap occurs. Hypnagogic naps provide a jolt of energy but the amount is insufficient if actual rest is needed. Hypnagogic naps are best performed as part of an experiment and exploration into the many states of consciousness.
Creatives such as Edgar Allan Poe and Salvador Dali used hypnagogic naps in their creative pursuits.
Transition from sleep into wakefulness is known as hypnopompic. Hypnagogic and hypnopompic are transitional "threshold consciousness" phases where hallucinations, lucid thought, sparks of genius, and lucid dreaming can occur.
Using binaural beats can make achieving a hypnagogic nap easier. Theta 4-8 Hz brainwaves are most dominant during a wake to sleep transition, so playing 5.55 Hz binaural beats primes brainwaves of that frequency. Use the video below for short hypnagogic naps or for longer theta binaural beat brainwave therapy.
How to Perform a Hypnagogic Nap
Below are the instructions on how to setup a hynagogic nap via the classic method (ball in hand).
Take a comfortable seated position and lay your arms over the top of the armrests. In one hand, place a heavy object like a stone or a metal ball. Turn on binaural beats if using. 42 Hz binaural beats is recommended instead of the 5.55 Hz track if trying to achieve lucid states and generate radical ideas.
Relax, close your eyes, and begin taking long deep breaths.
Sink deeper into relaxation by focusing on the breath and the thoughtlessness beyond. Deeper….deeper…
POW! The ball has dropped and you’re back!
Another easier way to perform a hynagogic nap is to set a timer for 15 minutes. Though you might not wakeup at the instant you transition to sleep, if a timer is set for 10-15 minutes before dozing off, it’ll start ringing while you’re still in stage 1 of sleep, providing the same benefits as the classic method. I prefer using a 15 minute timer because I find holding onto an object stops me from being able to fall asleep easily.
Entering into the nap calm and rested and a hypnagogic nap cycle takes about 5-10 minutes in total. If agitated and not at ease it can take 10+ minutes to eventually relax enough to then transition to sleep.
The best time to perform hypnagogic naps is on a quiet day free of stress. Mid-afternoon is a good time as there is a natural drowsy lull that sometimes occurs yet wakefulness is still dominant.
The Importance of Sleep
Sleeping is incredibly important for best mental health, lifespan, health, injury…every system in the body suffers if sleep is compromised. Hynagogic naps are one way to quickly rest and boost energy levels but they are not a replacement for regular deep sleep. Everything can be going great but if sleep has been poor then it needs to be the primary wellness focus.
Caffeine Usage and Tolerance Reset Guide
Caffeine is the world's most widely used stimulant for good reason because it has a host of beneficial heath effects when used appropriately. If caffeine is overused and a tolerance develops, there are a few ways to reset a caffeine tolerance that exist. Learn how caffeine works, it's health benefits, recommended usage, withdrawal symptoms, and how to reset a caffeine tolerance with this guide.
Article by Stefan Burns - Updated June 2022. Join the Wild Free Organic email newsletter!
Other than water, coffee and tea are the most popular beverages worldwide, both of which contain caffeine. Caffeine is a neurostimulant which has a variety of effects on the brain and body, most notably caffeine increases attention, arousal, power output, and fat oxidation. Beyond the simple pleasure in enjoying a cup of tea or coffee, people use both beverages, as well as other forms of caffeine, for increasing focus, productivity, and to help stay awake. In moderation caffeine usage poses little risk to health and for most people caffeine usage is beneficial to overall wellness.
In this guide we discuss the psychological benefits of caffeine if used in moderation, what those dosages are, the symptoms that may arise with caffeine overuse, caffeine withdrawal symptoms, how to reset a caffeine tolerance, and recommendations on the best ways to consume caffeine.
How Caffeine Works
The main mechanism of action that explains caffeine’s effects throughout the body is that it blocks the effects of the naturally occurring neuromodulator adenosine.
Adenosine is one of four nucleoside building blocks to DNA and RNA, which are essential for all life. Adenosine mono-, di-, and triphosphates, also known as AMP/ADP/ATP, are organic compound that provides energy to many of the cellular processes vital to life. Adenosine causes sedation and relaxation when it acts upon its receptors.
The chemical structure of caffeine
Caffeine binds to some of the same receptors as adenosine, acting as competitive antagonists and in the process blunting the sedative effects of adenosine. Caffeine’s effect on adenosine changes the activity of neurotransmitters noradrenaline, acetylcholine, dopamine, and others. When caffeine is overused adenosine receptors alter in behavior away from normal and as such the behavior of the important aforementioned neurotransmitters is also changed.
If caffeine is being over used at dosages of >3 mg/kg bodyweight per day, then it takes several days or weeks of caffeine abstinence to return all systems back to normal. With moderate usage (<3 mg/kg) overnight abstinence from caffeine is sufficient in preventing tolerance formation in central nervous system adenosine receptors systems. If you don’t drink more than a couple cups of coffee or tea in a day, and you don’t drink any at night, then it’s unlikely that you have a caffeine tolerance.
Beneficial Effects of Caffeine
There’s the common saying that coffee makes the world go around, and it’s such a popular beverage because of it’s caffeine content of approximately 95 mg per cup of coffee. Caffeine is a mild and relatively safe stimulant that has a number of beneficial health effects. Because caffeine blocks adenosines sedative properties, caffeine is an energy boost for the brain and body. For most people, caffeine usage in moderate dosages at <300 mg/day has the following beneficial effects:
Caffeine improves simple and choice reaction time
Caffeine increases the speed of processing new stimuli
Caffeine increases alertness and reduces fatigue in low arousal situations such as in the early morning, when working at night, when experiencing a cold, with sleep loss, or it can even remove the sedative effects of certain drugs
With illnesses such as the common cold, caffeine can improve mood
For tasks requiring sustained attention, caffeine increases alertness and vigilance when already in a normal alert state
Caffeine eliminates the sleepiness produced by the consumption of lunch
Caffeine usage during the day reduces the slowing of reaction times seen at the end of the day, helping maintain performance levels
Caffeine at night maintains the performance of individuals as seen during the day
Fatigued people show a larger performance boost from caffeine than well-rested people.
High consumption of caffeine (2-3 cups of coffee everyday for long periods of time) is associated with better mental performance in the elderly.
Caffeine reduces depression
Caffeine improves fat oxidation and power output
The standard scientific definition of caffeine moderation is <300 mg per day. The beneficial effects of caffeine start at around 30 mg which is the amount found in a cup of green tea.
When doing performance tasks, the beneficial effects of caffeine are most pronounced when circadian alertness is low. Little evidence suggests there are any impairments following the consumption of normal amounts of caffeine, and while caffeine changes alertness levels, it does not noticeably increase or decrease distractibility.
The benefits of moderate caffeine usage discussed here are what the majority of people who use caffeine will experience. That said, everyone is as different on the inside as they are on the outside, and individual response to caffeine consumption can vary quite a bit among individuals.
Caffeine Sensitive Individuals and Caffeinism
If sensitive to the effects of caffeine, then potential negative side effects of caffeine usage may appear at doses below 3mg/kg bodyweight per day. For others, these symptoms may appear at doses above 3 mg/kg. The main negative symptoms of caffeine which are sometimes experienced include:
Sleep loss
Increased anxiety, especially if stress is encountered
Reduced fine motor control, aka jitteriness
To feel the negative symptoms of caffeine usage, one typically has to consume amounts greater than 300 mg/day. Studies that have shown these negative effects using dosages of 6 mg/kg, 10 mg/kg, or bolus doses such as 600 mg at once.
Daily intake of caffeine in the range of 1000 mg and beyond is known as caffeinism, and at these very high intakes the associated symptoms are virtually indistinguishable from severe chronic anxiety. Anyone that suffers from anxiety is recommended to keep their caffeine intake below 300 mg/day, and if especially sensitive to the effects of caffeine, then lower than 100 mg/day is my recommendation.
How Long does it take for Caffeine to Kick In?
Peak plasma levels of caffeine occur 15-45 minutes after ingestion and begin to decrease from there. The plasma half-life of caffeine is 5-6 hours. If 100 mg of caffeine is ingested, as would be found in a cup of coffee, then caffeine blood concentrations will be highest for the first 2 hours and then decrease steadily.
Metabolism of Caffeine
Most of the beneficial effects of caffeine follow a linear dose-response relationship (that is, the more given the bigger the effect) up to about 300 mg. Beyond 300 mg the beneficial effects typically flatline or even begin to decrease again as undesirable symptoms like anxiety and jitteriness may develop.
How Caffeine and Cortisol Interact
Caffeine has an effect on cortisol levels. Cortisol is a hormone that most notably rises and falls everyday as part of the circadian rhythm. In concert with light and temperature, it’s a peak in cortisol blood concentrations that causes someone to wake up in the morning.
When caffeine isn’t used regularly, then caffeine will cause a robust increase in cortisol during morning, afternoon, or evening usage. When consuming caffeine on a daily basis, then morning caffeine usage doesn’t impact cortisol significantly but afternoon caffeine usage will elevate cortisol blood concentrations for up to six hours. Even if caffeine creates an afternoon cortisol increase, cortisol levels will drop to normal levels by nighttime.
Since it is the circadian rhythm and cortisol which plays a large part in the wake and sleep cycles of the body, it is important to be mindful of caffeine usage throughout the day and to limit usage of caffeine to time windows that won’t affect normal sleep, unless that is the desired goal. A good rule of thumb to follow is to not have any caffeine after 2 pm.
Caffeine and Sleep
The fact that caffeine reduces or removes sleepiness means that it can interfere with normal sleep. Caffeine’s interactions with normal sleep at night depend on how much is taken and when. If large amounts of caffeine are consumed shortly before bed, then for most people sleep will be disturbed.
Caffeine in these situations increases sleep latency, which is how long it takes to fall asleep, and caffeine also decreases sleep duration. The latency increasing effect of caffeine occurs in the first half of the night and reduces as caffeine is metabolized. Interestingly, people who use caffeine frequently will report less sleep disturbances than people who are infrequent users. Infrequently using caffeine makes the effects of caffeine more pronounced as less tolerance has developed, as it is with me. I am caffeine sensitive because I rarely enjoy more than 100 mg of caffeine on any given day.
Green tea is a common source of caffeine, though weaker than coffee, and it’s worth pointing out that green tea also contains an amino acid known as L-theanine. L-theanine has been shown to improve sleep quality because it helps stabilize and increase in amplitude 8-12 Hz alpha brainwaves. As the body and mind wind down at night in preparation for sleep, brainwave frequency decreases from predominately 12-30 Hz beta brainwaves to alpha brainwaves and lower. Deep sleep is characterized by strong 0-4 Hz delta brainwaves and REM sleep is characterized by strong 4-8 Hz theta brainwaves.
Green tea is a unique caffeine containing beverage because consumption of green tea in the morning or early afternoon will provide the user the same beneficial effects of caffeine that many get from coffee while simultaneously improving their sleep at night. L-theanine has also been show to reduce anxiety and to help with the jitteriness that caffeine can cause in high doses. It’s for these reasons I don’t drink coffee often and instead prefer green tea, as it’s a better nootropic compound that also improves gut health and metabolism.
Is 200 mg of Caffeine a lot?
For the average person, 200 mg of caffeine in a day, either taken at once or spread out across 2+ usages, is a moderate amount of caffeine. 200 mg of caffeine would equal about 2 cups of coffee or a few cups of tea.
For a sensitive individual, 200 mg of caffeine can be a significant amount that may cause unpleasant side effects such as anxiety and jitteriness. I’m caffeine sensitive myself, especially if I drink coffee on an empty stomach, and I know that if I have more than 100-150 mg of caffeine at once I become shaky, experience symptoms of low blood sugar, and in general feel unwell. One reason I am caffeine sensitive is because I don’t use large amounts of caffeine often. I drink green tea around 4-5 times a week but even with 3 cups of green tea throughout the day I don’t ingest more than ~100 mg of caffeine.
Since caffeine takes 15-90 minutes to reach peak blood concentrations, I recommend only having one caffeine containing beverage at a time and then waiting to see how you feel. I only recommend the usage of foods that naturally contain caffeine like coffee, tea, or yerba matte, and I advise avoiding high-dosage caffeine containing beverages that are full of sugar, artificial flavors and colors, and other chemicals of questionable nature. The research is clear that when consuming caffeine as found naturally in food products such as coffee and tea, it’s rare to experience negative side effects and most people will intuitively control their caffeine intake to maximize the positive benefits.
Caffeine Withdrawal Symptoms
Caffeine withdrawal symptoms are generally the same as those experienced by caffeine sensitive individuals. The main symptom is headache, followed by increases in anxiety and generalized fatigue. Since the adenosine receptors are recalibrating from the removal of caffeine, extra drowsiness and feelings of low energy may be experienced.
Unless a severe caffeine tolerance has developed, caffeine withdrawal is typically fairly mild and lasts a few days at most. If large amounts of caffeine (>3 mg/kg bodyweight per day) have been consumed for months without break, then caffeine withdrawal will be more severe and can be quite difficult. Most people are able to control their caffeine intake to maximize the benefits while limiting the negatives, but for those whose caffeine usage has gotten out of hand, resetting their caffeine tolerance is highly recommended for overall health reasons
How to Reset Caffeine Tolerance
Heavy habitual caffeine usage leads to an insurmountable tolerance in which more caffeine usage no longer leads to any useful effects except for it’s ability to delay sleep. To reset a caffeine tolerance, the two main methods strategies are to reduce caffeine usage slowly over time, or to completely stop caffeine usage over a period of time. Let’s examine each.
Weaning off Caffeine
The first method available for resetting a caffeine tolerance is to slowly reduce caffeine usage over the course of 2-6 weeks. If consuming 600 mg of caffeine daily, then reducing caffeine usage by 100 mg per week until reaching zero would cause little if any withdrawal symptoms. Once no caffeine is being used, staying at zero usage for a few weeks is recommended. Caffeine’s effects on adenosine receptors in the brain are not yet fully understood and it’s likely best to cycle off from caffeine from time to time in order to return to normal baseline brain activity, and this goes for all users.
While weaning off caffeine it’s also useful to narrow the consumption time window. If coffee is normally consumed anywhere from 6 am to 6 pm, narrowing these hours to 8 am to 12 pm will create less of an impact on cortisol and be beneficial for the overall circadian rhythm.
Quitting Caffeine Cold Turkey
The second method for resetting a caffeine tolerance is to stop all usage of caffeine immediately. While quitting caffeine cold turkey is the fastest method in resetting a caffeine tolerance, it’s also the most likely to produce noticeable withdrawal symptoms. Some individuals don’t do well with weaning off things slowly and though the withdrawal effects may be more severe, they may be most successful with a complete halting of all caffeine. If quitting caffeine dead stop, then a tolerance may be gone in as little as one week, though it’s typically best to stop caffeine usage for 2-6 weeks before reintroducing caffeine back into the diet in moderation.
The Importance of Ritual
Drinking coffee or tea every morning creates a daily habit, and the enjoyable ritual of brewing a steaming cup may be one of the reasons why it’s tough to break the habit of using caffeine. In this case, the ritual of brewing a cup of coffee or tea can be used to one’s advantage. If a heavy coffee drinker, brewing green tea doesn’t break the ritual but provides only about 1/3rd of the caffeine that coffee does, while also having the aforementioned heath benefits that go beyond just those of caffeine. Brewing a cup of decaf coffee also works, though it contains <10 mg caffeine per cup. Mixing regular and decaf coffee into a blend is one way to brew coffee of certain caffeine concentrations.
While rare, if dealing with a caffeine tolerance as a tea drinker, switching to a non-caffeinated peppermint tea for example is a great option. Peppermint tea is tasty and fantastic for brightening the mood while improving gut health.
The Coffee Bean Method
Another effective way of weaning off excess caffeine consumption, more specifically from coffee, is to use coffee beans.
Instead of brewing less coffee day by day, quit coffee cold turkey and have a few coffee beans available at all times. If caffeine withdrawal symptoms appear, simply eat a single coffee bean and move on. At the beginning many coffee beans may be eaten, but fairly quickly into the reset they’re only rarely or no longer needed and the caffeine tolerance is gone. To make it extra effective, eat dark chocolate covered coffee beans! The theobromine found in chocolate is similar to caffeine in effect but functions differently metabolically and won’t affect a caffeine tolerance reset.
Want a Better Coffee?
Coffee can be made better with the addition of a few herbals that support cognition and energy metabolism while have general synergistic effects on health and longevity. I call this herbal coffee blend a dark mocha, learn more about how cacao, cinnamon, chaga mushroom, and cistanche will revolutionize your relationship with coffee.
Switch from Coffee to Tea
While coffee has a bunch of wonderful health effects when consumed black and with no sugar, it’s often a vehicle for more sugar, cream, and calories to enter into the body. Coffee can also overstimulate the digestive system to hurry on up, negatively impacting normal gut motility unless constipated (which requires examination in and of itself).
Because of it’s lower caffeine content, green tea is a gentler way to enjoy the benefits of caffeine while reducing the negatives like increased anxiety and jitteriness. Additionally it’s really easy to add other herbs to green tea and create herbal tea blends that can be used for various medicinal effects. In general I recommend you check out the herb section of this website and explore the many uses and health benefits of herbs more!
I purchase my green tea from two places, Mountain Rose Herbs and Pique Tea.
Mountain Rose Herbs has a bunch of different types of green, white, black and other teas, as well as many other herbs which can also be brewed into tea. For green tea simply heat water to 170 F (75C), pour, and let steep for 5-8 minutes.
My favorite way to brew green tea is part of a vitality blend which also includes ginger root, Siberian ginseng, and Reishi mushroom. All the products from Mountain Rose Herbs are organic and are very cost-efficient.
If convenience is the ultimate goal, then Pique Tea sells tea crystals in small packets which are incredibly easy to use and can be dissolved into hot or cold water. I like their ginger green fasting tea and matcha green fasting tea, available separately or together. Pique Tea has dozens of different teas available in their unique tea crystal packets at different quantities, and even if you primarily brew your tea using using loose ingredients like I do, having some tea crystal packets on hand comes in handy more often than you’d think. Use WILDFREEORGANIC for 5% off at checkout
I hope you found this guide on caffeine and how to reset a caffeine tolerance useful. Overconsumption of caffeine can lead to undesirable effects and many people who overuse caffeine feel trapped because they don’t want to experience the withdrawal symptoms which can be quite unpleasant. If you know someone who is searching for guidance on how to reset a caffeine tolerance, please share with them this guide, they’ll be glad you did!
References:
Smith A. Effects of caffeine on human behavior. Food and Chemical Toxicology. 2002;40(9):1243-1255. 10.1016/S0278-6915(02)00096-0
Lovallo WR, Whitsett TL, al’Absi M, Sung BH, Vincent AS, Wilson MF. Caffeine stimulation of cortisol secretion across the waking hours in relation to caffeine intake levels. Psychosomatic Medicine. 2005;67(5):734-739. 10.1097/01.psy.0000181270.20036.06
Juneja L. L-theanine—a unique amino acid of green tea and its relaxation effect in humans. Trends in Food Science & Technology. 1999;10(6-7):199-204. 10.1016/S0924-2244(99)00044-8
Medical Disclaimer: All information, content, and material of this website is for informational purposes only and is not intended to serve as a substitute for the consultation, diagnosis, and/or medical treatment of a qualified physician or healthcare provider.
Disclosure: Wild Free Organic is a member of various affiliate programs and if a purchase is made through one of our affiliate links a small commission is received. This does not affect your purchase price. Visit our disclosure page for more information.
Other Articles on Performance
Five Wellness Habits to Follow
Life moves fast, and when responsibilities and stress begin to pile up, bad habits can form which make the situation worse. While it takes time to create the wellness lifestyle you desire, you can speed up the process and reduce your stress in the process by following these five simple wellness habits.
Article by Stefan Burns - Updated November 2021. Join the Wild Free Organic email newsletter!
Depending on your current lifestyle, life can move fast, with responsibilities and stress pilling up. When this happens, unhealthy habits are created and used as coping mechanisms which only serve to make things worse. Once habits are formed, it can be hard to get out of those unhealthy routines. Humans are creatures of habit - and that isn't necessarily a bad thing! If mindfulness throughout the creation of a new habit, we can let our unconscious actions better serve our health and wellness.
To make sure that the changes you want to make become healthy habits that don’t cut into your free time or morph into an added stress, start with the basics. The goal is to make life less stressful, and to aid you in the journey here are five easy-to-follow habits to speed your growth into a healthier you!
Drink More Water
Everyone knows the importance of drinking water for optimal health, but 75% of Americans are chronically dehydrated. Dehydration causes fatigue, lead to heat exhaustion, or even cause death in extreme cases. When you keep your body in a state of chronic dehydration, all the major systems of the body are stressed to critical levels. If you were hoping to find a magic wellness potion that will change your life forever, water is the closest thing you've got! Below is a small slice of how water intake impacts your health:
Drinking enough water improves mood, aids concentration, and promotes a clarity of mind.
The detoxification system of the body, led by the kidneys and liver, uses water to filter and flush out toxins through sweat, urine, and feces.
Water is absolutely vital for skin health, and remember the skin is the largest organ of the body!
Water aids in digestion, improving and stabilizing intestinal motility.
Adequate water intake can balance blood pressure to healthy levels by lowering or raising it.
“Water is the foundation of all life as we know it”
If you’ve never made a habit to drink pure water consistently and in adequate volume, then you’ve been missing out of a whole new level of health and wellness. To remedy that, make it a habit to drink water at certain times of day. For instance, have 16 - 32 oz of filtered water everyday right when you wake up. Pairing water intake to events like waking up, finishing work, or before a meal is a good way to ensure you drink the recommended 1 gallon (4 liters) of water per day. There are many ways to make sure you're staying hydrated throughout the day, brainstorm what works for your current lifestyle, so even if you're busy, you’re well hydrated and your fluid intake isn’t a stress factor.
Incorporate Movement into your Life
If you don't have time everyday to exercise or go for a long walk, that doesn't mean you can't move! By squeezing in some movement in-between your regular activities, you can improve your energy levels while laying the foundation for a more structured exercise routine.
If you already work, small bouts of movement done consistently throughout your day will accelerate your fitness goals.
Burn some calories, make small health improvements, and all without a trip to the gym. That’s a win-win and a textbook example of a healthy habit.
To start incorporating more movement into your everyday life, choose exercises you can do quickly and without any equipment. Connect those simple exercises to activities you do often, and eventually that daily task acts as a movement trigger, becoming a habit.
Movement Habits to Follow
Before or after you use the restroom, do 15 squats.
If you're reading a long email or article, hold your arms up high above your head as you're reading and stretch a bit. Don’t be surprised by how quickly your shoulders start to work!
If you watch TV, use the natural breaks to exercise! If you're watching cable, perform sit-ups during the commercial breaks. If you're watching a streaming service like Netflix, do a 1-minute plank or push-ups a couple short of failure in-between episodes.
While heating up food, do some stretching! Quad and hamstring stretches are particularly accessible and can be done anywhere.
Perform a wall sit while brushing your teeth! The guideline for oral health is to brush your teeth for 2 minutes; work your way towards holding the wall sit for the entire duration.
If you're walking up stairs, do 15 calf raises from a step when you get to the top of the flight. The step lets you get a full range of motion, and really gets the calves burning. Practice your balance on the bottom step.
For a more structured exercise routine calisthenics is highly recommended as zero equipment is required, and calisthenics can be performed by all ages. Calisthenics is easy to scale to the individual; if you don’t know how to start, follow a simple calisthenics routine.
Plan Your Meals
Meal-prepping is a game changer, not only for your finances, but also for your diet and time management.
If you have a hectic schedule, once or twice a week, plan out your lunch and dinners for that period of time. Knowing exactly what to shop for while you're at the grocery store keeps your trips short and effective, and keeps you from wasting money on impulse food purchases, which might be more unhealthy or go unused. Cooking ahead of time and having a prepared lunch means you'll consistently be eating healthier, nor will you misuse money or time ordering out. Planning ahead on what to eat for dinner saves you time, money, and increases your schedule flexibility. If a time crunch arises, a healthy meal has been prepared and is ready to go.
For some, meal prepping is the end destination. Personally I like cooking my meals fresh everyday, but meal prepping was certainly a very valuable step on the way towards fully intuitive healthy eating. make sure when meal prepping that you store your food in glass containers to avoid exposing yourself to endocrine disruptors like phthalates, BPA/BPS/BPF.
Eat More Vegetables
As you're preparing your meals, make it a habit to include a serving or two of vegetables with every container. You've already made the decision to eat healthier, and eating more vegetables is universally recognized as one of the best ways to accomplish that goal. 7-9 servings of fruits and vegetables per day should be your target, and it's easy to accomplish that since if meals are pre-made and ready to go. As an added benefit, changing the vegetable side dish to a meal helps keep every lunch and dinner interesting, so you can prepare your carbs and protein in bulk and then add fresh vegetables with every meal. To prepare veggies fresh really quickly and healthily, use an air fryer. Lightly cooking broccoli, cauliflower, or squash in an airfryer only takes 5-10 minutes and doesn’t require the use of any oils.
Pack Healthy Snacks
It's okay to get hungry between meals, and if energy levels hit a slump, having a healthy snack on hand can support your health and wellness goals by keeping you aware from tempting junk food. Fruits like an orange or apple contain satiating fiber, or a granola mix with nuts and seeds can help improve your fat metabolism.
Practice Mindfulness
Taking a few moments for yourself every day, breathing, and practicing mindfulness is a great way to reduce stress, prevent burnout, and lead to a healthier happier life.
When and how you want to use your time is up to you, but make a habit of spending some me time to yourself at least once a day. Spending time in nature and grounding is of the best things you can do everyday for your mental health, and can reduce feelings of anxiety, loneliness, and depression.
In the morning, this "Me time" could be taking a few extra moments after waking up to stretch, do your daily hygiene, and prepare a delicious breakfast. At work, it could mean pausing from an assignment to step outside and take ten deep breaths of fresh air. Later in the evening a walk of any length clears and calms the mind while also incorporating more movement into your daily routine.
All these recommendations seem like common sense, but when caught in the rat race it takes a conscientious effort to make time for yourself and make wellness a priority in your life. Once mindfulness habits are set, you’ll be amazed by how much less stress you have in your life, how much calmer you are, and how much more focused and productive you’ve become!
Sleep a Full Eight Hours
When responsibilities pile up and there is so much to do, it's convenient to think that getting a couple hours less sleep per night will be OKAY. well, It isn't. The eight hours of rest you should be getting every night is the time when the mind and body heal and restore.
““Our bodies used long periods of sleep to restore and rejuvenate, to repair tissues, grow muscle, prune synapses, and synthesize hormones.””
Sleep is when the brain takes the information from the previous day, parses it, and turns it into long term memories. It may seem like staying up to finish work is the better option, but 9 times out of 10 you're better off getting a good night's rest and coming back to finish your work in the morning. Quality sleep is crucial to productivity and overall happiness.
If you have trouble establishing a set bedtime, set an alarm an hour before your desired bedtime and begin your bedtime routine. Turn down the lights, place your phone on the charger, brush your teeth, and do all the things you want to do in order to wake up the next morning bright and alert. Be conscientious of your circadian rhythm and let the cycle of the sun guide your morning, afternoon, and evening activities. Plan your bedtime slightly earlier than the eight hours of sleep you need, that way in case it takes a while to fall asleep, you still get eight quality hours of sleep per night.
Improving your sleep is one of the best things you can do for your health and wellness, and it’s really quite easy with the creation of some habits and a little discipline.
Five Habits to Healthy
There you have it, five wellness strategies to help you live a happier, healthier, and more appreciative life. Be patient during the process and start by adding one new habit at a time, and as one becomes a permanent habit, add another in. There is no first place winner as it relates to your wellness journey, everyone’s life if unique and takes a different path. The best way to see long term success is with small consistent steps forward which result in accelerating forward progress.
The Importance of Sleep
Everyone knows of the importance of sleep. Good sleep improves your health by nearly every health metric known, whether mental, emotional, or physical. If you suffer from poor sleep, or from the symptoms of poor sleep, then it is critical you understand how great sleep can improve wellness, and the steps you can take to improve your sleep.
Article by Stefan Burns - Updated November 2021. Join the Wild Free Organic email newsletter!
Sleep is a very important part of everyday life. The prevailing recommendation is that 8 hours of sleep everyday is ideal amount for health and wellness. Less or more than eight hours and negative health implications start to increase. The health effects of sleep deprivation is also well studied fact. Sleep is so important that sleep deprivation studies on rats and dogs have shown that extreme sleep deprivation can be fatal.
Health Impacts of Sleep
Here are some quick facts from the American Sleep Association (1):
50 - 70 million US adults have a sleep disorder.
37% of 20-39 year-olds report short sleep duration
40% of 40-59 year-olds report short sleep duration
35.3% adults report < 7 hours of sleep during a typical 24-hour period.
Sleep can take many forms. Most people sleep once a day in a single unbroken event lasting, sleep involves a 5 to 9 hours in length. Others follow a biphastic sleep schedule in which there are two periods of sleep everyday, typically one long and one short. Then there are extreme sleep schedules like those developed by the famous late Buckminster Fuller (which we do not recommend you try). However your sleep schedule is divided, a total of 8 hours of sleep per day is recommended. If you get less sleep than what your body and mind require for restoration every night, then there are some health complications you should be aware of.
In a study of over 100,000 volunteers, researchers observed that cognitive performance is impaired in people who deviate from the recommended 7–8 hours per night (2). A deviation from the 7-8 hours had little impact on short-term memory performance, but reasoning and verbal skills were heavily impaired. Those who self-reported sleeping less than 4 hours per night had lower scores compared to those who slept well, and had similar cognitive performance to people 8 years older then them. In persons sleeping less than 8 hours, reduced leptin and elevated ghrelin hormones were observed (3). This skewed leptin/ghrelin ratio has been found to be responsible for increasing appetite and hunger cravings. In fact, increased body mass index (BMI) was found to be proportional to decreased sleep. Sleeping for less than 7 hours per night conferred a 12% greater risk of death (4).
Without a proper 8 hours of sleep per night you’re more likely to be cognitively older, fatter, and one step closer to death than if you had slept a full eight hours per night. Poor sleep can be avoided through! This article will guide you through the science of why you might be having poor sleep and how to counteract this. At the end there is an action plan you can follow to improve your sleep right away.
The Sleep Cycle and Naps
Sleep can be broken down into sleep cycles 90 minutes in length. When you sleep for 8 hours, if everything is normal you will go through 5-6 sleep cycles. A sleep cycle can be further broken down into the stages of sleep: Wakefulness, Rapid Eye Movement (REM), Stage 1, Stage 2, and Stage 3.
Stage 3 is slow-wave deep sleep, and slow-wave-sleep is when the body heals and the brain consolidates memories (5). Stages 1 and 2 are short intermediate stages between stage 3 and REM sleep. Rapid eye movement (REM) sleep is when you experience dreams. Having adequate REM sleep every night has shown to be important for how alert, focused, and sharp you are the next day, and less REM sleep puts you at a higher risk of death (6).
While most of this article will focus on why you should get a good eight hours of sleep per night, daytime naps will also be discussed. When sleep deprived, naps can be a quick effective way to mitigate many of the effects of sleep deprivation. Longer naps have a more lasting effect than shorter naps, but the goal should be to resume a normal 8 hour sleep cycle as soon as possible. Keeping in tune with the circadian rhythm is important for many reasons, one of them being that brain waste clearance works better during sleep at night compared to daytime sleeping (7). The process of sleeping is important, but so is when you sleep. With that covered, here are the different types of naps you can take.
15 Minute Nap
If you’re feeling drowsy, fatigued, or have brain fog, a 15 minute nap can have you come feeling refreshed for 1-3 hours afterwards. The secret of the 15 minute nap is that very quickly you can descend into stage 2 sleep (see above). During stage 2 mental performance is increased, and in fifteen you’ll have gotten a mini tune-up, and the effects are immediate (8). A fifteen minute nap is too short to experience sleep inertia (that period of fatigue and drowsiness post sleep), so when you need a quick mental boost take a nap rather than reach for a cup of coffee. Naps used this way to help to improve your sleep and wellness overall.
The 15 minute nap is the best sleep option to utilize when you only have 15 minutes in the near future to catch some rest, and/or you require a cognitive boost right away.
30 Minute Nap
If you have longer than 15 minutes but less than the 90 minutes required for a full sleep cycle, then a 30 minute nap is a better option to improve mental clarity and also remove some physical fatigue. 30 minute naps enhance performance in reaction time and alertness compared to if you didn’t take a nap (9). A thirty minute nap extends your time in stage 2 sleep, improving the benefits compared to a shorter 15 minute nap. Sleep inertia will be slightly higher with a 30 minute nap that a 15 minute nap, but that should only last a few minutes at max.
If you sleep longer for thirty minutes you’ll enter into stage 3 sleep, and waking up from stage 3 sleep carries with it a lot of sleep inertia. It’s best to stick to a thirty minute nap or if you have the time go for a full 90 minute sleep cycle, and nothing in-between.
90 Minute Nap
The 90 minute nap is special because it encompasses one entire sleep cycle, from stage 1 and stage 2 sleep, through stage 3 slow-wave-sleep, and finally to REM sleep. If you need the biggest physical and mental boost midway through the day, a 90 minute nap is the way to go. 90 minute naps will boost performance for up to ten hours (10). The drawback of the 90 minute nap compared to the 15 and 30 minute options are that it creates more sleep inertia. Going through the sleep stages all the way to REM sleep takes one relatively close back to wakefulness though, and the sleep inertia from a 90 minute nap is slightly more than that from a 30 minute nap.
0 Minute Nap (Hypnagogic)
Hypnagogia is the experience of the transition from wakefulness to sleep. Ranging from a few seconds to a few minutes, this transition period takes people from conscious to unconscious experience, and unusual sleep phenomenon such as lucid dreaming, hallucinations, and sleep paralysis can sometimes be experienced during hypnagogia.
A hypnagogic nap is a nap that only lasts for seconds. To experience a hypnagogic nap without having learned to control the hypnagogia state, sit in a chair and hold an object such as a metal ball in your hand and try to fall asleep. Right before you’ll fall asleep, your hand will relax, dropping the ball, waking you up from the hypnagogia state. With practice, the balls will no longer be needed. Visionaries such as Albert Einstein, Benjamin Franklin, Nikola Tesla, Ludwig van Beethoven, Salvador Dalí, Isaac Newton, Thomas Edison, Aristotle, and more all have credited hypnagogic naps with boosting their creativity and insight. I personally can attest to this phenomenon. All of my best ideas and revelations come to me as I straddle wakefulness and rest, and I’ve found that if I transition back to wakefulness instead of sleep after experiencing hypnagogia, I feel rested with my mind firing at max creative capacity.
Factors that Influence Sleep
There are a many factors that influence sleep, and they range from minor to major in effect. It is important to be aware of these different factors, which range from light exposure to diet, and how they affect the circadian rhythm. The circadian rhythm is a natural, internal process that regulates the sleep-wake cycle. When making changes to improve sleep quality and/or quantity focus on the most encompassing changes that positively effect the circadian rhythm. The methods that are the most effective in improving sleep often require the biggest lifestyle changes, so expect these changes to take time. Patience will be required if you wish to make lasting change and create a lifestyle which supports quality sleep and overall health and wellness.
Below is a list of the most important factors that can influence sleep. At the end of the article is a quick-start guide that will condense this information into actionable steps.
Chemicals: It’s well known that chemicals like caffeine affect sleep, but other chemicals, some of which are naturally produced, can also impact sleep.
Exogenous Sleep Disruptors
Nicotine - the additive chemical found in tobacco, is a stimulant and disrupts sleep by increasing sleep latency (how long it takes to fall asleep), reduces quality, fragments sleep, and reduces overall time slept.
Alcohol - a depressant, the more drinks that are consumed before bed, the greater the impact on sleep quality. You might fall asleep faster, but REM sleep (which is mentally restorative) is notably reduced after a few hours.
THC/CBD - cannabinoids produced from cannabis, THC is a psychoactive chemical while CBD is non-psychoactive. Both promote feelings of relaxation but THC triggers dopamine release.
Exogenous Continued
Caffeine - a stimulant found in coffee beans and green tea leaves, caffeine promotes wakefulness and releases adrenaline. The half-life of caffeine is ~6 hours, so if you have 100 mg caffeine upon first waking, 18 hours later when it is time to sleep you will still have 12.5 mg of caffeine in your system.
Theobromine - a stimulant found in cacao, theobromine is very similar to caffeine in its effects.
Phthalates - chemicals commonly found in plastic products, phthalates are endocrine disruptors and by affecting hormones can disrupt sleep through phenomenon such as hot flashes. Bedding materials commonly degas phthalates.
Endogenous Sleep Influencers
Dopamine - a naturally produced feel-good neurotransmitter, increases in response to things that bring pleasure, and higher levels of dopamine disrupt sleep.
Cortisol - a steroid hormone, cortisol peaks in the morning when you wakeup. Cortisol is released by the adrenal glands when stressed, though the overall cortisol release schedule is dependent on your circadian rhythm.
Melatonin - a hormone primarily released by the pineal gland, melatonin helps regulates the sleep–wake cycle.
Consistency: More consistent day-night schedules improve sleep quality. The circadian rhythm is based on the light and temperature cycles of the sun, and the further you stray from these natural variations, the more disrupted your circadian rhythm becomes. All the factors in this list affect your circadian rhythm, and therefore your sleep, but what also effects your sleep is how consistent you keep these factors everyday. Changing any factor, whether for the positive or negative creates circadian rhythm volatility, so move the needle slowly, introducing one optimization at a time, and make it a lasting habit.
Sometimes it’s not possible to be fully consistent, such as with jet lack from travel or life events, and in this case do your best to stay calm and reduce the volatility to your circadian as much as you can using the different takeaways that you glean from this list.
Electromagnetic Radiation: The Earth is buzzing with electromagnetic energy, both naturally occurring and now man-made. Little is known on how magnetic fields influence our physiology. Our bioelectrical system is just as developed as any other system in the body like the circulatory system, it’s just not well understood. There is evidence that the frequency and amplitude of electromagnetic fields can impact sleep (11), and if you’re experiencing poor sleep you might consider turning the WiFi routers in your home off ever night and keeping note of your sleep patterns.
I personally have done this and I notice I sleep better with the WiFI router off.
Environment: Environment is a multi-faceted word that means many things. Environment means more obvious factors like temperature and background noise, but environment can also mean more nebulous factors. Maybe you live with other individuals with volatile schedules who are highly stressed and emotional. Perhaps a family pet needs to be let out every night to do their business, or there is temporary construction nearby that starts at 6 am. There are endless ways your environment effects your sleep schedule and quality of sleep, and you can influence these factors to various degrees.
“God, grant me the serenity to accept the things I cannot change, courage to change the things I can, and wisdom to know the difference.”
This quote is very true as it relates to your sleep environment. Make the changes and optimizations you can in order to sleep better, but remain calm with what you can’t change. Getting stressed or worried about what you can’t change will only make you sleep worse.
Food: Food has a big impact on your sleep. The timing and composition of meals determines your blood sugar levels, which in turn impacts your energy level and brain activity. Depending on what you eat right before bed can have an impact on how well you sleep that night meal right before bed. Fiber increased slow wave sleep and reduced stage 1 sleep (light sleep) whereas sugar and saturated fat increased stage 1 sleep and arousals (12).
When meal timing is kept consistent, the body adapts and the circadian rhythm normalizes, even if the meals are very early or very late. When the timing of meals change, the circadian rhythm shifts and sleep is disrupted (13)
Alcohol is a well known sleep disruptor. As a depressant, a few servings of liquor might help you fall asleep faster, but overall sleep quality will be worse, with REM stages suffering the most (14).
Light: Our existence is light, so it is no surprise to find out that light has a huge impact on sleep. Light is the main input the circadian rhythm bases its calculations off of, and the intensity, wavelength (color), and timing of light all change the response of the circadian rhythm (15). The transition of dim to bright light in the morning induces an immediate rise in cortisol (16), the stress hormone, promoting wakefulness. During the day, blue and green light dominate the sky, promoting alertness through changes in brain activity (17). At night blue light suppresses melatonin production, the sleep hormone, in a dose dependent manner (18). Any light after dark disrupts melatonin production and has an influence on sleep onset and quality (19), it’s just lower wavelength light has the least impact.
Being mindful of all light, and it’s effects on your sleep, is one of the biggest things you can do to positively impact your sleep quality and quantity.
Medications: There is a chance with any drug or medication for one of the side-effects to be sleep disruption. Alpha and beta blockers, SSRI antidepressants, statins, corticosteroids, ACE inhibitors, and diuretics are just some of the drugs which can cause insomnia, daytime drowsiness, decreased REM sleep, nightmares, the list goes on.
Getting good sleep every night is foundational to good health, and every effort should be made to get off medications which impact sleep. Every holistic effort should be taken to return to a healthy lifestyle not requiring any drugs or medications, but that desire has to manifest internally as a deep seated desire.
Pain: It’s no surprise that pain can disrupt sleep, it is something everyone has experienced. Chronic pain can cause regular sleep disruptions, whereas acute pain might only temporarily disrupt sleep. The issue with pain is that it can disrupt sleep, and then the lack of sleep can cause worsening health outcomes, which serve to further increase the pain. It’s a troubling cycle, and to break it pain and anti-inflammatory supplements can be of use. Curcumin, sulforaphane, and CBD are all effective natural anti-inflammatories which can reduce chronic and acute pain depending on their application.
Sex: We know that poor sleep negatively impacts your time in-between the sheets, but how does sex impact sleep? How sex can impact sleep is very individual. During sex, dopamine and oxytocin are released, which can create pleasant feelings which reduce stress, and after sex other hormones like prolactin can cause feelings of relief, relaxation, and sleepiness. These naturally produced chemicals can improve sleep, but for some sex might be too energizing. Likewise, if you’re disrupting your regular sleep schedule by staying up late and being frisky, this will only impact your sleep negatively.
Stress/Anxiety/Depression: Stress and anxiety can deeply disturb your sleep (20), and overtime this can lead to chronic sleep issues. How stress and anxiety affect sleep is similar to the pain-sleep downward cycle. Stress can disturb sleep which can worsen stress and so on. Overtime, or due to other factors, depression can become an issue, which can range from mild to life threatening.
Depression and sleep are closely linked. Decreased REM sleep can exacerbate depression, and depression can lead to insomnia.
Temperature: The temperature of the environment and your body temperature have a big impact on sleep. Finding the right balance between hot and cold is important for sleep quality. When sleep environments are too warm, slow wave and REM sleep are decreased, while wakefulness increases (21). In cold environments, shivering will negatively affect your sleep, but when bundled up the issue is mitigated. The best solution is to sleep in a cool to cold environment and then add warmth to your desired level with bedding materials.
Heat therapy which has many benefits, raises internal body temperatures and can impact sleep. Heat therapy at night (via a bath) while on the decline of the circadian rhythm was found to improve sleep onset, increase the deepest stage of slow-wave-sleep, but decrease REM sleep (22). Typically you don’t want to decrease REM sleep. The same heat therapy done during the incline of the circadian rhythm (think late afternoon) didn’t have any effect on sleep.
Keep Sleep Simple
As you can tell, a lot of the health factors which disrupt sleep end up feeding their own condition, making it worse and creating a downward spiral. When or before this happens, it is important to intervene with wellness therapies which are proven effective in helping improve sleep, reduce stress, reduce pain, and increase happiness. Unless positive change is inserted into the equation, healing will not occur. Wellness activities as simple deep abdominal breathing or time spent in nature being in awe can change the conversation, getting wellness and sleep back on track.
Countering bad sleep habits with wellness activities is especially important as you can tell there is significant overlap in the categories above. When on a quest to improve sleep quality, it is best not to pick and choose which habits you’ll change and which you won’t. A holistic lifestyle approach is needed, and once normal sleep patterns have resumed, then you can patiently experiment with what minor changes you’d like to try to accommodate.
First, lets lay out desired sleep goals:
Sleep schedule in-sync with natural circadian rhythm
8 hours sleep per night
Fast sleep onset
Reduced disruptions from elevated alertness and wakefulness.
Quality slow-wave-sleep
Regular REM sleep
Upon waking you feel alert and refreshed.
To accomplish the above sleep goals, lifestyle modifications will need to be made. These modifications are done with the best intentions and creating wellness habits out of these tips will positively impact your life given consistency and time. Some of these modifications might go against your established behaviors, so before you start the below program make sure you are 100% committed to improving your sleep. Only if you have a strong innate desire to improve your sleep and be healthier will these changes stick.
Holistic Sleep Improvment Protocol
Establish a hard bedtime 8.5 hours before when you would like to wake up every morning. If you need to be up by 4 am that means bedtime is 7:30 pm. 6 am wake-up means 9:30 pm your head is on the pillow. The extra half hour is a cushion that accounts for the time it takes to fall asleep. You need to be consistent with this. Even if you’re not tired initially, create the habit and go lay in bed. Do you best to make your wake-up in the morning coincide with the rising of the sun.
Make the bedroom a place for sleep maybe sex and nothing else. If you have a TV in the bedroom, move it elsewhere. If you charge your phone or tablet on your bed stand, move the chargers to a different room. Actions dictate how we respond in different environments, and if you want the bedroom to be a place where you sleep, then it needs to be a place of sleep and nothing more. Watching TV or being on your phone gives your mind the expectation of alertness and activity in an environment where that strictly shouldn’t be allowed. Removing electronics and bright lights from the bedroom also reduces light exposure and melatonin production will be unaffected.
Keep the sleeping environment cool and exposed to the outside temperature, even in some small way. The circadian rhythm is driven by the light and temperature cycles of the Earth and Sun, and the further you remove yourself from the natural world the more your sleep will suffer. This goes for your electromagnetic connection to the Earth too, and being grounded at night can further improve sleep and reduce inflammation.
Be conscious of light throughout the day, and when the sun starts to set, all electronics should be put away and not used. The use of electronics 2-3 hours before sleep is strongly not recommended. Bright lights in the house should be dimmed, replaced with hue light bulbs (and set to a low kelvin temperature) or candles can be used. Dim lighting at night is better for your circadian rhythm and melatonin production while also being a more passionate creative environment. I have hue color changing lights and highly recommend them for reducing light exposure at night and also to schedule them to slowly turn on with the sun. They’re a game changer. At night put on some blue blocking glasses to further reduce the effect of having lights on. It might seem like overkill, but at night its very dark outside, and even dim lights affect the circadian rhythm. I use Felix Gray blue blocking glasses and notice if I use them consistently at night I sleep better.
Cut the caffeine and other stimulants. Caffeine has a long half-life and drinking a cup every morning builds up a chronic dependence on caffeine to be alert and wakeful. Having any caffeine in the afternoon or evening is a strict no. The occasional cup of coffee or tea isn’t a problem, but don’t make it a habit. Likewise, nicotine and alcohol are obvious sleep disruptors, and for health reasons overall shouldn’t be used at any time other than extremely sparingly. Skip the claw, la croix is a better alternative, and if you are addicted to nicotine, try transitioning off cigarettes to cannabis dry vaporization, a healthier alternative which is easy to stop. The cannabinoids might help you sleep too.
Exercise in the morning or afternoon, but not evening. Besides a peaceful walk at night, exercising at night stokes the energy systems of the body to ramp up, releases cortisol, and will delay sleep onset. Exercise and movement is foundational to a healthy life, but not at the expense of good sleep. The best way to make sure you exercise in the morning is to establish a consistent morning routine. Start your morning with a movement flow, yoga, calisthenics, a run or walk, there are so many options, and if you do this you’ll feel great throughout the rest of the day.
Start a journal and keep track of your sleep. Recording when you go to sleep, wake up, and sleep quality is a good way to pair your diet, daily actions, and habits to your quality of sleep. If your mind is still spinning before going to bed, committing these thoughts to paper can quiet the storm helping you fall asleep faster.
Meditate every day for at least 15 minutes. Meditation is the best way to practice calming your mind, it increases mindfulness, and provides an opportunity to raise your level of consciousness. The act of physically doing nothing might seem counterproductive, but through meditation you can unlock many internal and external secrets and truths that would have remained hidden to understanding. Meditation will impact your life in wide-ranging ways, and it will improve your sleep a lot.
Spend time in nature every day, increasing your consciousness of the world around you while also enjoying the mind clearing and emotionally calming benefits. You can practice your meditation during this time, focus on deep abdominal breathing, and feel the stress melt away.
Eat a healthy diet rich in fruits and vegetables and don’t eat too close to bed time. Additionally, keep your meal timing consistent so as to not disturb your circadian rhythm. For your last meal, at most 2 hours before bed, have a salad or high fiber vegetable like squash. Change your dietary mindset to not seek out foods you crave but instead the nutrition your body needs. Avoid all sugar before bed.
To aid the sleeping process, there are some supplements which are known to help. 200-400 mg of magnesium glycinate an hour or two before bed will help improve sleep quality (23, 24), or simply eat 1/4 cup of nutrient-dense pumpkin seeds. 10-20 grams of glycine-rich collagen, or a meal composed of pulses (beans, lentils, chickpeas) which also contain a lot of glycine, before bed will improve sleep onset and quality (25).
Drink plenty of water throughout the day. The human body is made up of 70% water, and being in a state of chronic dehydration has serious long term health consequences. Upon waking, drink 24-32 oz pure filtered water and do the same before bedtime. Being dehydrated means your mouth and nasal passages will be more dry, increasing your chance of snoring and waking up with dry mouth. Dehydration will also increase your chances of getting leg cramps at night, an unpleasant and wakeful experience. Drink water everyday to stay healthy, skip the other liquids and aim for a gallon of water daily.
Sleeping is an Advantage, Use It
It is clear that sleep is a critically important component towards achieving optimal human health, for achieving mental clarity, and for healing your body.
Modern culture doesn’t emphasize wellness, and has yet to fully realize the importance of a well rested 8 hours of sleep. Be cutting edge by going low-tech with your sleeping habits. You’ll experience a calmer mind, less turbulent emotional states, feel stronger and be better rested, and you’ll be less likely to die. Without good sleep you will not age gracefully and experience the quality of life you want.
Updated September 2020
References:
Sleep and Sleep Disorder Statistics. Sleep Association
Wild CJ, Nichols ES, Battista ME, Stojanoski B, Owen AM. Dissociable effects of self-reported daily sleep duration on high-level cognitive abilities. Sleep. 2018;41(12)
Taheri S, Lin L, Austin D, Young T, Mignot E. Short sleep duration is associated with reduced leptin, elevated ghrelin, and increased body mass index. PLoS Med. 2004;1(3):e62.
Cappuccio FP, D'elia L, Strazzullo P, Miller MA. Sleep duration and all-cause mortality: a systematic review and meta-analysis of prospective studies. Sleep. 2010;33(5):585-92.
Todorova R, Zugaro M. Isolated cortical computations during delta waves support memory consolidation. Science. 2019;366(6463):377-381.
Leary EB, Watson KT, Ancoli-israel S, et al. Association of Rapid Eye Movement Sleep With Mortality in Middle-aged and Older Adults. JAMA Neurol. 2020;
Hablitz, L.M., Plá, V., Giannetto, M. et al. Circadian control of brain glymphatic and lymphatic fluid flow. Nat Commun 11, 4411 (2020).
Lovato N, Lack L. The effects of napping on cognitive functioning. Prog Brain Res. 2010;185:155-66.
Rosekind MR, Smith RM, Miller DL, et al. Alertness management: strategic naps in operational settings. J Sleep Res. 1995;4(S2):62-66.
Gillberg M. The effects of two alternative timings of a one-hour nap on early morning performance. Biol Psychol. 1984;19(1):45-54.
Bagheri hosseinabadi M, Khanjani N, Ebrahimi MH, Haji B, Abdolahfard M. The effect of chronic exposure to extremely low-frequency electromagnetic fields on sleep quality, stress, depression and anxiety. Electromagn Biol Med. 2019;38(1):96-101.
St-onge MP, Roberts A, Shechter A, Choudhury AR. Fiber and Saturated Fat Are Associated with Sleep Arousals and Slow Wave Sleep. J Clin Sleep Med. 2016;12(1):19-24.
Wehrens SMT, Christou S, Isherwood C, et al. Meal Timing Regulates the Human Circadian System. Curr Biol. 2017;27(12):1768-1775.e3.
Ebrahim IO, Shapiro CM, Williams AJ, Fenwick PB. Alcohol and sleep I: effects on normal sleep. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2013;37(4):539-49.
Dijk DJ, Archer SN. Light, sleep, and circadian rhythms: together again. PLoS Biol. 2009;7(6):e1000145.
Leproult R, Colecchia EF, L'hermite-balériaux M, Van cauter E. Transition from dim to bright light in the morning induces an immediate elevation of cortisol levels. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2001;86(1):151-7.
Vandewalle G, Collignon O, Hull JT, et al. Blue light stimulates cognitive brain activity in visually blind individuals. J Cogn Neurosci. 2013;25(12):2072-85.
West KE, Jablonski MR, Warfield B, et al. Blue light from light-emitting diodes elicits a dose-dependent suppression of melatonin in humans. J Appl Physiol. 2011;110(3):619-26.
Wright HR, Lack LC. Effect of light wavelength on suppression and phase delay of the melatonin rhythm. Chronobiol Int. 2001;18(5):801-8.
Al maghaireh DF, Abdullah KL, Chong MC, Chua YP, Al kawafha MM. Stress, Anxiety, Depression and Sleep Disturbance among Jordanian Mothers and Fathers of Infants Admitted to Neonatal Intensive Care Unit: A Preliminary Study. J Pediatr Nurs. 2017;36:132-140.
Okamoto-mizuno K, Mizuno K. Effects of thermal environment on sleep and circadian rhythm. J Physiol Anthropol. 2012;31:14.
Horne JA, Shackell BS. Slow wave sleep elevations after body heating: proximity to sleep and effects of aspirin. Sleep. 1987;10(4):383-92.
Nielsen FH, Johnson LK, Zeng H. Magnesium supplementation improves indicators of low magnesium status and inflammatory stress in adults older than 51 years with poor quality sleep. Magnes Res. 2010;23(4):158-68.
Held K, Antonijevic IA, Künzel H, et al. Oral Mg(2+) supplementation reverses age-related neuroendocrine and sleep EEG changes in humans. Pharmacopsychiatry. 2002;35(4):135-43.
Inagawa, K., Hiraoka, T., Kohda, T. et al. Subjective effects of glycine ingestion before bedtime on sleep quality. Sleep Biol. Rhythms 4, 75–77 (2006).
Break Sugar Addiction by Avoid Added Sugars
Look at the ingredients label for most foods and you'll see that sugar was added. Sugar is cheap to produce and has addictive properties, therefore processed food manufacturers love adding it as it helps their bottom line and keep customers coming back. Healing a sugar addiction by avoiding added sugars is one of the first steps to reclaiming your health.
Article by Stefan Burns - Updated December 2021. Join the Wild Free Organic email newsletter!
Being healthy and free from sickness, pain, and disease is as simple as consistently following and adhering to a collection of small healthy habits. Depending on your current state of health, becoming well can seem impossibly daunting, for one, where do you start? If you keep a lifestyle unchanged, but add one healthy habit, then wellness has been improved. To create a healthy habit, you must first be hyper-conscious of your actions until they become second nature, becoming a habit you do unconsciously. The hard part of being healthy isn’t following wellness habits, but rather forming the habits one at a time, and performing them long enough that they become second nature.
One of the most impactful wellness habits you develop is to kick a sugar addiction (1). Like other addictive chemicals, sugar is toxic (2), creates widespread inflammation in the body (3) when consumed in excess, shifts the microbiome to a less diversified pathogenic state (4), and desensitizes dopamine receptors (5). The average American consumes 10 times more sugar than 100 years ago; in 2017 this totaled 90.7 grams of added-sugar everyday (6).
For reference, Canada clocked in about 1/3 lower than the USA in 2017 at 58.5 grams per day (7), and the average per-capita added-sugar consumption for rural China in 2017 was only 3.75 grams. In India, Israel, and Russia, people on average consume 5.1, 14.5, and 20 grams of additional sugar per day respectively (8).
For most countries in the world, the processed food industry is driving the ever increasing consumption of sugar, and the health complications are piling up. Over-consumption of sugars together with other factors contributes to the current obesity epidemic
A healthy habit to form which would transform your life would be to kick a sugar addiction. Some sugar in a diet from natural foods and sugars is fine, but a strong effort should be made to avoid heavily processed added-sugars if true health and wellness is the goal.
Symptoms and Complications of Sugar Addiction
Sugar addiction has many of the same symptoms of other common addictions like tobacco or opioids. When sugars are consumed, natural endogenous opioids get released. Outside the context of a healthy balanced diet, substantial parallels between sugar and drugs of abuse can be observed in behavior and brain neurochemistry.
Animal studies have shown sugar to be addictive than cocaine (9). You might be a sugar addict if you display any of the following behaviors:
Free yourself from the toxic behavioral influences of sugar
You make excuses to consume more sugar.
You make special trips to buy more sugar laden products
You drink sugar sweetened beverages.
You eat sugar dominant foods to breakfast.
You reward yourself with a sweet for motivation or as a reward.
You have a secret stash that you binge from when alone.
You previously tried to stop eating sugar, and couldn’t.
Beyond these behavioral patterns, there are two types of symptoms when it comes to sugar addiction. There are symptoms present when actively feeding the sugar cycle, and there are the symptoms of sugar withdrawal.
Symptoms of Sugar Addiction
Persistent brain fog
Volatile swings in energy
Intense cravings disguised as hunger
Mental health issues such as depression, anxiety, ADHD
Persistent fatigue
Racing thoughts
Strong sexual urges
Regular foods like fruit and vegetables taste bland and dull
Vehement denial of a sugar addition when questioned
Being overweight or obese
Symptoms of Sugar Withdrawal
Intense cravings
Depression
Fatigue
Anxiety
Nausea
Irritability
Altered sleep patterns
Cognitive issues, brain fog
Low blood sugar, dizziness
Other symptoms associated with drug withdrawal
These symptoms themselves can cause serious complications towards everyday life, but there are more insidious long term health complications from being addicted to sugar.
When naturally occurring sugars are paired with a healthy dose of fiber, like with fruit and vegetables, overall the known negative health effects of sugar appear to be negligible. The issue with sugar is when it is consumed without fiber. When sugar is consumed in excess and without fiber, inflammation in the body rises dramatically. Inflammation is not the root cause of disease, but it is a complicating factor in 100+ diseases such as diabetes, heart disease, cancer, mental health disease, and more. More sugar also means more cavities, so oral health and hygiene is also affected (10).
Chronic levels of inflammation keep the body in a state of fight-or-flight, with the now dominant sympathetic nervous system being out of balance with the rest-and-relax parasympathetic nervous system. This over activity places stress on all the major systems of the body such as the immune system, liver, digestive system, circulatory system, and more.
Besides being predisposed to 100’s of different chronic health ailments, chronic inflammation increases body fat storage and can lead to obesity. Obesity itself is another complicating health factor, and now what was one health issue became two.
We are what we eat, and sugar is toxic. We know excess sugar consumption leads to inflammation, obesity, and disease, but what is the step that sits in-between sugar consumption and chronic inflammation?
Sugar and the Digestive System
After sugar is consumed, before it can supply energy to the body through the mechanisms of insulin transport, it needs to be digested. Different sugars have different chemical structures and therefore different rates of digestion and absorption. Sugar is a general term used for sweet-tasting soluble carbohydrates. There are simple sugars which composed of a single sugar molecule, or compound sugars, where two sugar compounds are connected together. Whether sugars are consumed as simplex, compound, or as a starch (a chain of many sugar compounds), the digestive system will break apart and hydrolyze carbohydrates into simple sugars for transport into the blood stream. Let’s examine the most commonly consumed simple sugars:
Monosaccharides
Fructose - Fruit Sugar
Glucose - The basic form of sugar used by the body
Galactose - Present in milk
Disaccharides
Sucrose - One fructose and Glucose sugar combined
Lactose - One glucose and galactose sugar combined
Maltose - Two glucose molecules combined
There are also alcohol sugars, polysaccharides (which are larger chains of sugars), artificial sugars, and many more. The chemistry of sugars is complex, but what is clear is that excess sugar consumption is dangerous, and it all starts with the gut.
The microbiome is the collection of symbiotic (helpful), commensal (indifferent), and pathogenic (bad) microorganisms that inhabit your gut. Your gut is technically “outside” of your body, and it contains 10x more organisms than cells in your body, over 100 trillion! When the microbiome is well diversified and balanced (containing primarily symbiotic organisms) food will digest best and qualitative health markers are improved across the board.
The villi connect the digestive, immune, and circulatory systems.
We know the body only transports simple sugars into the circulatory system by passive and active transport through the cell membranes of the finger-like villi structures of the gut. Fats, proteins, and carbs which are still too large for transport need to be broken down. This is where the microbiome plays a critical role in digestion. The chemical and mechanical processes of the digestive system help break down food into smaller pieces, and the microbiome performs the finishing touches breaking apart food into sufficiently small compounds.
When excess simple sugars are consumed, it becomes much easier for the microbiome to access the energy of the sugar first for their own survival needs rather than needing to break chemical bonds first. Over time, this can shift the balance of the microbiome, creating sugar craving microbes with a mind of their own. In order to keep their over-sized populations stable, an unbalanced microbiome will directly interact with the body and brain through the release of chemicals and neurotransmitters. The gut is the second brain of the body, and for many people it’s not under their control. This will manifest as the affectionately known “sweet tooth”.
With an unbalanced microbiome, issues like irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) or more serious complications like small intestinal bacterial overgrowth (SIBO), irritable bowel disease (IBD), and Crohn’s disease can arise. Considering the gut is the boundary between the barbarian (microbes) and gate keepers (epithelial cells), the immune system is most active at the gut. A compromised digestive system with failing tight junctions which lets microbes and undigested molecules slip into the bloodstream is the source of inflammation that sugar causes. Sugar without fiber or not existing in long polysaccharide chains is too easily accessed and used by the microbiome, shifting the balance towards pathogenic microbes. It is this easy access to cheap resources with no nutritional value beyond calories that compromises the integrity of the entire digestive system, leading to chronic inflammation, and therefore obesity and disease.
And there are other complicating factors. Where did the sugar come from? Depending on the plant a sugar ultimately derives from is very important. Modern agricultural practices use heavy amounts of herbicides, insecticides, and fungicides which contaminant everything they are sprayed on. These compounds have can take decades to break down. A GMO cane sugar will be genetically modified to survive when exposed to greater amounts of dangerous herbicides like glyphosate. Glyphosate is an effective herbicide because it interferes with the The shikimate pathway, an ancient seven-step metabolic pathway used by bacteria, archaea, fungi, algae, some protozoans, and plants for the biosynthesis of folates and some amino acids.
While the shikimate is not found innately in humans, it is found and utilized for the survival of our microbiome. Unless sugar is label organic, and even that can have its flaws, it is mostly likely contaminated with glyphosate and other compounds which interfere with the shikimate pathway and other similar metabolic processes. Consumption of this sugar will disrupt the growth of symbiotic microorganisms which might be content munching on fiber all day, and simultaneously fuel the growth of short-lived commensal and pathogenic microbes. Natural sources of sugar like honey are best because they are free or much less contaminated by these dangerous herbicides, insecticides, and fungicides.
When the food source is taken away from these overgrown and unbalanced microbiomes, microbes will release chemicals and neurotransmitters in an effort to acquire more resources (aka you need to eat some sugar NOW) while simultaneously having their population die-off in the wait for more resources. This die-off reaction can release built-up toxic compounds, stressing your gut and liver while you simultaneously experience volatile swings in energy as you’ve become insulin resistant and blood sugar levels have dropped dangerously low.
It’s a terrible health predicament that can be frightening to experience, but feeding the microbiome with more sugar will only make breaking the addiction harder or inevitably lead to the genesis of a deadly disease down the line.
Does your microbiome work for you, or against you?
There is no one living without a microbiome, a healthy microbiome is a critical component to living a healthy disease-free life. If conscious awareness isn’t given to the microbiome through a healthy, organic, unprocessed diet, the microbiome will make itself known to you, either physically, chemically, or behaviorally, demanding nutrients. Understanding the 100 trillion microorganisms that make up your microbiome is the the key to unlocking your health, and the first step towards breaking a sugar addiction.
Now that we’ve laid everything out, lets formulate a strategy that best increases your chances to kick sugar while also reducing the negative health effects that will be experienced during the healing process.
How to Kick a Sugar Addiction
To kick a sugar addition, you need to be aware of what drives a sugar addicition, and how you can break the cycle. Below is a simplified version of the vicious cycle that can form when consuming excess sugar. To break an addition, there isn’t any one strategy that will work, you must first have the innate desire to be free of addiction, have the willpower and discipline to see it through, devote time, and have strategies developed for each step of the cycle. Relapse can occur at any of the stages, so preparation is required for each stage.
In preparation for the following sugar reset, your environment must be made to be conductive to change. Follow the steps below first:
Eliminate all sugar from the household. This means throwing out all sweets, treats, desserts, sources of simple carbohydrates, etc.
Make a list of your favorite sugar pit stops (convenience markets, coffee shops) and blacklist them, vowing to not visit them again.
Practice saying no. Other people might offer you sugar-rich or other unhealthy foods during this reset, rehearse your line and practice saying no in order to avoid temptation, such as: “No thank you John, I am currently working to break my addiction to sugar”. The more truthful and to the point your words are, the less others will try to convince you that taking a bite or having one small treat isn’t a big deal.
Identify your trigger foods. Tracking your diet, mood, and energy in a journal for a week before starting the reset will help you identify your trigger foods that must be completely avoided during the reset.
Develop a plan for how you will drink 1 gallon of filtered water a day. Tap water containing fluoride kills microbes, so for the microbiome to survive more sugar is required, and they will release neurotransmitters for this. Filtered or spring water is pure and free of chemicals.
Once the steps above have been taking, find a 7 day chuck of time in your schedule which is expected to be lower stress. Breaking a sugar addiction takes longer than seven days, but the first week accomplished 80% of the work. Stress triggers sugar cravings, so to increase the chance of success this should be scheduled around a time period of low stress.
The fastest and most painless way to get the ball rolling is to start this week long period with a 24 hour fast, that is no eating from dinner on day to dinner the next. Unless you’re in a state of serious health complications, a 24 hour is safe and achievable by anyone to do. A 48 hour fast is even better as it takes you right to the edge of ketosis (fat only metabolism), but this can be trickier for those really dependent on sugar for their energy levels.
Fasting simultaneously does the following:
Improves blood sugar levels
Sensitizes insulin
Kills off an overactive microbiome
Reduces inflammation
Heals the digestive system
Burns body fat
Fasting promotes health in the exact opposite ways sugar addiction promotes disease. Fasting is a powerful wellness methodology. Fasting also removes many of the questions “like what should I eat instead” and removes analysis paralysis; there are only two objects, don’t eat and drink water! If you carry significant levels of body fat, an every other day strategy for fasting has been shown to be highly effective in breaking the sugar cycle, improving microbiome diversity, and lowering body fat.
An every other day 24 hour fasting schedule would look like this:
Day 1 fasting, drinking only water (1 gallon recommended)
Day 2 refeed with organic fruits, vegetables, nuts, seeds, minimally processed grains, animal protein
Day 3 fasting
Day 4 refeed
Repeat
If you do this, expect body fat to melt off as it is used to cover your energy needs throughout the week. Blood sugar, lipid, and insulin markers will improve, energy levels will stabilize, mood will brighten, and sleep will improve. Fasting is the “rip the band-aid” off approach. It’s the most effective and ultimately causes less pain and suffering in the long run, but can be nerve racking to start.
If you think you’ll be more comfortable with a gradual approach, then the first step is to cut out the main offenders. This means cutting out sugar and all sweetened beverages, desserts like cookies and ice cream, and bread products, anything that contains almost exclusively sugar.
Even if you just stop drinking soda, that has a huge impact over time! According to the CDC, 5 out of 10 adults and 6 out of 10 youth drink a sugar sweetened beverage at least once a day. This equates to on average an extra 145 calories for both adults and youth consumed everyday, with one 12 oz soda containing 39 grams of sugar, double than the upper limit we recommend of 20 grams.
If you’re overweight and carry an unhealthy amount of body fat, then either replacing 1 soda a day with water over the course of a month reduce your caloric consumption by 4200 calories, or 1.2 lbs of fat. Over the course of a year of no soda, that equals 14.4 lbs of fat gone.
Once the main sugar offenders have been removed from your diet, you’ll want to replace them when the cravings hit with healthy fats and fiber rich foods.
Foods Containing Healthy Fats
Avocado
Nuts - walnuts, almonds, cashews, pecans,
pistachios
Seeds - pumpkin, sunflower, chia, flax, etc
Animal Fats (grass-fed) - butter, ghee, cream, cheese
Eggs (pasture raised) - chicken, quail
Cacao (fair trade) - Dark Chocolate 70% +
Oils (cold pressed) - olive oil, coconut oil, red palm oil, avocado oil
Foods the contain both healthy fats and fiber:
avocado, nuts, seeds, olives, coconut, and cacao
Foods Containing Fiber
Squash - butternut, winter, zucchini
Seeds - pumpkin, sunflower, chia, flax, cacao
Nuts - almonds, cashews, walnuts, pecans, pistachios
Legumes - beans, lentils, peas, chickpeas, peanuts
Fruits - such as avocado, pear, jackfruit, berries, mango, banana, papaya, coconut, guava, kiwi, etc
Vegetables - carrots, eggplant, jalepeno, tomato, artichoke, cauliflower, cabbage, broccoli, sweet potato, radish, etc
Dark Leafy Greens - spinach, lettuce, swiss chard, mustard, etc
Grains - quinoa, popcorn, oats, black/brown/red rice,
As you can see, there are plenty of delicious foods which contain fiber and fats, excellent additions to any diet. All of the foods above are also micronutrient dense, and a sugar based diet is lacking in critical vitamins and minerals, the deficit of which can have massive health implications.
Homemade Raw Trail Mix
1/4 cup Almonds
1/2 cup Cashews
1/4 cup Walnuts
1/4 cup Pecans
1/2 cup Pumpkin Seeds
1/2 cup 70% Mini Dark Chocolate Chips
In your purse, bag, or on your person, keep a bag of raw trail mix with you. When a sugar craving hits, unless you’re in the middle of a fast, a few handfuls of trail mix is a nice healthy treat that will keep you satiated and content. Right now do not be concerned about calories.
Make sure to buy nuts and seeds which are raw. Raw foods are those that aren’t heated for pasteurization, and eating raw foods helps diversify your microbiome. Raw foods also contain higher levels of vitamins and minerals since the heat didn’t break them down.
Building your Fat Metabolism
A sugar dependent diet is skewed heavily towards carbohydrate metabolism for energy. Carbohydrate metabolism isn’t necessarily bad in and of itself, but often the carbohydrate metabolic cycle will be overdeveloped and out of balance with fat metabolism. The metabolism of fat for energy, either from food or body fat, provides longer lasting and more sustainable energy levels. Having a well-functioning fat metabolism fills in energy dips that are experienced when eating carbs. By stabilizing your energy levels, fats will help keep you calm and emotionally stable, reducing your chance of giving into temptation and reaching for that sugary treat when your sugar starved microbiome and low blood sugar levels are saying you need it most.
Fatty acid metabolism can be improved by eating a diet higher in fats for an extended period of time, or more quickly through a ketogenic diet. A ketogenic diet is a very low carb diet where the body has to produce ketones for use by the brain. The brain exclusively runs on simple sugars or ketones for energy. Since a ketogenic diet is <5% carbs and 70% of greater fat macronutrient wise, it will very quickly improve your ability to metabolize fatty acids. Be aware that you might initially experience what is known as keto flu. Keto flu is a set of flu like symptoms that people first transistioning to a ketogenic diet might experience. The same smptoms can be expereinced during longer duration fasts too as the body as enters ketosis 36-48 hours after fasting has begun.
The digestive system is the seat of power for the immune system, and there is a removal of sugar & nutrients, a die off reaction will occur and many diseased microbes will die. Now these microbes are diseased waste that need to be expelled by the body, causing immune symptoms until this occurs. If tight junctions of the intestines are compromised, then some of these dead microbes will filter into the blood stream and cause an immune response, hence flu-like symptoms can be experienced. If you wish to avoid these flu-like symptoms during the start of fasting or ketogenic diet, then it is important that the tight junctions of the body are healed and have no gaps that undigested food or microbes can exploit to enter into the blood stream. It’s also been shown that glyphosate damages tight junctions, so be mindful of that information. I wrote a guide on how to heal tight junctions naturally with four methods. Luckily the digestive system regenerates very quickly, so even just following those recommended steps for one or two weeks before kicking your sugar addiciton will greatly reduce your risk of experiencing flu-like symptoms when resetting your microbiome and metabolic systems.
Quit Sugar Quick Start Guide
Putting everything discussed into practice, below is a quick start guide with actionable steps you can follow to kick your sugar addiction, balance your microbiome, heal your digestive system, and build your fat metabolism.
Week 1 - Keep a food and mood journey for 1 week. This will help you identify your trigger foods which need to be blacklisted
Clean your Environment - Remove all junk food, sugar, and treats from your home, work, and car.
Practice Saying No - Be honest, and formulate a game plan for your first 7-14 days sugar free.
Prepare - Stock up and buy the healthy organic foods you require to be healthy and successful with this important health endeavor. Figure out your plan on how to drink 1 gallon of water daily (24 oz wakeup, 84 oz day, 24 oz bedtime)
Week 2 - Commit to one of the two dietary strategies listed above. Either do a 24 hour fast every other day, or keep a baggie of raw trail mix with you at all times for those moments when cravings strike.
Week 3 - The hardest part is over, continue with your wellness schedule. If fasting, you can ease up from the every other schedule and do two 24 hour fast every week instead. Keep eating whole unprocessed organic foods!
Week 4 and Beyond - It takes four weeks to create a habit, congratulations! Kicking a sugar addiction is a major accomplishment and over time your body will heal from the damage created by the consumption of added sugars. Now is not the time to relapse, stay disciplined!
If you’ve made it 30 days without added sugars, congratulations! At this point you might be tempted to experiment with “moderation” and have a bite of your favorite treat again, do not do this! Physiological addictions can be broken in a few weeks, but psychological addictions can take months or years to erase. The mind is a powerful thing, and overtime you’ll discover your old definition of moderation was not in fact moderation. By this point your taste buds will have changed, and sugary treats you once found delicious might now be revolting. Trust your instincts and give yourself the time needed to heal from that traumatic period of your life. Ask yourself, what was feeding my sugar addiction? Examine your emotions and look inwards. Food is often the cover for emotional turmoil, and true healing won’t occur until emotional healing can take place.
References
Dinicolantonio JJ, O'keefe JH, Wilson WL. Sugar addiction: is it real? A narrative review. Br J Sports Med. 2018;52(14):910-913.
Lustig RH, Mulligan K, Noworolski SM, et al. Isocaloric fructose restriction and metabolic improvement in children with obesity and metabolic syndrome. Obesity (Silver Spring). 2016;24(2):453-60.
Aeberli I, Gerber PA, Hochuli M, et al. Low to moderate sugar-sweetened beverage consumption impairs glucose and lipid metabolism and promotes inflammation in healthy young men: a randomized controlled trial. Am J Clin Nutr. 2011;94(2):479-85.
Di rienzi SC, Britton RA. Adaptation of the Gut Microbiota to Modern Dietary Sugars and Sweeteners. Adv Nutr. 2020;11(3):616-629.
Gene-Jack Wang, Et al. High sugar intake linked to low dopamine release in insulin resistant patients. Stony Brook University
Sugar and Sweeteners Yearbook Tables. USDA.
Consumption of Sugars in Canada. Canadian Sugar Institute.
Roberto A. Ferdman. Where people around the world eat the most sugar and fat. The Washinton Post
Shah SGS. A Commentary on "Ensuring safe surgical care across resource settings via surgical outcomes data & quality improvement initiatives" (Int J Surg 2019 Aug 5. https://doi.org/ 10.1016/j.ijsu.2019.07.036). Int J Surg. 2019;72:14-15.
Moynihan PJ, Kelly SA. Effect on caries of restricting sugars intake: systematic review to inform WHO guidelines. J Dent Res. 2014;93(1):8-18.











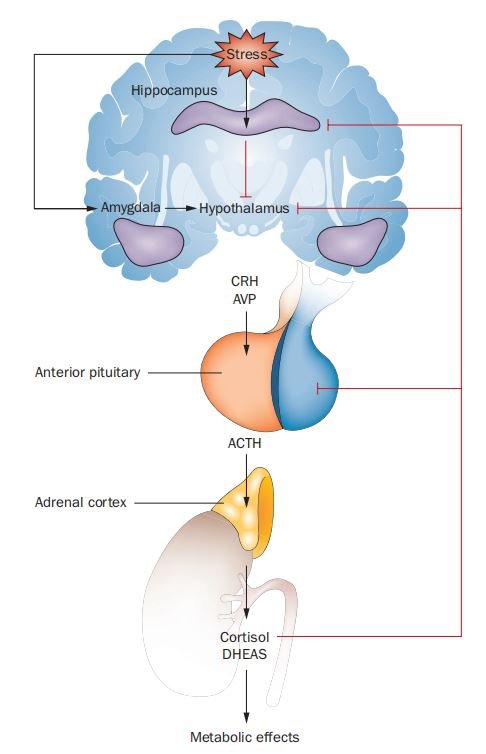


























Herbs that can significantly increase testosterone levels exist and are quite effective at helping remedy the symptoms of low testosterone such as low energy and strength, poor libido and fertility, depression and anxiety, reduced confidence and drive, and low muscle mass. Cistanche, tongkat ali, and ashwagandha are proven testosterone boosters that importantly, are also safe for use. Learn more!